-
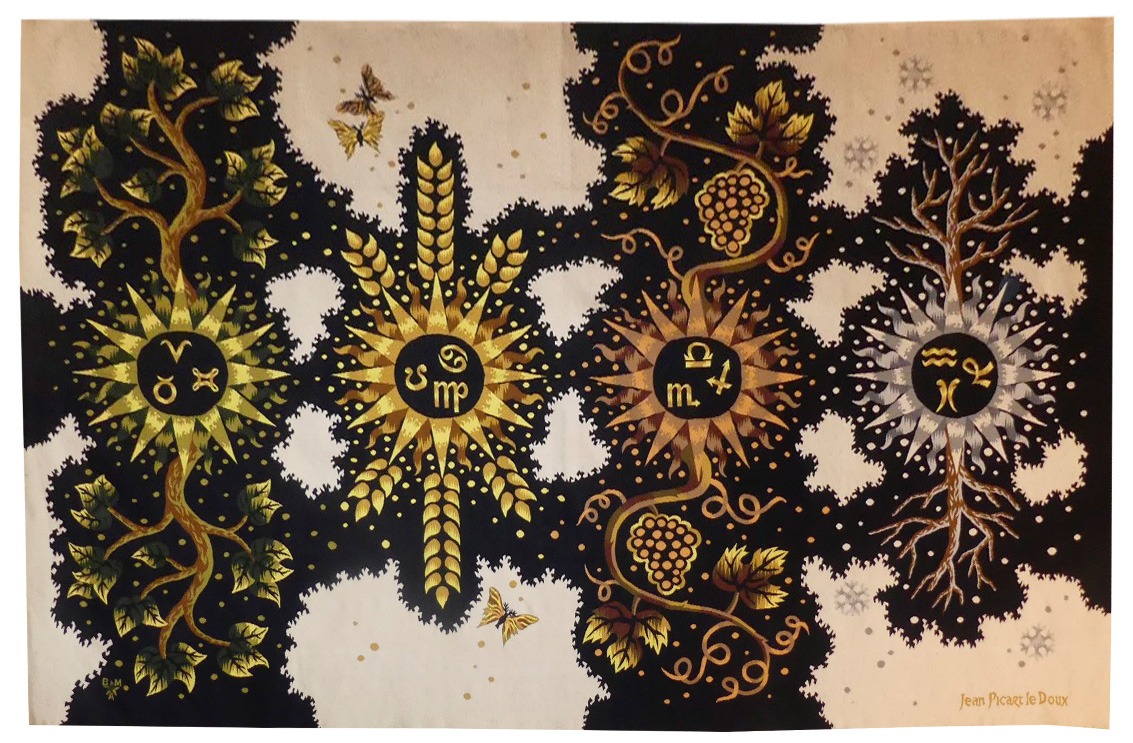
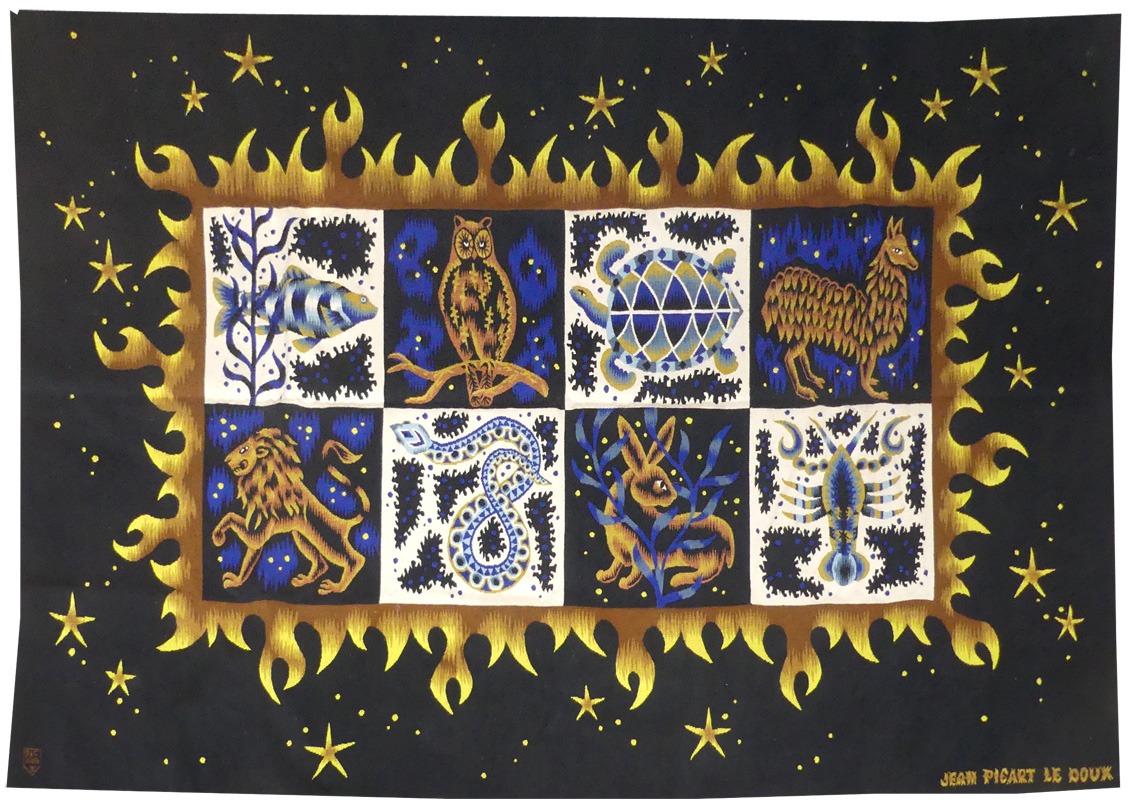
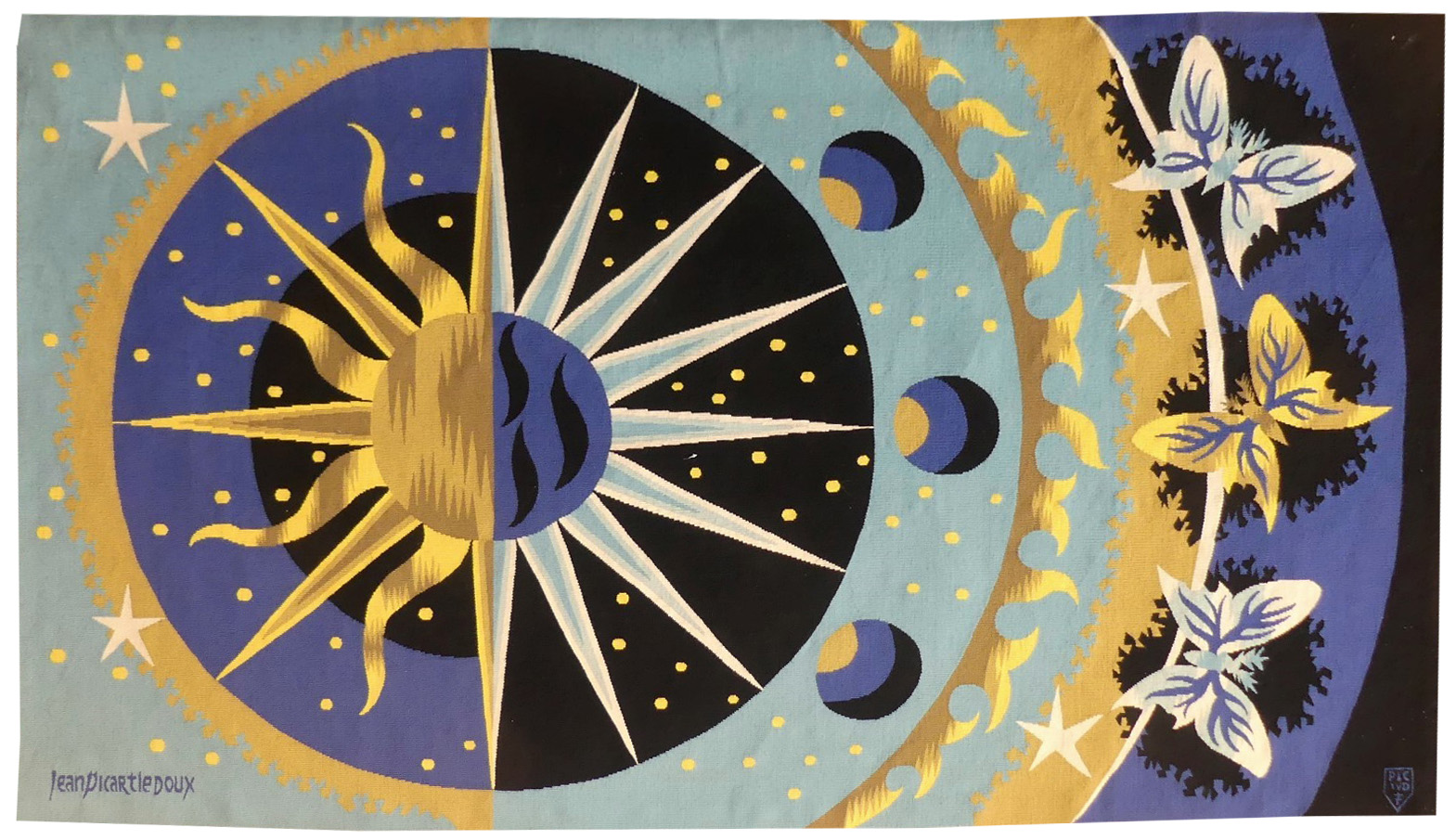
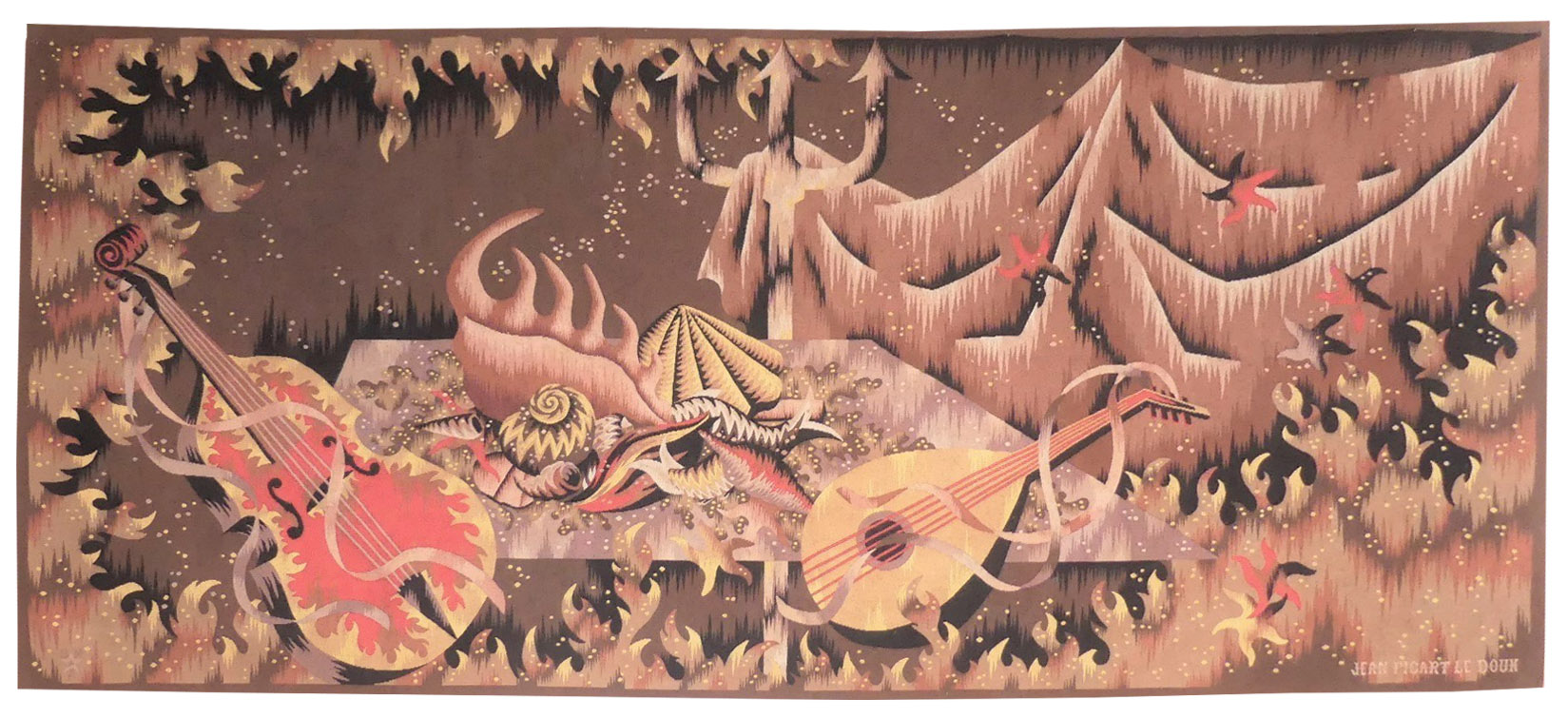
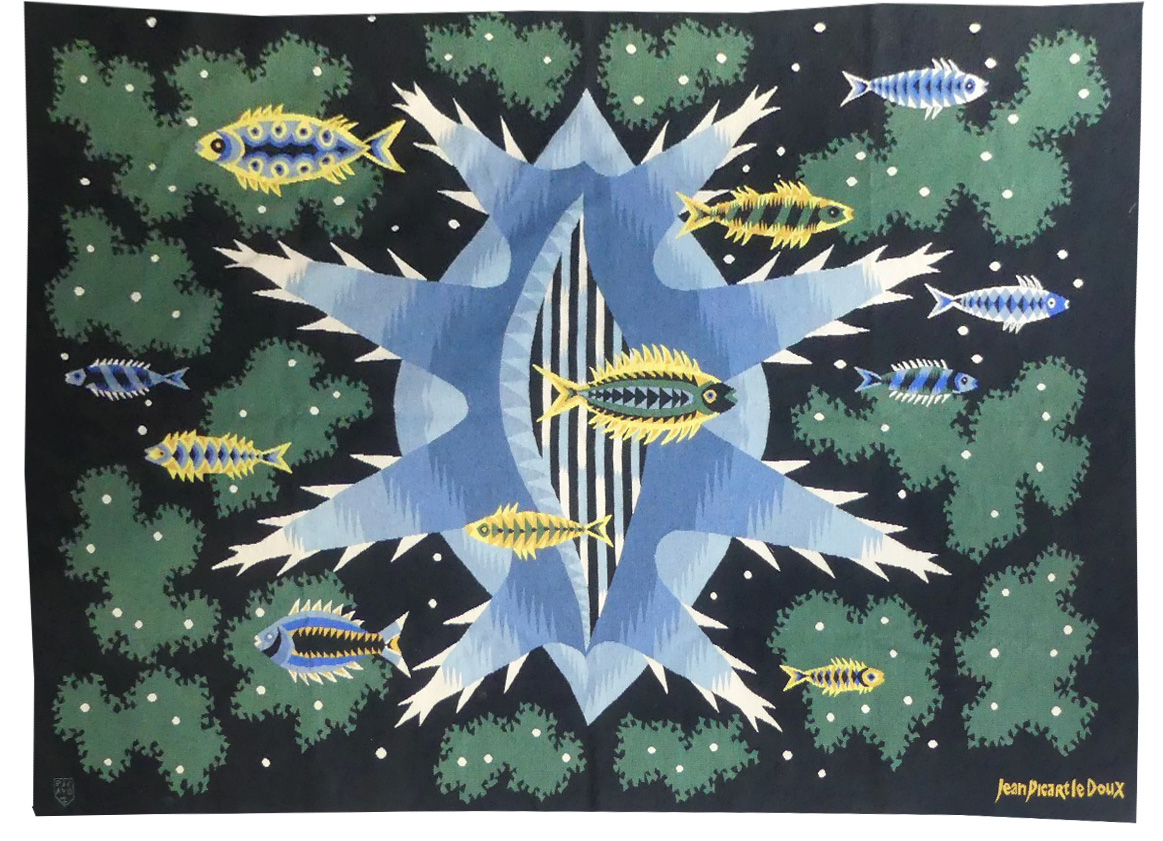
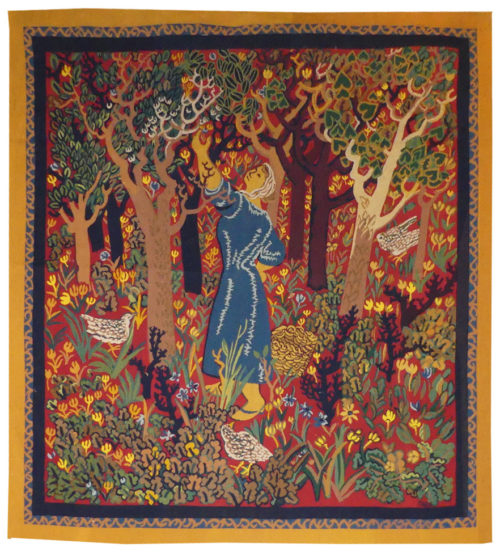
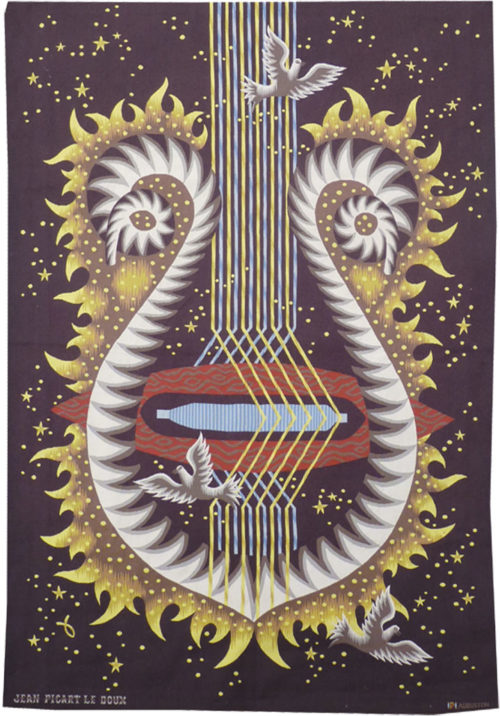
Cortège d'Orphée (Orpheus's procession)
Aubusson tapestry woven by the Berthaut workshop. 1961. Jean Picart le Doux is one of the foremost figures in the renaissance of the art of tapestry. His earliest contributions to the field date back to 1943 when he designed cartoons for the passenger ship “la Marseillaise”. A close associate of Lurçat, whose theories he would adopt (limited palette, numbered cartoons…), he was a founding member of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-cartonniers de Tapisserie), and soon after, a teacher at the Ecole Nationale Supérieure des Arts Décoratifs. The state gave him several commissions most of them at the Aubusson workshop, and some at the Gobelins : the most spectacular of these being for the University of Caen, the Theatre in Le Mans, the passenger ship France or the Prefecture of the Creuse département … In as much as Picart le Doux’s aesthetic is close to that of Lurçat, so also is his inspiration and his subject matter, although in a register which is more decorative than symbolic, where he brings together heavenly bodies (the sun, the moon, the stars…), the elements, nature (wheat, vines, fish, birds…), man, literary quotation … « The bestiary or Orpheus’ procession » is a collection of Poems by Apollinaire which would be illustrated with lithographs by Picart le Doux in 1962 (after Raoul Dufy’s work for the original edition). At the same time he designed a tapestry cartoon, using the form of a checkerboard popular with Lurçat, where each square figures a crayfish, a goat or a lion,..., in different and varied aspects of the animal kingdom. Bibliography : Marthe Belle-Joufray, Jean Picart le Doux, Publications filmées d’art et d’histoire, 1966, n°13 Maurice Bruzeau, Jean Picart le Doux, Murs de soleil, Editions Cercle d’art, 1972, n°108 Exhibition Catalogue, Jean Picart le Doux, tapisseries, Musée de Saint-Denis, 1976 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Picart le Doux, Boulogne sur Mer, Bibliothèque municipale, 1978 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Picart le Doux, Paris,Musée de la Poste, 1980 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Picart le Doux, Abbaye Saint Jean d’Orbestier, 1992 -
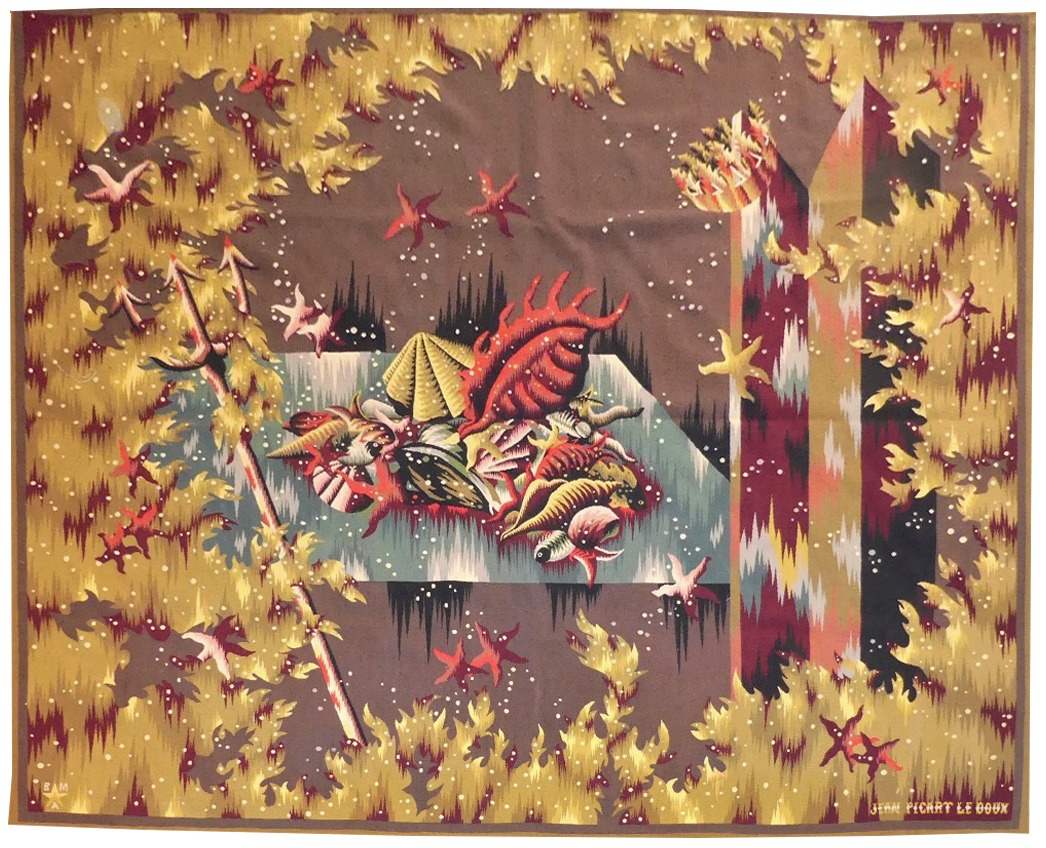
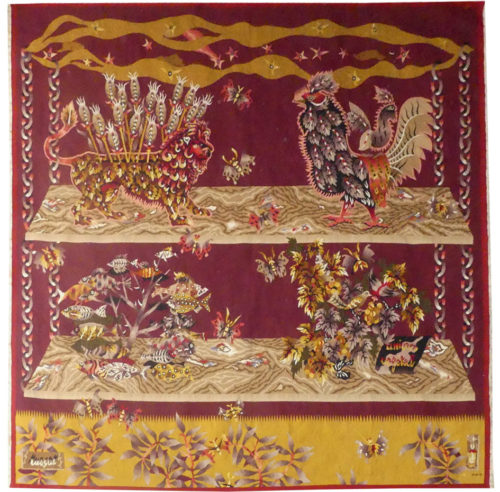
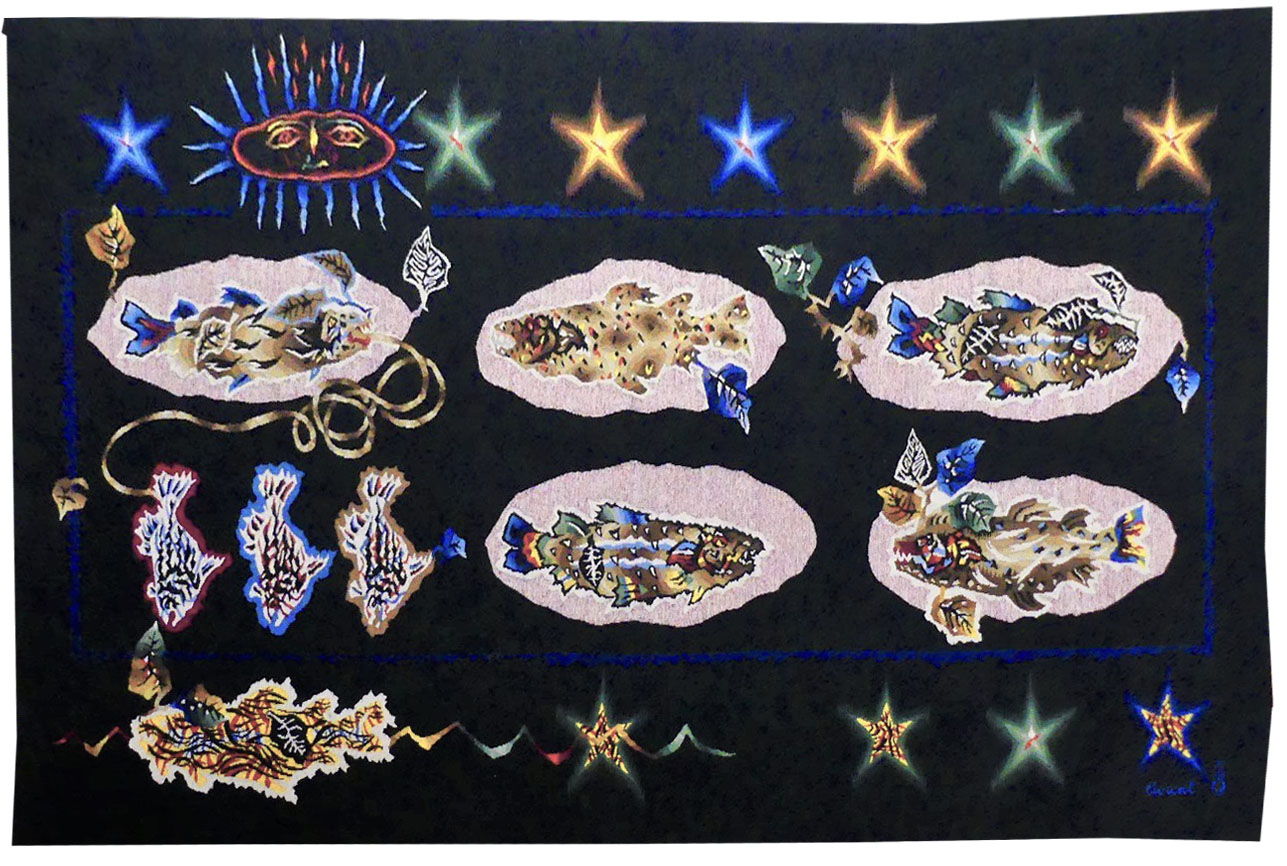
Le trident de Neptune (Neptune's trident)
Aubusson tapestry woven by the Berthaut workshop. 1946. Jean Picart le Doux is one of the foremost figures in the renaissance of the art of tapestry. His earliest contributions to the field date back to 1943 when he designed cartoons for the passenger ship “la Marseillaise”. A close associate of Lurçat, whose theories he would adopt (limited palette, numbered cartoons…), he was a founding member of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-cartonniers de Tapisserie), and soon after, a teacher at the Ecole Nationale Supérieure des Arts Décoratifs. The state gave him several commissions most of them at the Aubusson workshop, and some at the Gobelins : the most spectacular of these being for the University of Caen, the Theatre in Le Mans, the passenger ship France or the Prefecture of the Creuse département … In as much as Picart le Doux’s aesthetic is close to that of Lurçat, so also is his inspiration and his subject matter, although in a register which is more decorative than symbolic, where he brings together heavenly bodies (the sun, the moon, the stars…), the elements, nature (wheat, vines, fish, birds…), man, literary quotation … Our cartoon, one of the artist's first, reflects his allegorical and mythological references (see ‘Le trésor d'Amphitrite’ from 1949) in his treatment of the sea. A close tapestry, ‘Les algues’, is more literal. Bibliography : Marthe Belle-Joufray, Jean Picart le Doux, Publications filmées d’art et d’histoire, 1966 Maurice Bruzeau, Jean Picart le Doux, Murs de soleil, Editions Cercle d’art, 1972, n°6 Exhibition Catalogue, Jean Picart le Doux, tapisseries, Musée de Saint-Denis, 1976 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Picart le Doux, Boulogne sur Mer, Bibliothèque municipale, 1978 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Picart le Doux, Paris,Musée de la Poste, 1980 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Picart le Doux, Abbaye Saint Jean d’Orbestier, 1992 -
In 1987, Texier received a commission for the Human Rights tapestries ensemble to mark the bicentenary of the Revolution. The choice was unexpected, as the artist, still young, had never before produced tapestry cartoons. This commission brought together the Aubusson workshops that were still in operation at the time, with the seven tapestries covering a total of more than 130 woven sq.m. with literal quotations (the tables of the declaration are reproduced identically to the engraving from the revolutionary period), oscillating objects, signs, texts, etc. Texier went on to provide cartoons for both the Manufactures Nationales (a series of three tapestries and a carpet) and Aubusson. Our cartoon incorporates the visual symbols, scattered texts, and traces characteristic of the artist's graphic and visual universe, which constitute, to quote him, “maps where [he] introduces guiding elements” in order to reveal the eponymous « secret » to us. Bibliography : La Suite des Droits de l’Homme, Niort, 1989Aubusson tapestry woven by the Pinton workshop. With signed label, n°1/1. 2001.
-
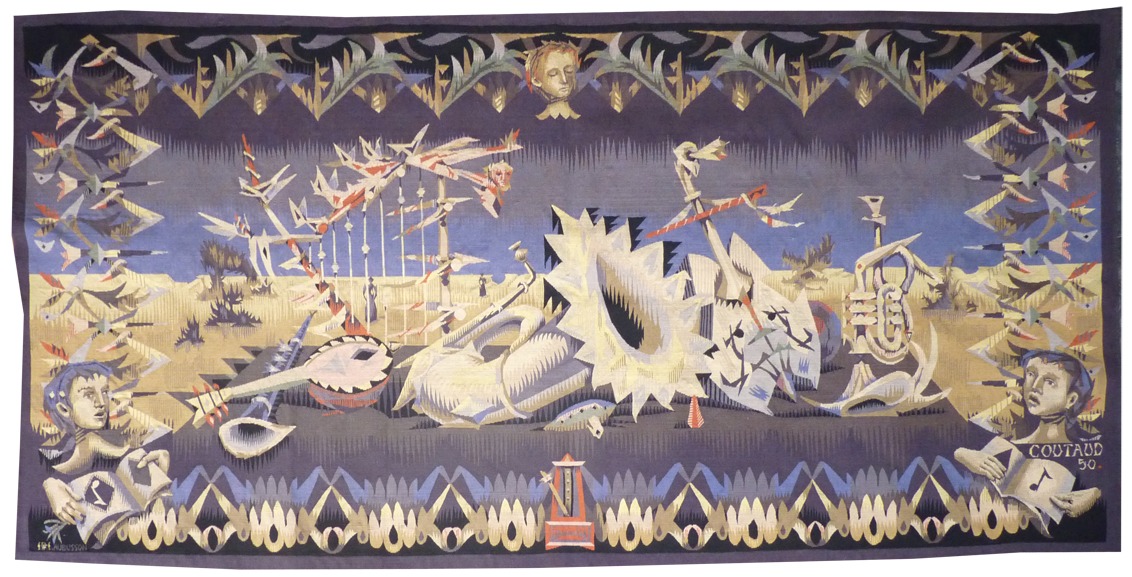
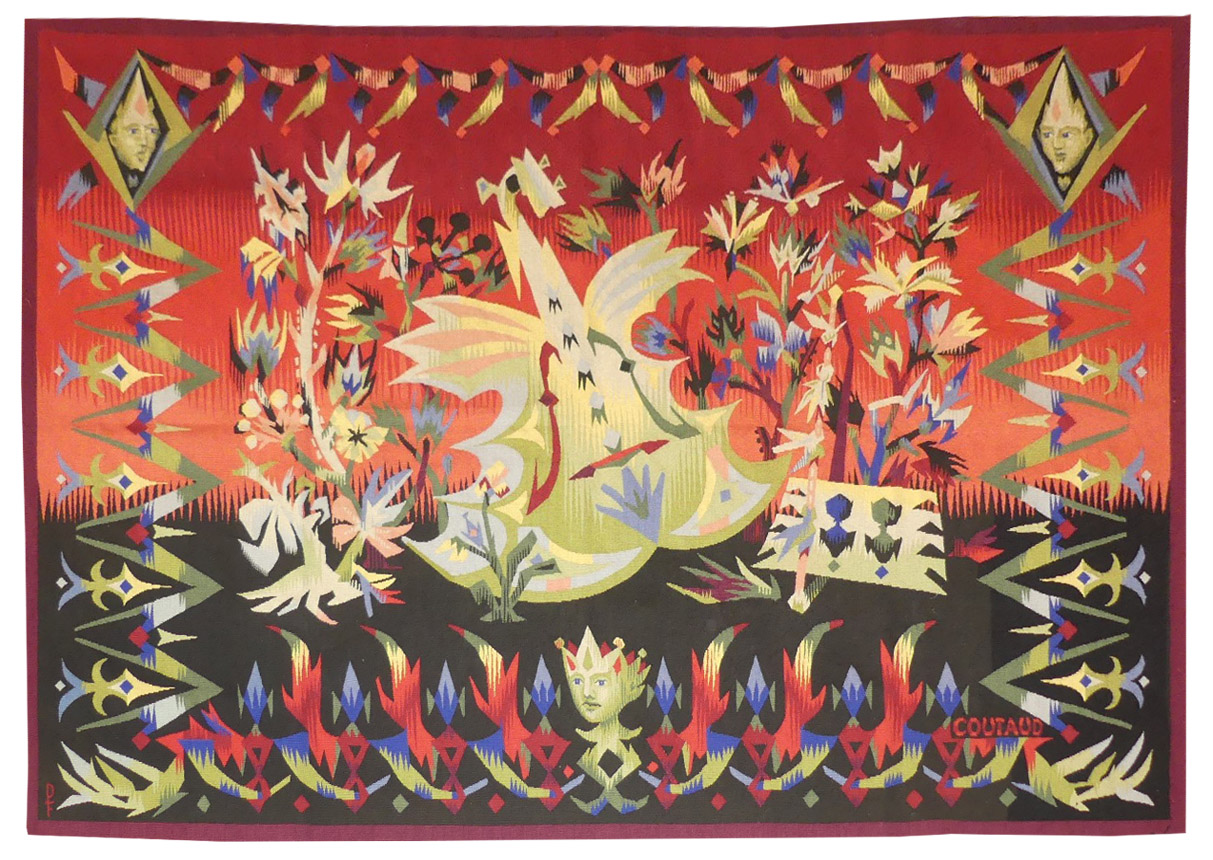
Instruments de musique lunaire (instruments for moonlight music)
A painter and engraver, Lucien Coutaud also worked in the theatre with Dullin, Barrault and designed numerous sets and costumes. However it was his encounter with Marie Cuttoli in 1933 which would introduce him to tapestry : she mainly commissioned seat cover designs. Most of the tapestries that followed were woven in the Pinton workshop for the Compagnie des Arts Français, whose main aim was to integrate tapestry as an element of interior decoration. The last 3 tapestries designed by the artist in 1960 are a tribute to his notoriety because “Jardins exotiques” was chosen to decorate the 1st class saloon on the “France” transatlantic liner.Elements of his work as a set designer, influenced by surrealism, are discernible in Coutaud’s woven art : the world he illustrates is figurative yet stylised (shapes are angular and harsh) contained in a dream world often incorporating unusual borders. The cartoon « Instruments de musique lunaire » (Coutaud painted his own cartoons in watercolours without having recourse to numbered cartoons) dates from 1950 : it’s one of the few tapestries designed by this artist (notable also are « Harpe marine » Marine harp and « Violon printanier » Spring violin », as examples of his taste for musical still lives) where the human figure is absent. The centre of the scene (the stage) is occupied by the instruments, while two heads (blowing into musical instruments in the pit) take up the two bottom corners, the whole meanwhile being an austere scene, night time (hence the moonlight) a good representation of the dream-like universe inhabited by this artist’s creations. The municipal theatre in Göteborg possesses a copy of this tapestry. Bibliography : J. Cassou, M. Damain, R. Moutard-Uldry, la tapisserie française et les peintres cartonniers, Tel, 1957, ill. p.86 Exhibition Catalogue Lucien Coutaud, œuvre tissé, Aubusson, Musée Départemental de la Tapisserie, 1988-1989, ill. p.42-43 Exhibition Catalogue Le théâtre en tapisserie, Cavaillès, Lurçat, Matisse, Sorèze, Abbaye-école Musée dom Robert, 2017, ill. n°8Aubusson tapestry woven by the Pinton workshop. 1950. -
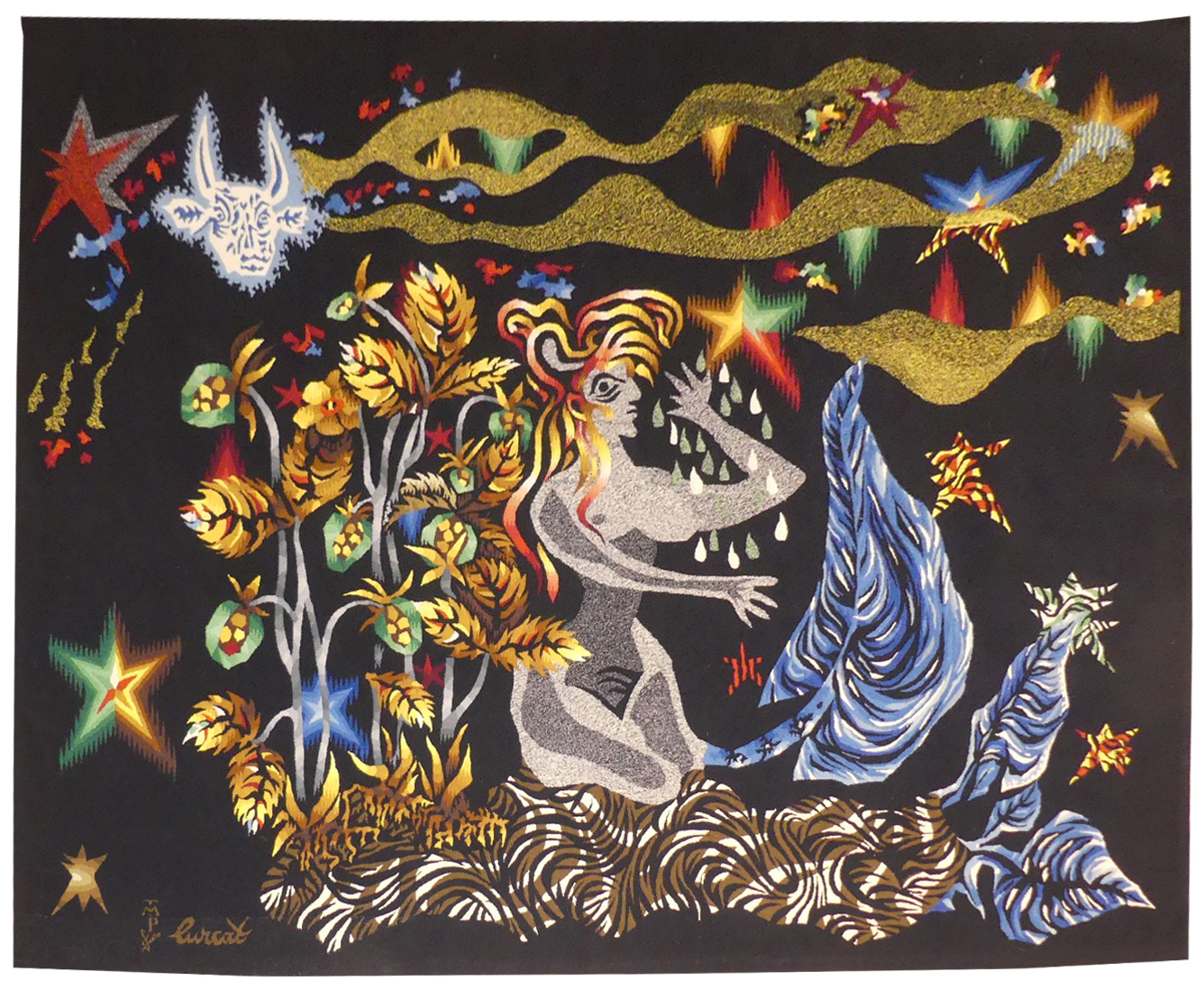
Eve
Lurçat’s artistic production was immense : it is however his role as the renovator of the art of tapestry design which ensures his lasting renown. As early as 1917, he started producing works on canvas, then in the 20’s and 30’s, he worked with Marie Cuttoli. His first collaboration with the Gobelins workshop dates back to 1937, at the same time he discovered the tapestry of the Apocalypse which was essential in his decision to devote himself to tapestry design. He first tackled the technical aspects with François Tabard, then on his installation at Aubusson during the war, he established his technique : broad point, a simplified palette, outlined cartoons with colours indicated by pre-ordained numbers. A huge production then follows (over 1000 cartoons) amplified by his desire to include his painter friends, the creation of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-Cartonniers de Tapiisserie) and the collaboration with the art gallery La Demeure and Denise Majorel, and then by his role as a tireless advocate for the medium around the world. His tapestries reveal a pictorial world which is specifically decorative, with a very personal symbolic iconography : cosmogony (the sun, the planets, the zodiac, the four elements…) stylised vegetation, fauna (rams, cocks, butterflies, chimera …) standing out against a background without perspective (voluntarily different from painting) and, in his more ambitious work, designed as an invitation to share in a poetic (he sometimes weaves quotations into his tapestries) and philosophical (the grand themes are broached from the wartime period onwards) vision whose climax is the “Chant du Monde” (Song of the World) (Jean Lurçat Museum , ancien hôpital Saint Jean, Angers) which remained unfinished at his death. The total or partial re-use of cartoons is a characteristic of Lurçat’s working method : thus Eve is a replica in reverse of « La Poésie » (poetry), the antepenultimate panel of the « Chant du monde » series. Here the human face (? figure?) which had long been absent in the artist’s work, reappears. Was it his intention to create a biblical figure, an incarnation of woman, a poetic evocation, a sign of the zodiac (Virgo?)? The given title is Eve, probably out of respect for the artists widow’s wishes. Bibliography : Tapisseries de Jean Lurçat 1939-1957, Pierre Vorms Editeur, 1957 Exhibition Catalogue Lurçat, 10 ans après, Musée d'Art moderne de la ville de Paris, 1976 Exhibition catalogue Les domaines de Jean Lurçat, Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la tapisserie contemporaine, 1986 Symposium Jean Lurçat et la renaissance de la tapisserie in Aubusson, Aubusson, Musée départemental de la tapisserie 1992 Exhibition Catalogue Dialogues avec Lurçat, Musées de Basse-Normandie, 1992 Exhibition catalogue Jean Lurçat, Donation Simone Lurçat, Académie des Beaux-Arts, 2004 Jean Lurçat, le chant du monde Angers 2007 Gérard Denizeau, Jean Lurçat, Liénart, 2013 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Lurçat au seul bruit du soleil, Paris, galerie des Gobelins, 2016Tapestry woven in the Fino workshop, Portalegre. With label signed by the artist's widow. 1962. -
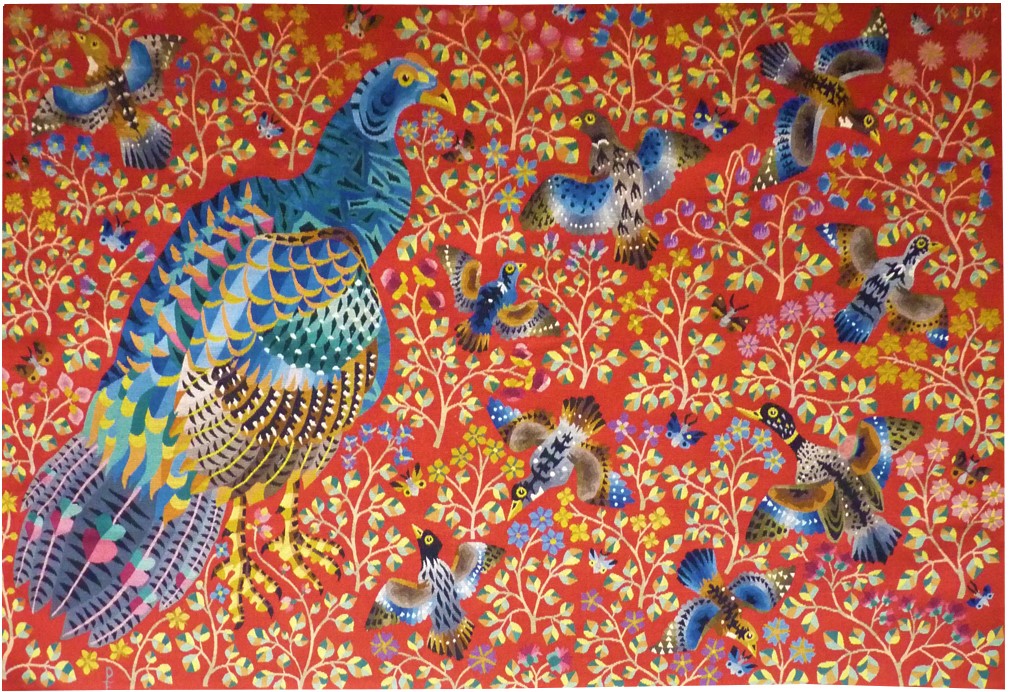
Le dindon (the turkey)
Perrot began his career as a cartoon designer at the end of the war, making almost 500 cartoons including numerous commissions from the state, most of which were woven at Aubusson. His style which is particularly rich and decorative is eminently recognisable : a crowd of butterflies or birds, most often, stands out against a background of vegetation, reminiscent of the millefleurs tapestries (which would also inspire Dom Robert). This tapestry is a typical example of the artist’s portraits of birds ; the turkey appears, as often in his work, associated with other birds, against a background inspired by the flower-strewn mediaeval tapestries. Another example was woven for the Ministry of Reconstruction. Bibliography : Tapisseries, dessins, peintures, gravures de René Perrot, Dessein et Tolra, 1982 Tapisserie d’Aubusson, Association du développement du pays d’Aubusson, 1983, ill.p.40 Cat. Expo. René Perrot, mon pauvre cœur est un hibou, Aubusson, Cité de la Tapisserie, 2023Aubusson tapestry woven by the Pinton workshop. With label. Circa 1960. -
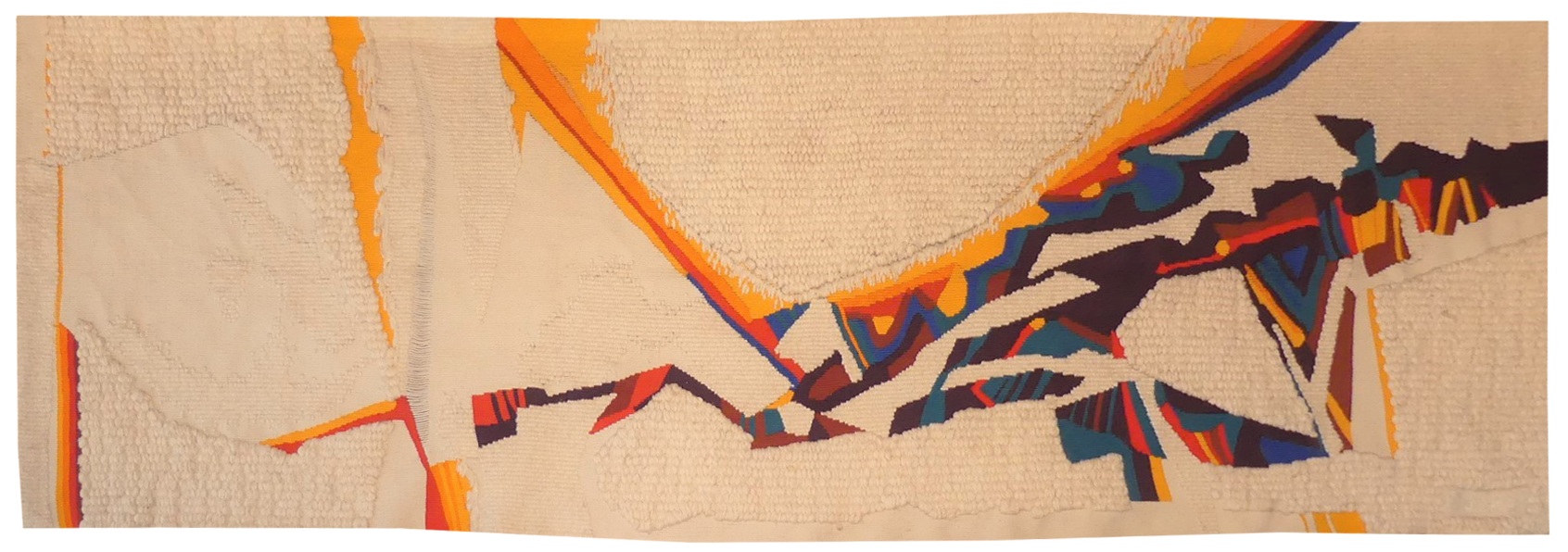
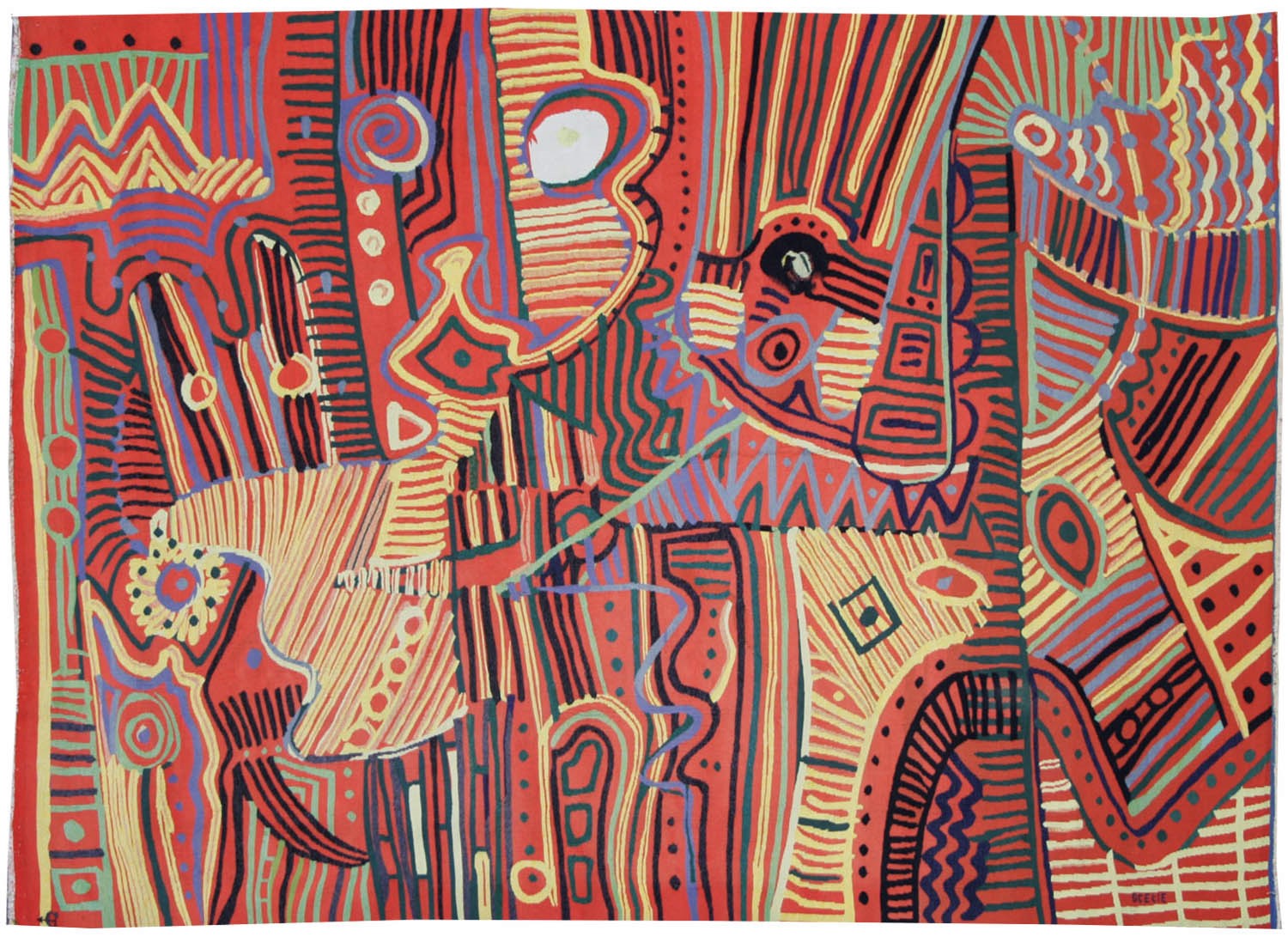
Sabulum
Jacques Brachet was an important protagonist of the « New Tapestry » movement ; woven by Pierre Daquin, exhibited by the « La Demeure » gallery in the 1970’s, his innovative and experimental approach to the medium, from the 1950’s onwards, was recognised by the Centre International d’études pédagogiques in Sèvres, by the scenography of “La Tapisserie en France, 1945 – 1985, la tradition vivante” at the Ecole Nationale Supérieure des Beaux-Arts, and by his inclusion in various promotional events right up to the present day. The specific techniques of his tapestry designs (as opposed to painting) : innovative use of shape and texture, themes taken from the natural world etc. took shape in the 1970s; he was then close to Pierre Daquin, who wove a number of his tapestries. Although he is known for his marine subjects, Brachet's inspiration also turns to the mineral world (Sabulum = sand in Latin), which gives a more figurative flavour to our cartoon, with a challenge : how to translate sand into wool? Bibliography : Exhibition catalogue Jacques Brachet, mémoires océanes, Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la tapisserie contemporaine, 1996Tapestry woven in the Saint-Cyr workshop. With signed label, n°EA. 1973. -
Le violon printanier (the spring violin)
A painter and engraver, Lucien Coutaud also worked in the theatre with Dullin, Barrault and designed numerous sets and costumes. However it was his encounter with Marie Cuttoli in 1933 which would introduce him to tapestry : she mainly commissioned seat cover designs. Most of the tapestries that followed were woven in the Pinton workshop for the Compagnie des Arts Français, whose main aim was to integrate tapestry as an element of interior decoration. The last 3 tapestries designed by the artist in 1960 are a tribute to his notoriety because “Jardins exotiques” was chosen to decorate the 1st class saloon on the “France” transatlantic liner.Elements of his work as a set designer, influenced by surrealism, are discernible in Coutaud’s woven art : the world he illustrates is figurative yet stylised (shapes are angular and harsh) contained in a dream world often incorporating unusual borders. There's a close link between music and fantasy in Coutaud's world: he creates musical still lifes where instruments come to life (cf. “harpe marine”), underlined by eccentric borders. Bibliography : Exhibition catalogue Lucien Coutaud, œuvre tissé, Aubusson, Musée Départemental de la Tapisserie, 1988-1989, illustrated p 50Aubusson tapestry woven by the Pinton workshop. With signed label, n°2/6. 1956. -
La pluie (rain)
A painter and engraver, Lucien Coutaud also worked in the theatre with Dullin, Barrault and designed numerous sets and costumes. However it was his encounter with Marie Cuttoli in 1933 which would introduce him to tapestry : she mainly commissioned seat cover designs. Most of the tapestries that followed were woven in the Pinton workshop for the Compagnie des Arts Français, whose main aim was to integrate tapestry as an element of interior decoration. The last 3 tapestries designed by the artist in 1960 are a tribute to his notoriety because “Jardins exotiques” was chosen to decorate the 1st class saloon on the “France” transatlantic liner.Elements of his work as a set designer, influenced by surrealism, are discernible in Coutaud’s woven art : the world he illustrates is figurative yet stylised (shapes are angular and harsh) contained in a dream world often incorporating unusual borders. “La pluie” and its counterpart “la neige” take up the theme of Man (medieval in this case, given his attire) in harmony with Nature, as in “La pluie et le beau temps”. We also find the artist's taste for narrow vertical formats, sometimes woven as folding screens (cf. “Passe-temps”). Bibliography : J. Cassou, M. Damain, R. Moutard-Uldry, la tapisserie française et les peintres cartonniers, Tel, 1957, ill. p.88-89 Exhibition catalogue Lucien Coutaud, œuvre tissé, Aubusson, Musée Départemental de la Tapisserie, 1988-1989, illustrated p.36Aubusson tapestry woven by the Pinton workshop, for the Compagnie des Arts Français. 1946. -
Fireworks
Mark Adams made his first tapestry cartoons in 1952 (a multi-talented artist he also painted murals and designed stain-glass windows…). He arrived in France in 1955, working with Lurçat at Tours Saint-Laurent and also at the Ecole Nationale d’Art Décoratif in Aubusson. One of the very few American peintres-cartonniers, he participated in the Biennales de Lausanne, and produced over a hundred cartoons most of which were woven in Aubusson, notably by Paul Avignon. Recognised above all for his tapestry designs featuring wing motifs, Mark Adams sought inspiration in many and varied fields. Our "tapestry is related to the "Fire fountain" tapestry, and is another design that focuses on the display pattern from the light and sparks of a fireworks display against the dark sky (Multi-authored, Mark Adams, catalogue raisonné of tapestries, Stanford University Press, 2012, n°033, p.91). Bibliography : Multi-authored, Mark Adams, catalogue raisonné of tapestries, Stanford University Press, 2012Aubusson tapestry woven by the Avignon workshop. 1960. -
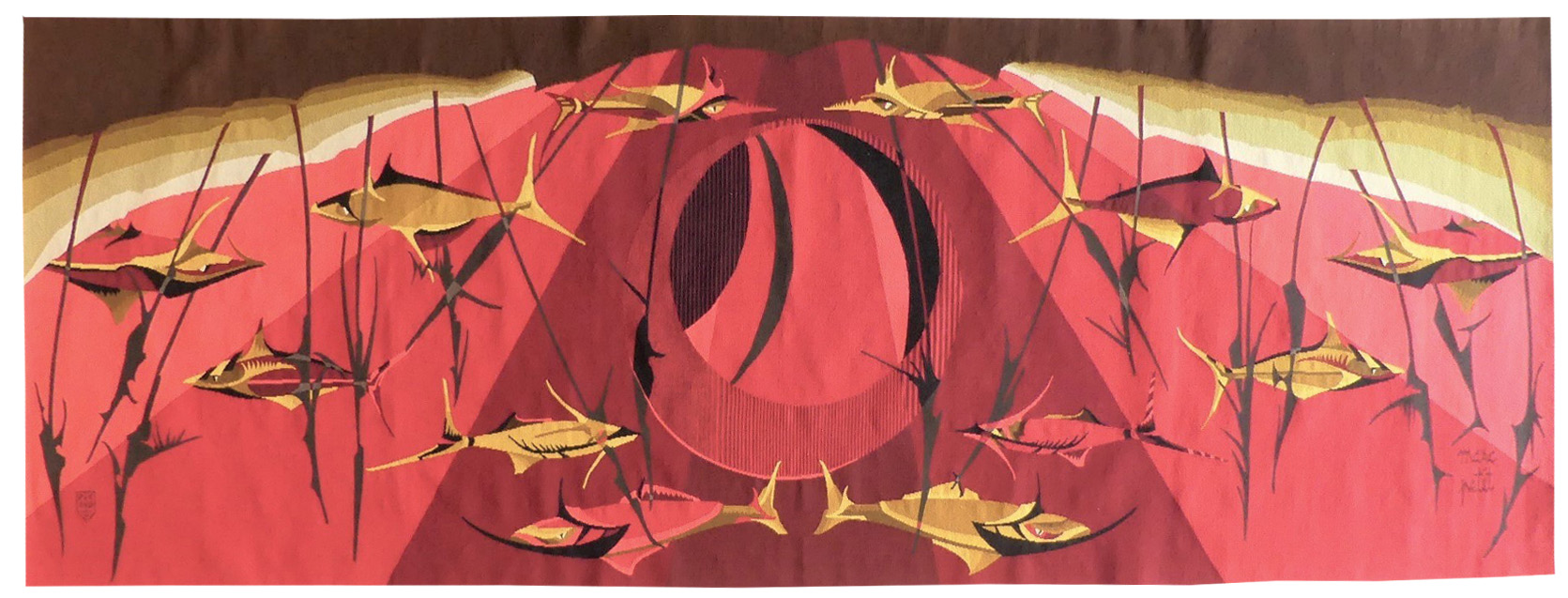
Brochette (skewer)
Lurçat’s artistic production was immense : it is however his role as the renovator of the art of tapestry design which ensures his lasting renown. As early as 1917, he started producing works on canvas, then in the 20’s and 30’s, he worked with Marie Cuttoli. His first collaboration with the Gobelins workshop dates back to 1937, at the same time he discovered the tapestry of the Apocalypse which was essential in his decision to devote himself to tapestry design. He first tackled the technical aspects with François Tabard, then on his installation at Aubusson during the war, he established his technique : broad point, a simplified palette, outlined cartoons with colours indicated by pre-ordained numbers. A huge production then follows (over 1000 cartoons) amplified by his desire to include his painter friends, the creation of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-Cartonniers de Tapisserie) and the collaboration with the art gallery La Demeure and Denise Majorel, and then by his role as a tireless advocate for the medium around the world. His tapestries reveal a pictorial world which is specifically decorative, with a very personal symbolic iconography : cosmogony (the sun, the planets, the zodiac, the four elements…) stylised vegetation, fauna (rams, cocks, butterflies, chimera …) standing out against a background without perspective (voluntarily different from painting) and, in his more ambitious work, designed as an invitation to share in a poetic (he sometimes weaves quotations into his tapestries) and philosophical (the grand themes are broached from the wartime period onwards) vision whose climax is the “Chant du Monde” (Song of the World) (Jean Lurçat Museum , ancien hôpital Saint Jean, Angers) which remained unfinished at his death. The skewers are discreet (in some cartoons, Lurçat does not hesitate to place fish on tridents), and the fish appear as if on a stall, an arrangement that echoes the partitioning of his famous wardrobes. Bibliography : Tapisseries de Jean Lurçat 1939-1957, Pierre Vorms Editeur, 1957 Exhibition Catalogue Lurçat, 10 ans après, Musée d'Art moderne de la ville de Paris, 1976 Exhibition catalogue Les domaines de Jean Lurçat, Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la tapisserie contemporaine, 1986 Symposium Jean Lurçat et la renaissance de la tapisserie in Aubusson, Aubusson, Musée départemental de la tapisserie 1992 Exhibition Catalogue Dialogues avec Lurçat, Musées de Basse-Normandie, 1992 Exhibition catalogue Jean Lurçat, Donation Simone Lurçat, Académie des Beaux-Arts, 2004 Jean Lurçat, le chant du monde Angers 2007 Gérard Denizeau, Jean Lurçat, Liénart, 2013 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Lurçat au seul bruit du soleil, Paris, galerie des Gobelins, 2016Aubusson tapestry woven in the Tabard workshop. With signed label. Circa 1955. -
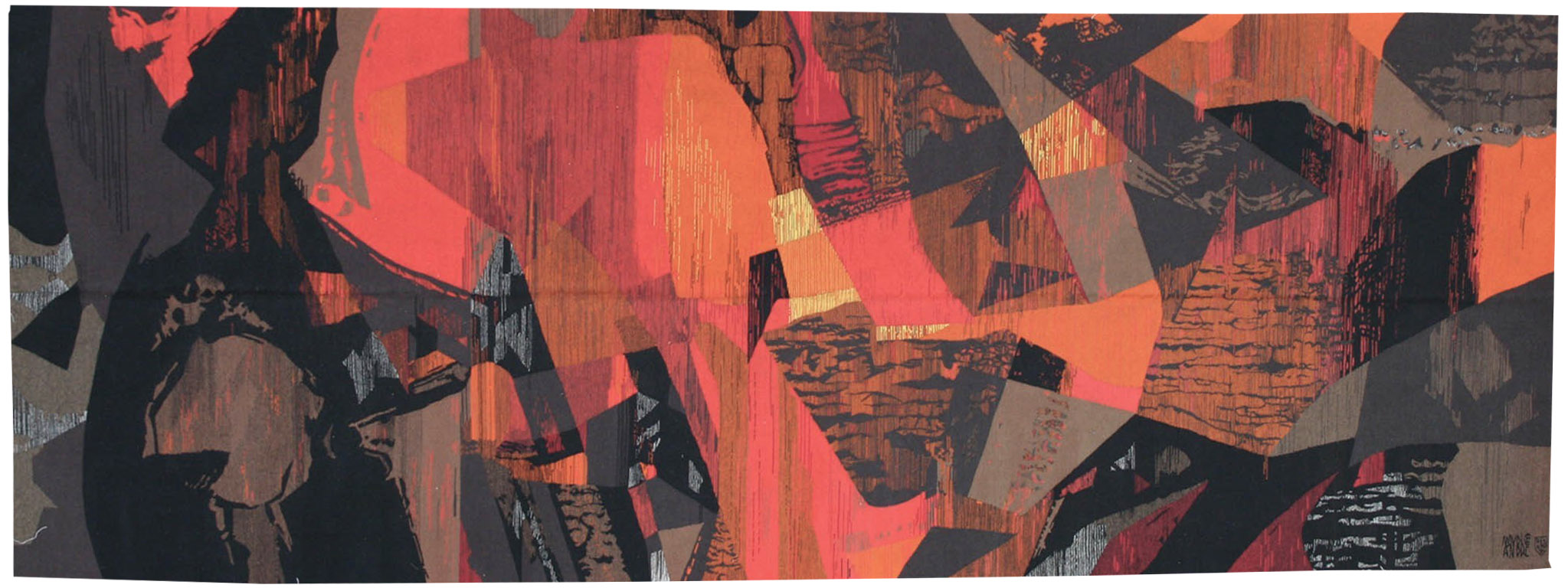
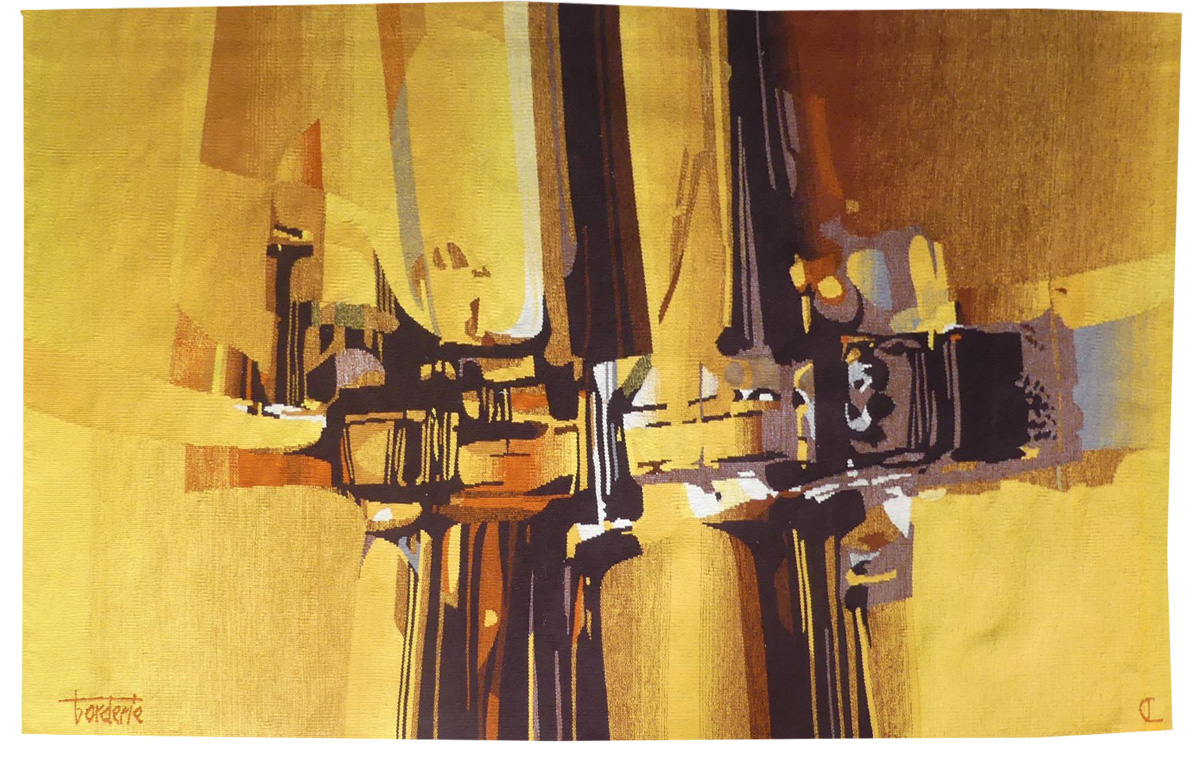
D'or et d'ombre (of gold and shade)
Originally a sculptor exploiting very diverse materials (steel, concrete, clay…), Borderie came to tapestry with immense enthusiasm in the 1950’s with the weaving of his first cartoon in 1957. Receiving encouragement from Denise Majorel, he was awarded the Grand Prix National de la Tapisserie in 1962. In 1974 he was appointed as director at the Ecole Nationale des Arts Décoratifs at Aubusson but he resigned from this post shortly thereafter. He designed over 500 painted cartoons, abstracts using simple shapes, shading in a limited palette of colours and weaving with gros points. Here we find the same preoccupations with light (and shadow) as in ‘les armes de la lumière’ (and as in Matégot's work). Borderie was also woven by workshops other than Legoueix in Aubusson, Rado, Daquin and, more confidentially, Chartron in Angers (who wove Jorj Morin in particular). Bibliography : Exhibition catalogue André Borderie « pour l’homme simplement », Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la Tapisserie Contemporaine, 1998 Exhibition Catalogue André Borderie et la tapisserie d’Aubusson, Aubusson, Manufacture Saint-Jean, 2018Tapestry woven in the Cartron workshop. With signed label, n°1/1. Circa 1970. -
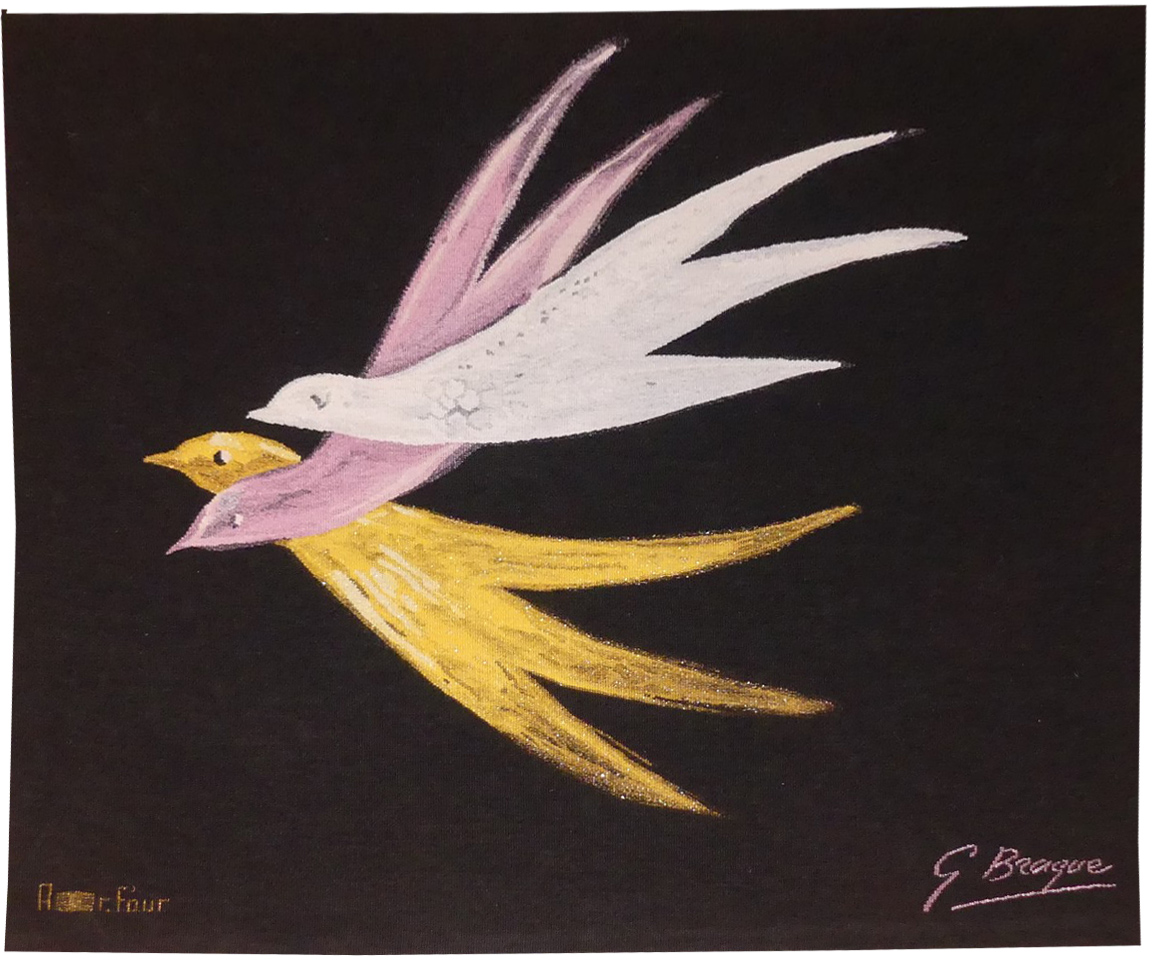
Les 3 Grâces (the 3 Graces)
Braque is another 20th century artist who produced, however modestly, works in tapestry form. It was originally at the request of Marie Cuttoli in 1933, that he submitted works for reproduction as tapestries (Nature morte au guéridon [Still life on an occasional table], conserved at the Musée des Beaux Arts in Grenoble). In the 1950’s and 60’s it was Pierre Baudouin, in association with the weavers of Aubusson and the Nationale Manufactures, who would be asked to transcribe to cartoon format some of the artist’s productions. At the same time, shortly before his death in 1963, Braque made a last series of images in gouache, taking as their theme metamorphoses, which were destined for reproduction in various different media. Tapestry would be one of these. “The three graces”, 1962, is one which would appear in sculpture, or as jewelry. In it we observe the lyrical and synthetic style to be found in the artist’s last works (obviously the decor of the ceiling in the Henri II room at the Louvre, les Oiseaux [the birds] 1953 comes to mind).Aubusson tapestry woven by the Four workshop. N°3/6. Woven circa 2000, after a 1962 gouache. -
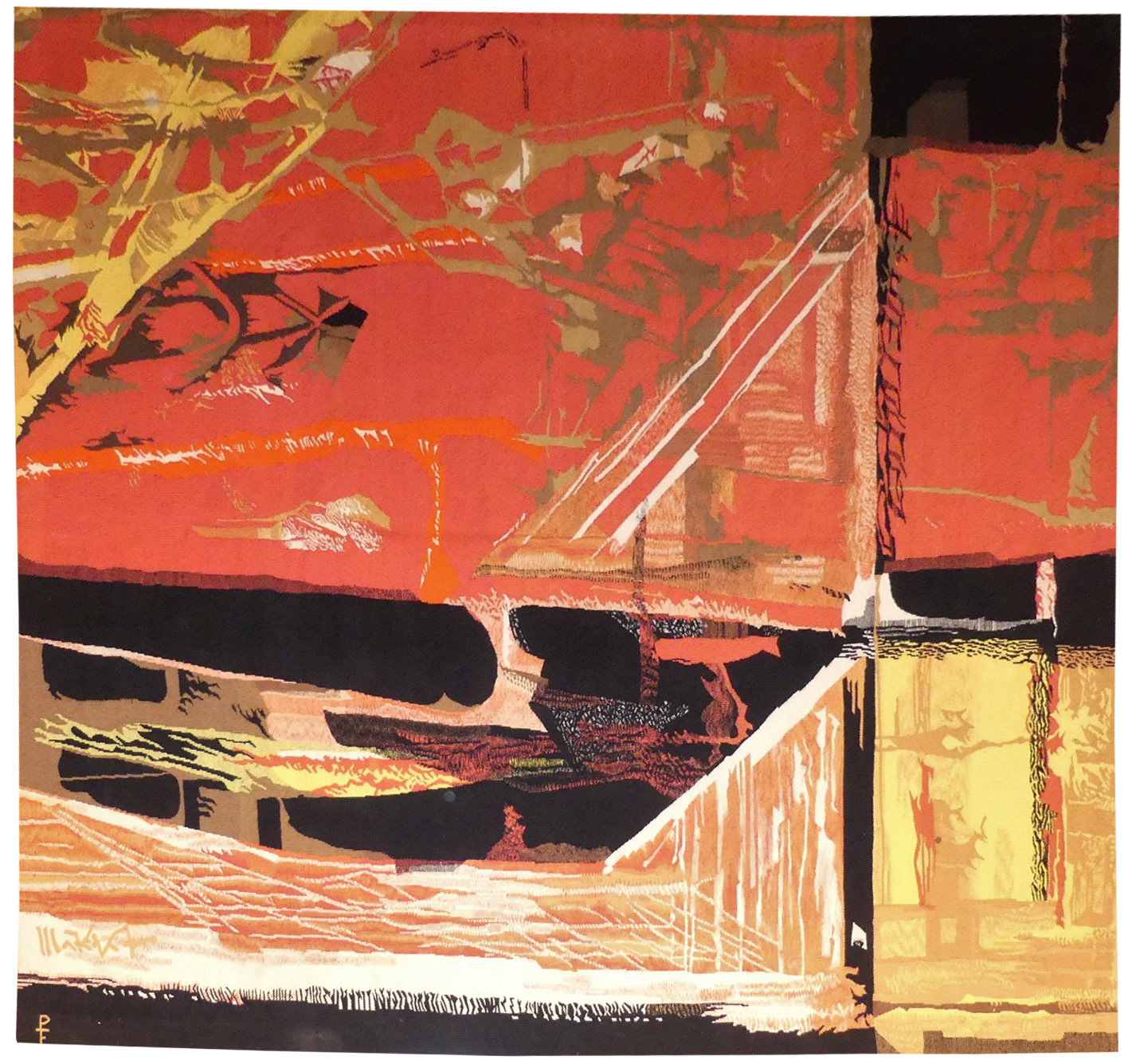
Soleil orange (orange sun)
Aubusson tapestry woven by the Bertaut workshop. N°3/8. 1964. Jean Picart le Doux is one of the foremost figures in the renaissance of the art of tapestry. His earliest contributions to the field date back to 1943 when he designed cartoons for the passenger ship “la Marseillaise”. A close associate of Lurçat, whose theories he would adopt (limited palette, numbered cartoons...), he was a founding member of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-cartonniers de Tapisserie), and soon after, a teacher at the Ecole Nationale Supérieure des Arts Décoratifs. The state gave him several commissions most of them at the Aubusson workshop, and some at the Gobelins : the most spectacular of these being for the University of Caen, the Theatre in Le Mans, the passenger ship France or the Prefecture of the Creuse département ... In as much as Picart le Doux’s aesthetic is close to that of Lurçat, so also is his inspiration and his subject matter, although in a register which is more decorative than symbolic, where he brings together heavenly bodies (the sun, the moon, the stars...), the elements, nature (wheat, vines, fish, birds...), man, literary quotation ... Our cartoon repeats, asymmetrically, ‘Winter Solstice’: the evocation of the Seasons, a major theme for the artist, will continue throughout his work. Bibliography : Marthe Belle-Joufray, Jean Picart le Doux, Publications filmées d’art et d’histoire, 1966 Valentine Fougère, Tapisseries de notre temps, les éditions du temps, 1969, reproduced p.84 Maurice Bruzeau, Jean Picart le Doux, Murs de soleil, Editions Cercle d’art, 1972 Exhibition Catalogue, Jean Picart le Doux, tapisseries, Musée de Saint-Denis, 1976 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Picart le Doux, Musée de la Poste, 1980 -
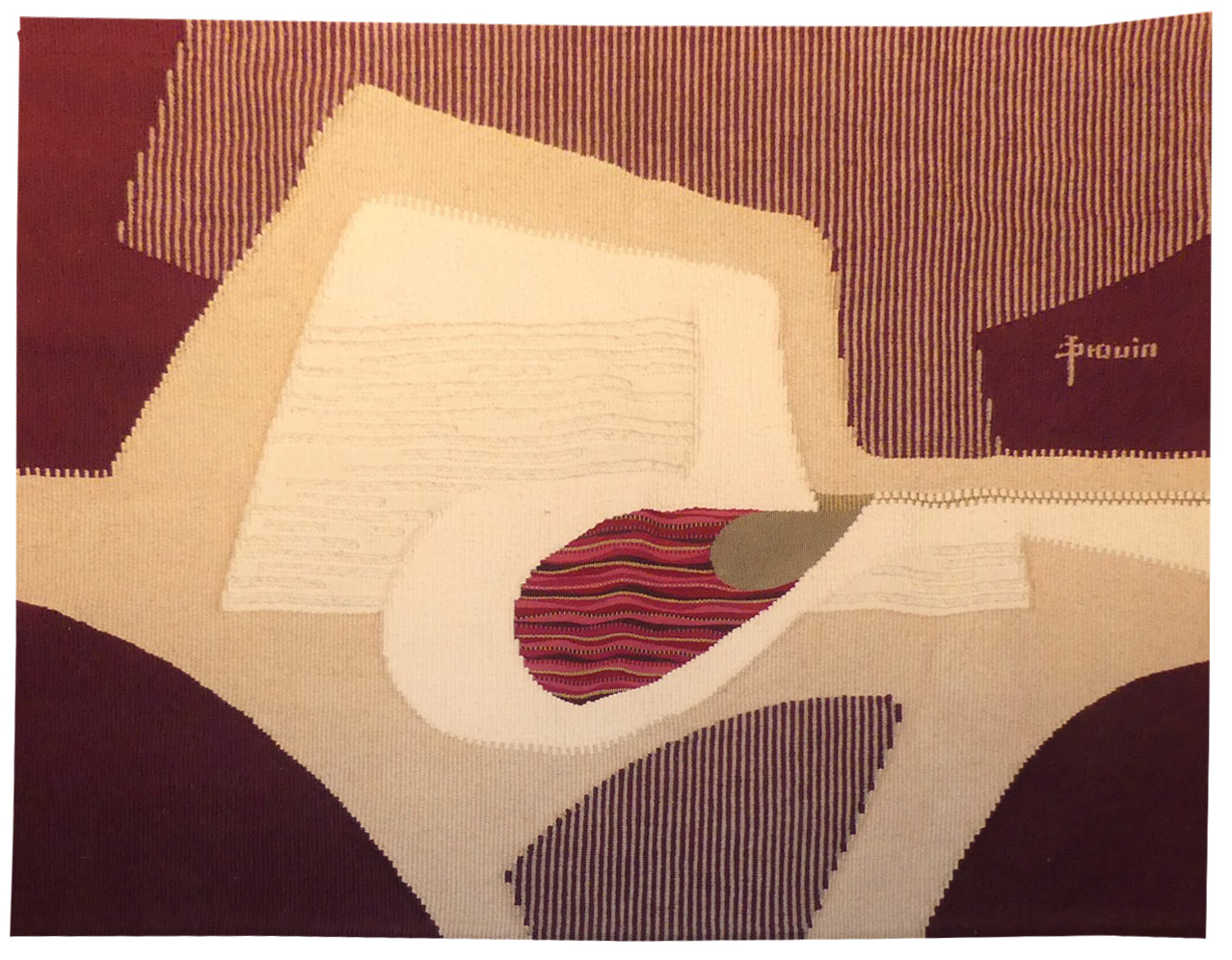
Melinjana
After having established himself at the Gobelins, Daniel Drouin moved to Venasque. He designed numerous tapestries woven on a high-warp loom. The variety of the materials used, his propensity for abstraction and the fact that the artist wove his own designs conformed to certain preoccupations of the “Nouvelle Tapisserie” movement of the time, without however escaping from the 2 dimensional nature of the artform.Tapestry woven in the atelier de la Tuilière. With label. Circa 1970. -
Le grand-duc (the eagle-owl)
Lurçat’s artistic production was immense : it is however his role as the renovator of the art of tapestry design which ensures his lasting renown. As early as 1917, he started producing works on canvas, then in the 20’s and 30’s, he worked with Marie Cuttoli. His first collaboration with the Gobelins workshop dates back to 1937, at the same time he discovered the tapestry of the Apocalypse which was essential in his decision to devote himself to tapestry design. He first tackled the technical aspects with François Tabard, then on his installation at Aubusson during the war, he established his technique : broad point, a simplified palette, outlined cartoons with colours indicated by pre-ordained numbers. A huge production then follows (over 1000 cartoons) amplified by his desire to include his painter friends, the creation of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-Cartonniers de Tapisserie) and the collaboration with the art gallery La Demeure and Denise Majorel, and then by his role as a tireless advocate for the medium around the world. His tapestries reveal a pictorial world which is specifically decorative, with a very personal symbolic iconography : cosmogony (the sun, the planets, the zodiac, the four elements…) stylised vegetation, fauna (rams, cocks, butterflies, chimera …) standing out against a background without perspective (voluntarily different from painting) and, in his more ambitious work, designed as an invitation to share in a poetic (he sometimes weaves quotations into his tapestries) and philosophical (the grand themes are broached from the wartime period onwards) vision whose climax is the “Chant du Monde” (Song of the World) (Jean Lurçat Museum , ancien hôpital Saint Jean, Angers) which remained unfinished at his death. Lurçat's naturalistic representations of animals are unusual (Maingonnat comes to mind). But the flat coloured backgrounds segment and distinguish the different species, in a contrasting partitioning that is characteristic of the artist. Bibliography : Tapisseries de Jean Lurçat 1939-1957, Pierre Vorms Editeur, 1957 Exhibition Catalogue Lurçat, 10 ans après, Musée d'Art moderne de la ville de Paris, 1976 Exhibition catalogue Les domaines de Jean Lurçat, Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la tapisserie contemporaine, 1986 Symposium Jean Lurçat et la renaissance de la tapisserie in Aubusson, Aubusson, Musée départemental de la tapisserie 1992 Exhibition Catalogue Dialogues avec Lurçat, Musées de Basse-Normandie, 1992 Exhibition catalogue Jean Lurçat, Donation Simone Lurçat, Académie des Beaux-Arts, 2004 Jean Lurçat, le chant du monde Angers 2007 Gérard Denizeau, Jean Lurçat, Liénart, 2013 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Lurçat au seul bruit du soleil, Paris, galerie des Gobelins, 2016Aubusson tapestry woven in the Tabard workshop. With label. Circa 1950. -
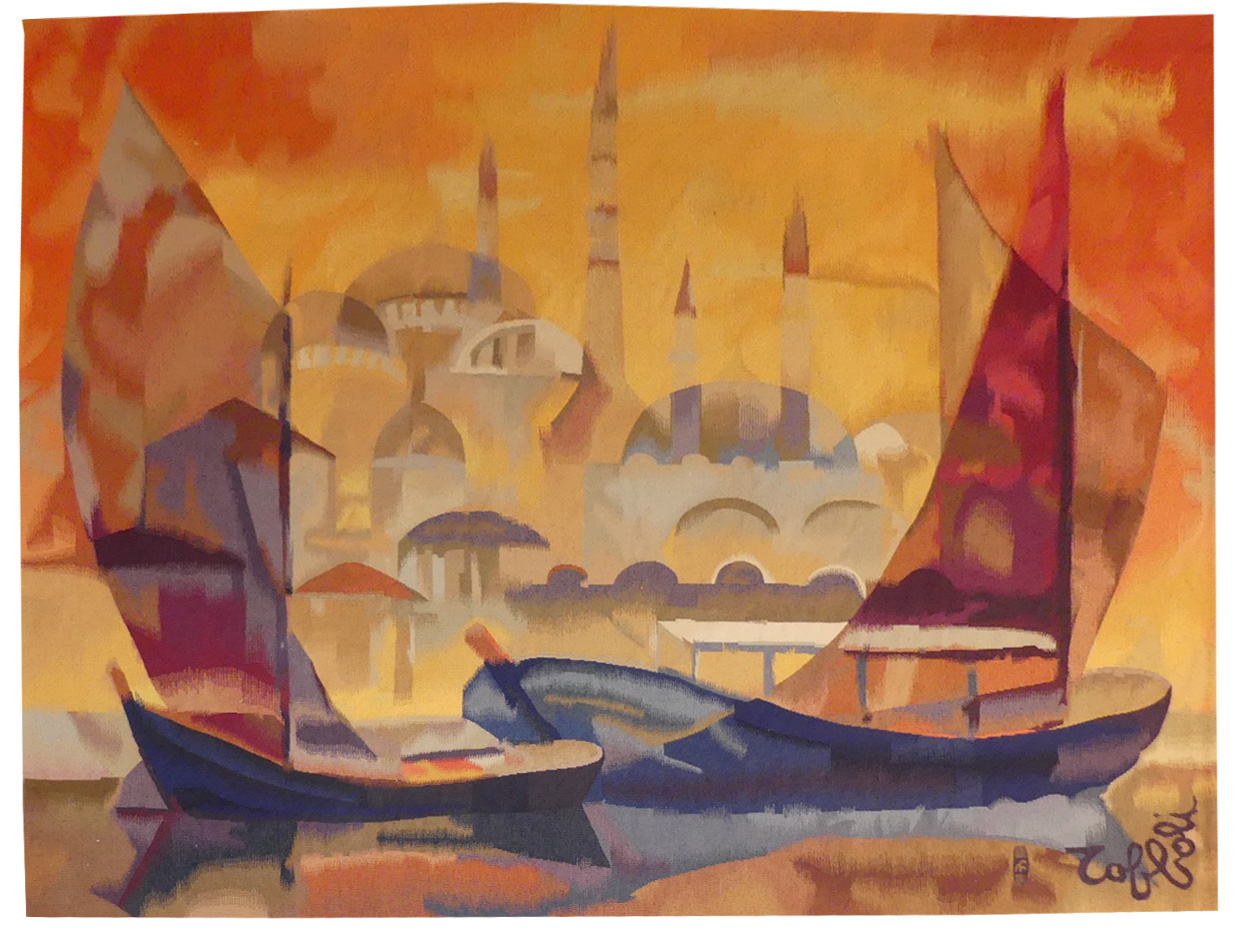
Byzance (Byzantium)
Toffoli produced a large number of tapestries in collaboration with the Robert Four workshop from 1976 onwards, designing several hundred cartoons. In them we find post-cubist transparent effects which are characteristic of the artist, as indeed are the subjects treated. Thus Toffoli’s tapestries do not differ from his painting : here the dome of Hagia Sophia and the Bosphorus transport the observer elsewhere.Aubusson tapestry woven by the Four workshop. With label, n°3/6. Circa 1980. -
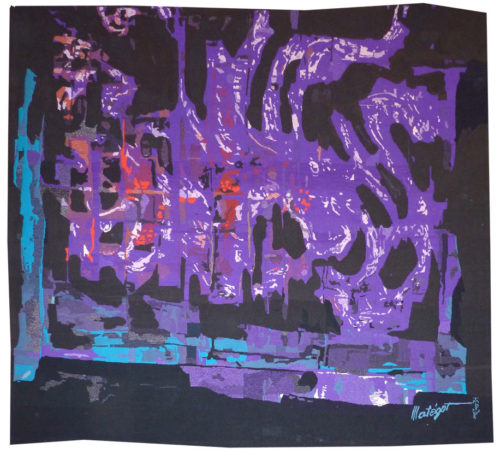
Algues en profondeurs (algae in the depths)
Matégot, originally a decorator, then creator of artefacts and furniture (an activity he abandoned in 1959) met François Tabard in 1945 and gave him his first cartoons, first of all figurative then rapidly of abstract design in the 1950’s. He became a member of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres Cartonniers de Tapisserie) in 1949, participated in many international exhibitions (Matégot, like Lurçat before him, was an untiring advocate of the art of tapestry) fulfilled numerous public commissions, sometimes of monumental proportions (“Rouen” 85m2 for the Préfecture of the Seine Maritime département, and also tapestries for Orly Airport, for the Maison de la Radio, for the IMF...) and designed no fewer than 629 cartoons up until the 1970’s. In 1990 the Matégot foundation for contemporary tapestry was inaugurated in Bethesda, U.S.A. Matégot is an artist, like Wogensky, Tourlière or Prassinos, who turns wool textiles resolutely towards the abstract: at first lyrical, geometric in the 70’s, exploiting various technical aspects of the loom : colour graduations, shading, irregularities... The palette of colours, “ camouflage style”,used in this tapestry heralds the look of cartoons to come from this artist but the lyrical treatment of shade and light are absolutely characteristic of the 1960’s. : if the subject (the seabed) is rare, we find the usual effects of transparency rendered by subtle gradations in a limited chromatic range. Bibliography : Waldemar Georges, Mathieu Matégot, Prisme des Arts special issue, 1957 Exhibition catalogue, Matégot, Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la Tapisserie Contemporaine, 1990-1991 Patrick Favardin, Mathieu Matégot, Editions Norma, 2014Aubusson tapestry woven by the Pinton workshop. With signed label, n°1/6. Circa 1960. -
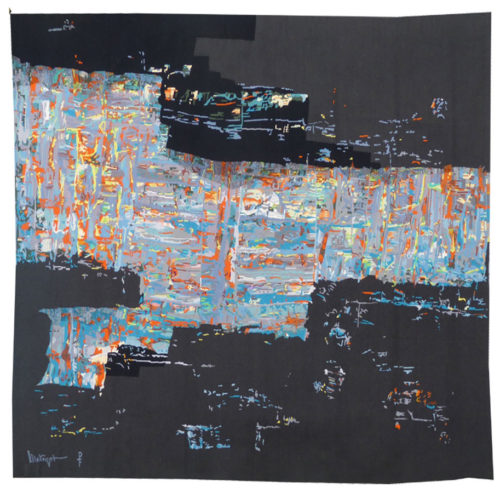
Les eaux dormantes (sleeping waters)
Matégot, originally a decorator, then creator of artefacts and furniture (an activity he abandoned in 1959) met François Tabard in 1945 and gave him his first cartoons, first of all figurative then rapidly of abstract design in the 1950’s. He became a member of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres Cartonniers de Tapisserie) in 1949, participated in many international exhibitions (Matégot, like Lurçat before him, was an untiring advocate of the art of tapestry) fulfilled numerous public commissions, sometimes of monumental proportions (“Rouen” 85m2 for the Préfecture of the Seine Maritime département, and also tapestries for Orly Airport, for the Maison de la Radio, for the IMF...) and designed no fewer than 629 cartoons up until the 1970’s. In 1990 the Matégot foundation for contemporary tapestry was inaugurated in Bethesda, U.S.A. Matégot is an artist, like Wogensky, Tourlière or Prassinos, who turns wool textiles resolutely towards the abstract: at first lyrical, geometric in the 70’s, exploiting various technical aspects of the loom : colour graduations, shading, irregularities... In these « sleeping waters » Matégot invites us into a familiar contrast in his universe between obscurity and brightness, darkness and light : a luminous abstraction revolving around red, yellow and black, a chromatic range that seems far removed from the title. Bibliography : Exhibition catalogue, Matégot, Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la Tapisserie Contemporaine, 1990-1991 Patrick Favardin, Mathieu Matégot, Editions Norma, 2014 Exhibition Catalogue, Lurçat/Matégot, Face à face, Paris, Galerie Chevalier, 2019Aubusson tapestry woven by the Pinton workshop. With signed label, n°2/6. Circa 1970. -
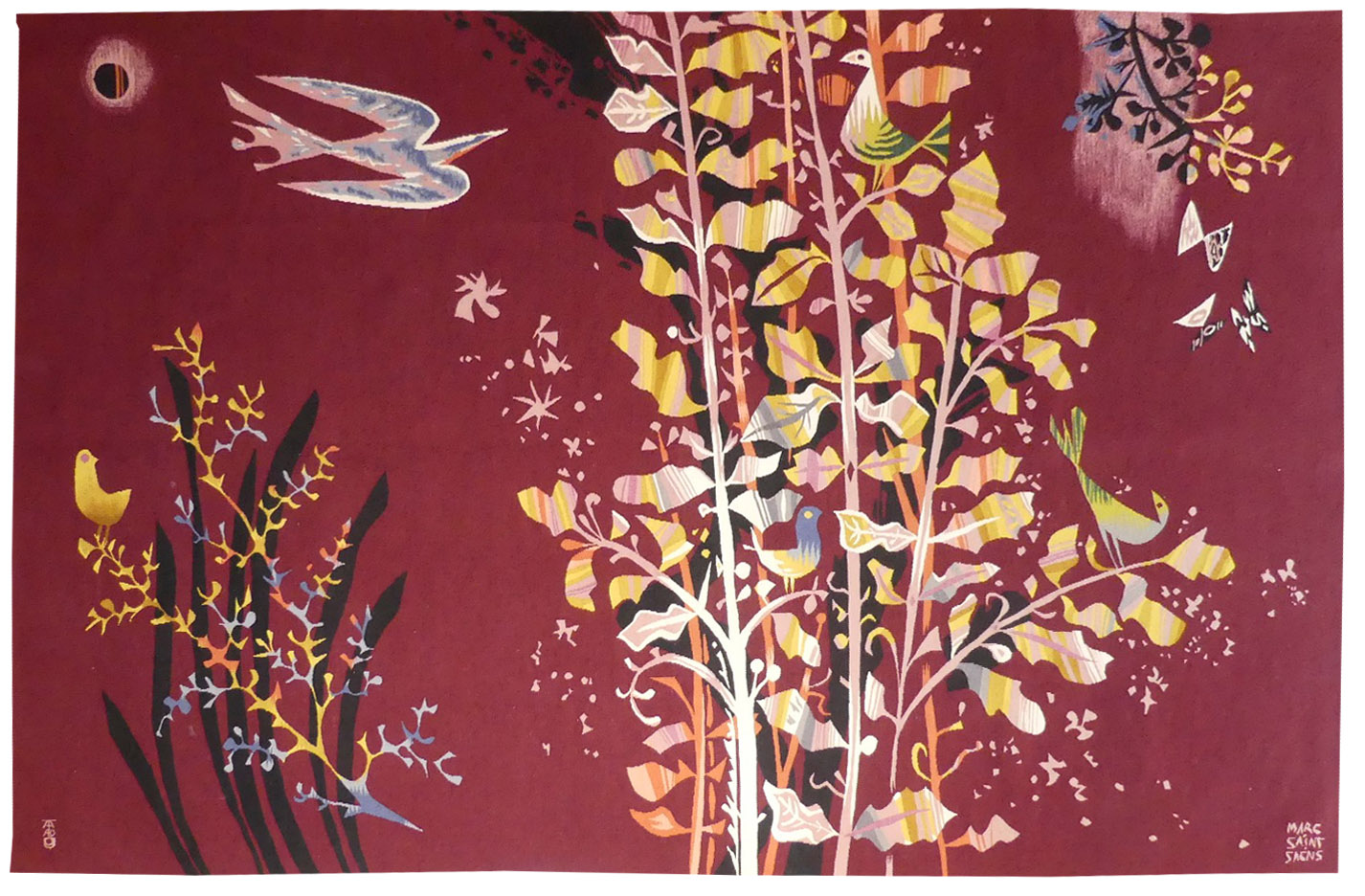
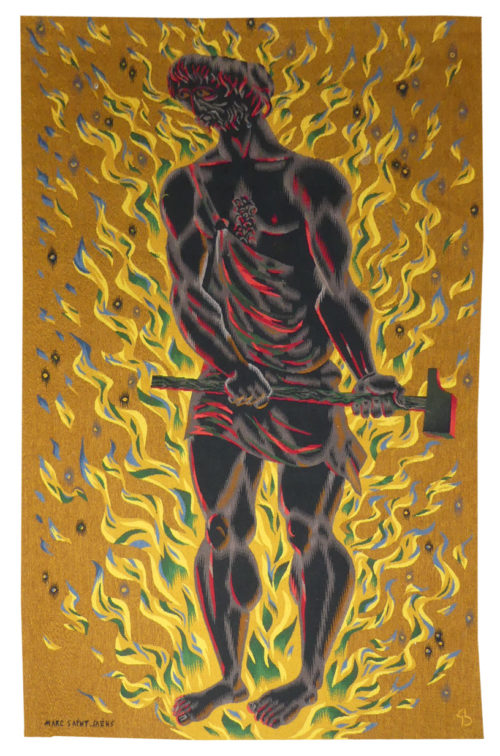
Oiseaux et feuillages (birds and leaves)
Aubusson tapestry woven in the Tabard workshop. With certificate of origin signed by the artist. 1961. Lurçat approached Saint-Saëns, originally a painter of murals, in 1940. And during the war the latter produced the first of his allegorical masterpieces, tapestries reflecting indignation, combat, resistance : “les Vierges folles (the foolish virgins), “Thésée et le Minotaure” (Theseus and the Minotaur). At the end of the war, as a natural development he joined up with Lurçat, whose convictions he shared (concerning a simplified palette, outlined cartoons with colours indicated by pre-ordained numbers, and the specific nature of tapestry design…) at the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-cartonniers de Tapisserie). His universe, where the human figure, stretched, elongated, ooccupies an important place (particularly when compared to his companions Lurçat or Picart le Doux), pivots around traditional themes : woman, the Commedia dell’arte, Greek mythology… refined by the brilliance of the colours and the simplification of the layout. His work would evolve later, in the 1960’s, towards cartoons of a more lyrical design, almost abstract where elemental and cosmic forces would dominate. ‘[This cartoon] was a success (7 copies) and there are 2 versions: one with a burgundy background, the other with a black background. Once again Saint-Saëns refers to the great tradition of "verdures tapestries" populated by animals and flowers, an art of unpretentious relaxation....’ (Michèle Heng in Exhibition catalogue Saint-Saëns, the tapestries, Aubusson, Musée départemental de la Tapisserie, 1987, p.34) Bibliography : Exhibition catalogue Saint-Saëns, the tapestries, Aubusson, Musée départemental de la Tapisserie, 1987 Exhibition catalogue Marc Saint-Saëns, tapestries, 1935-1979, Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la Tapisserie Contemporaine 1997-1998 -
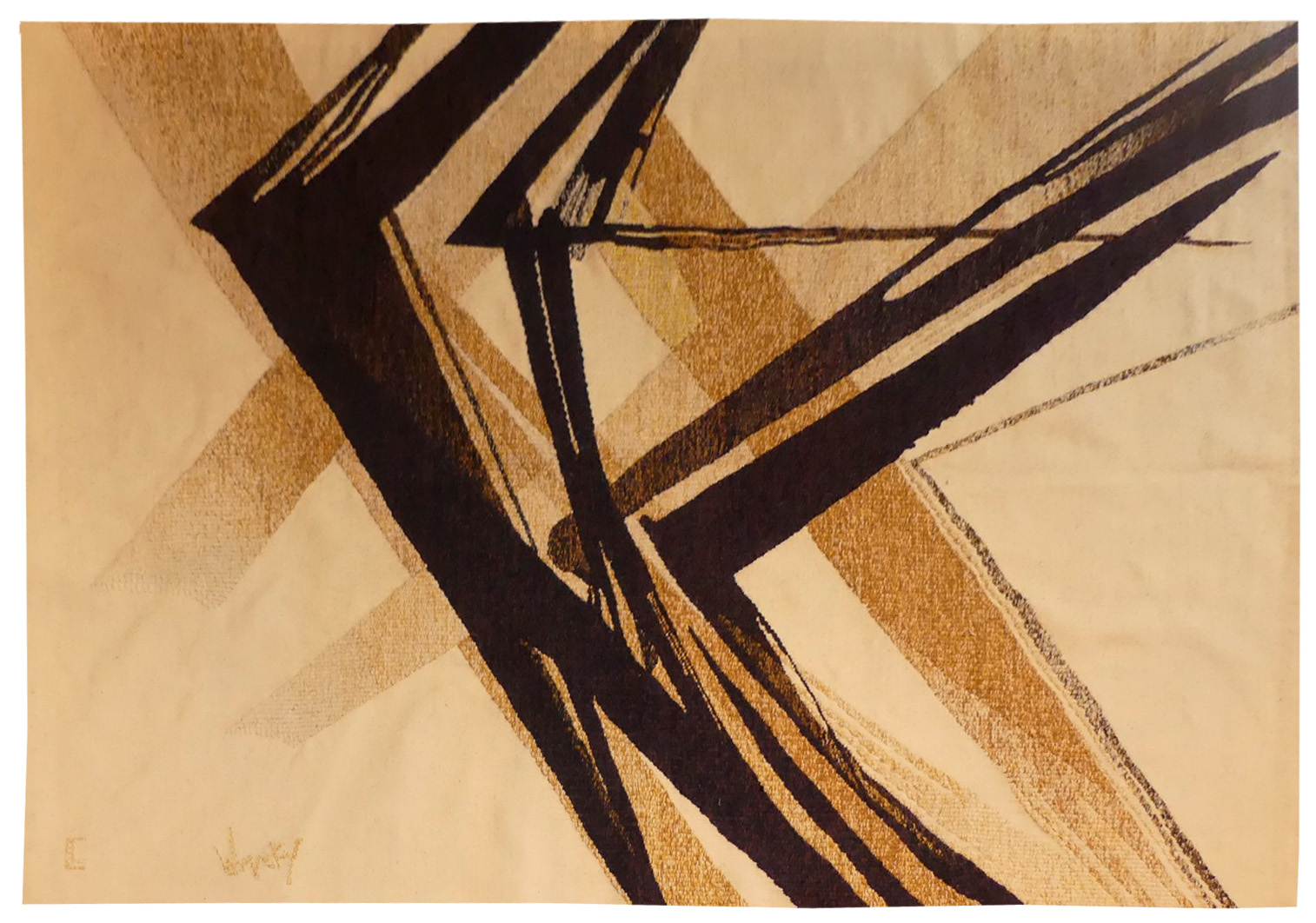
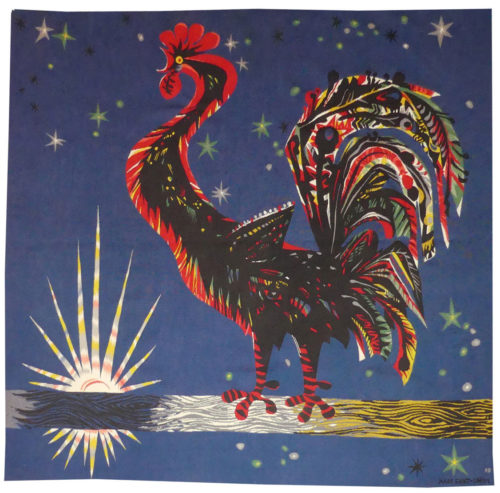
L'écarlate de jour (the day scarlet)
Lurçat’s artistic production was immense : it is however his role as the renovator of the art of tapestry design which ensures his lasting renown. As early as 1917, he started producing works on canvas, then in the 20’s and 30’s, he worked with Marie Cuttoli. His first collaboration with the Gobelins workshop dates back to 1937, at the same time he discovered the tapestry of the Apocalypse which was essential in his decision to devote himself to tapestry design. He first tackled the Gobelins, 2016technical aspects with François Tabard, then on his installation at Aubusson during the war, he established his technique : broad point, a simplified palette, outlined cartoons with colours indicated by pre-ordained numbers. A huge production then follows (over 1000 cartoons) amplified by his desire to include his painter friends, the creation of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-Cartonniers de Tapisserie) and the collaboration with the art gallery La Demeure and Denise Majorel, and then by his role as a tireless advocate for the medium around the world. His tapestries reveal a pictorial world which is specifically decorative, with a very personal symbolic iconography : cosmogony (the sun, the planets, the zodiac, the four elements…) stylised vegetation, fauna (rams, cocks, butterflies, chimera …) standing out against a background without perspective (voluntarily different from painting) and, in his more ambitious work, designed as an invitation to share in a poetic (he sometimes weaves quotations into his tapestries) and philosophical (the grand themes are broached from the wartime period onwards) vision whose climax is the “Chant du Monde” (Song of the World) (Jean Lurçat Museum , ancien hôpital Saint Jean, Angers) which remained unfinished at his death. If there is one motif that is omnipresent in Lurçat’s work over the years it is that of the cockerel, in an infinite variety of interpretations. Our model (this one a true scarlet) is an echo, larger and inverted, of ‘Blue Scarlet’ from 1953. Bibliography : Tapisseries de Jean Lurçat 1939-1957, Pierre Vorms Editeur, 1957 Claude Roy, Jean Lurçat, Pierre Cailler 1966, ill.n°100 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Lurçat, Nice, Musée des Ponchettes, 1968 Exhibition Catalogue Lurçat, 10 ans après, Musée d’Art moderne de la ville de Paris, 1976 Exhibition catalogue Les domaines de Jean Lurçat, Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la tapisserie contemporaine, 1986 Symposium Jean Lurçat et la renaissance de la tapisserie in Aubusson, Aubusson, Musée départemental de la tapisserie 1992 Exhibition Catalogue Dialogues avec Lurçat, Musées de Basse-Normandie, 1992 Exhibition catalogue Jean Lurçat, Donation Simone Lurçat, Académie des Beaux-Arts, 2004 Jean Lurçat, le chant du monde Angers 2007 Gérard Denizeau, Denise Majorel, une vie pour la tapisserie, Aubusson, Musée départemental de la tapisserie Gérard Denizeau, Jean Lurçat, Liénart, 2013 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Lurçat, Meister der französischen Moderne, Halle, Kunsthalle Exhibition Catalogue Jean Lurçat au seul bruit du soleil, Paris, galerie des Gobelins, 2016 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Lurçat, la terre, le feu, l’eau, l’air, Perpignan, Musée d’art Hyacinthe Rigaud, 2024Aubusson tapestry woven in the Goubely workshop. 1953. -
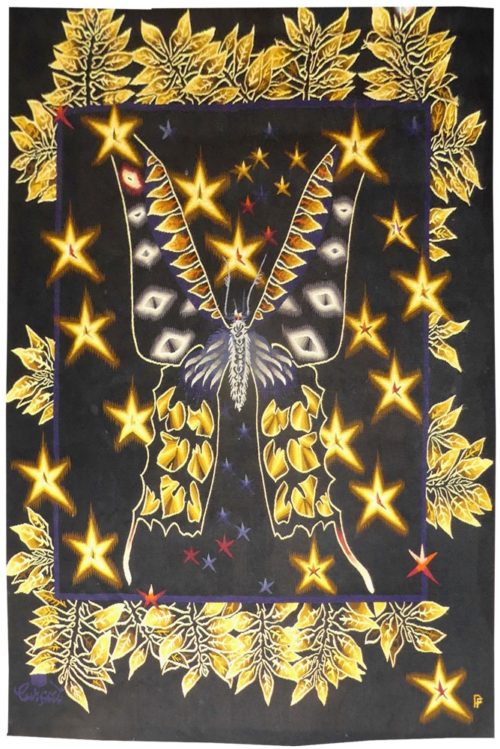
Les 3 papillons (the 3 butterflies)
Aubusson tapestry woven by the Picaud workshop. With label signed by the artist's widow, n°1/6. Circa 1980. Jean Picart le Doux is one of the foremost figures in the renaissance of the art of tapestry. His earliest contributions to the field date back to 1943 when he designed cartoons for the passenger ship “la Marseillaise”. A close associate of Lurçat, whose theories he would adopt (limited palette, numbered cartoons…), he was a founding member of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-cartonniers de Tapisserie), and soon after, a teacher at the Ecole Nationale Supérieure des Arts Décoratifs. The state gave him several commissions most of them at the Aubusson workshop, and some at the Gobelins : the most spectacular of these being for the University of Caen, the Theatre in Le Mans, the passenger ship France or the Prefecture of the Creuse département … In as much as Picart le Doux’s aesthetic is close to that of Lurçat, so also is his inspiration and his subject matter, although in a register which is more decorative than symbolic, where he brings together heavenly bodies (the sun, the moon, the stars…), the elements, nature (wheat, vines, fish, birds…), man, literary quotation … While butterflies are a favourite theme with Lurçat, they are less common with Picart le Doux. Even here, and despite the title, their presence is marginal : the cartoon actually repeats, in a minor mode, ‘Lumière’ (Light), from 1960. Bibliography : Marthe Belle-Joufray, Jean Picart le Doux, Publications filmées d’art et d’histoire, 1966 Maurice Bruzeau, Jean Picart le Doux, Murs de soleil, Editions Cercle d’art, 1972 Exhibition Catalogue, Jean Picart le Doux, tapisseries, Musée de Saint-Denis, 1976 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Picart le Doux, Musée de la Poste, 1980 -
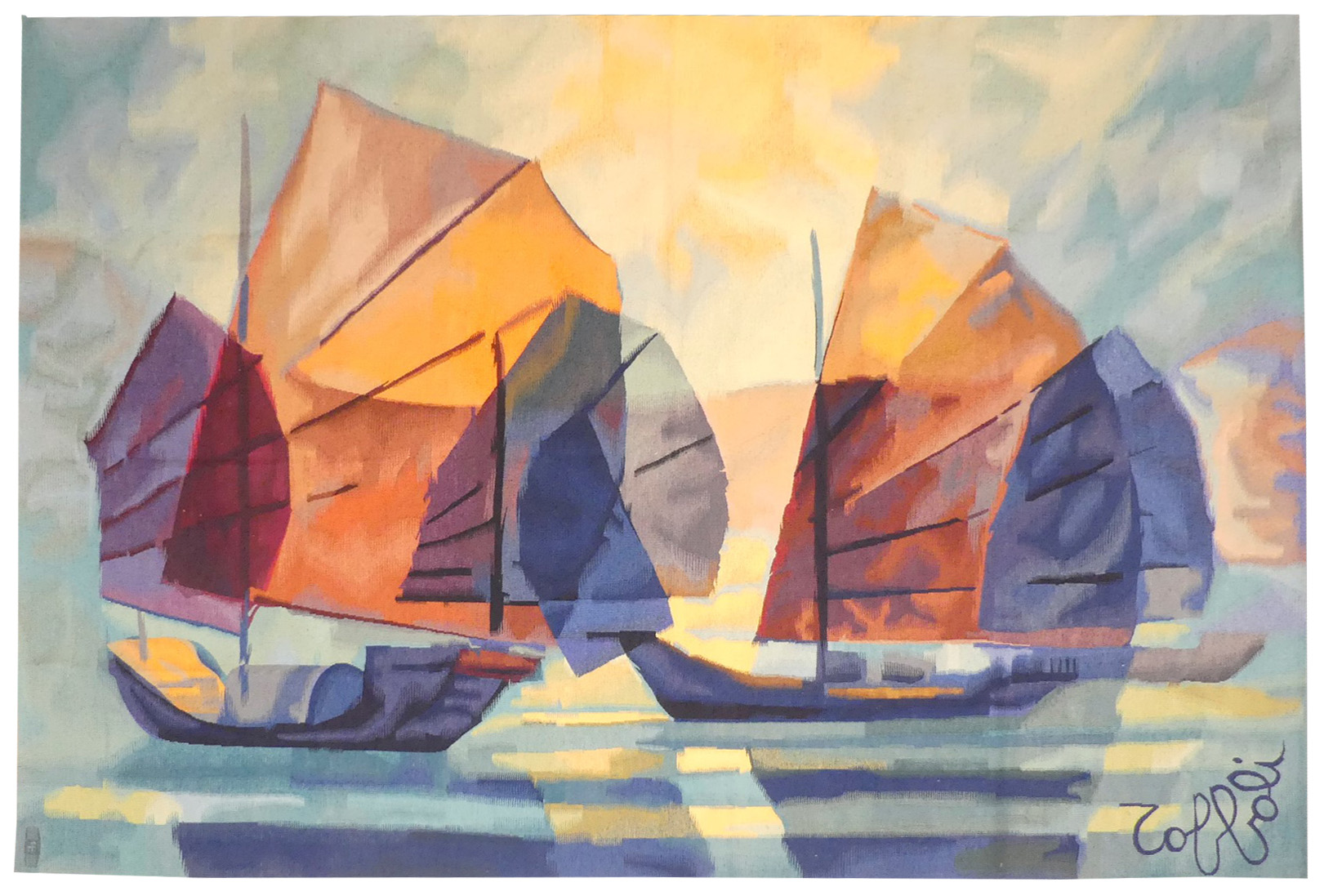
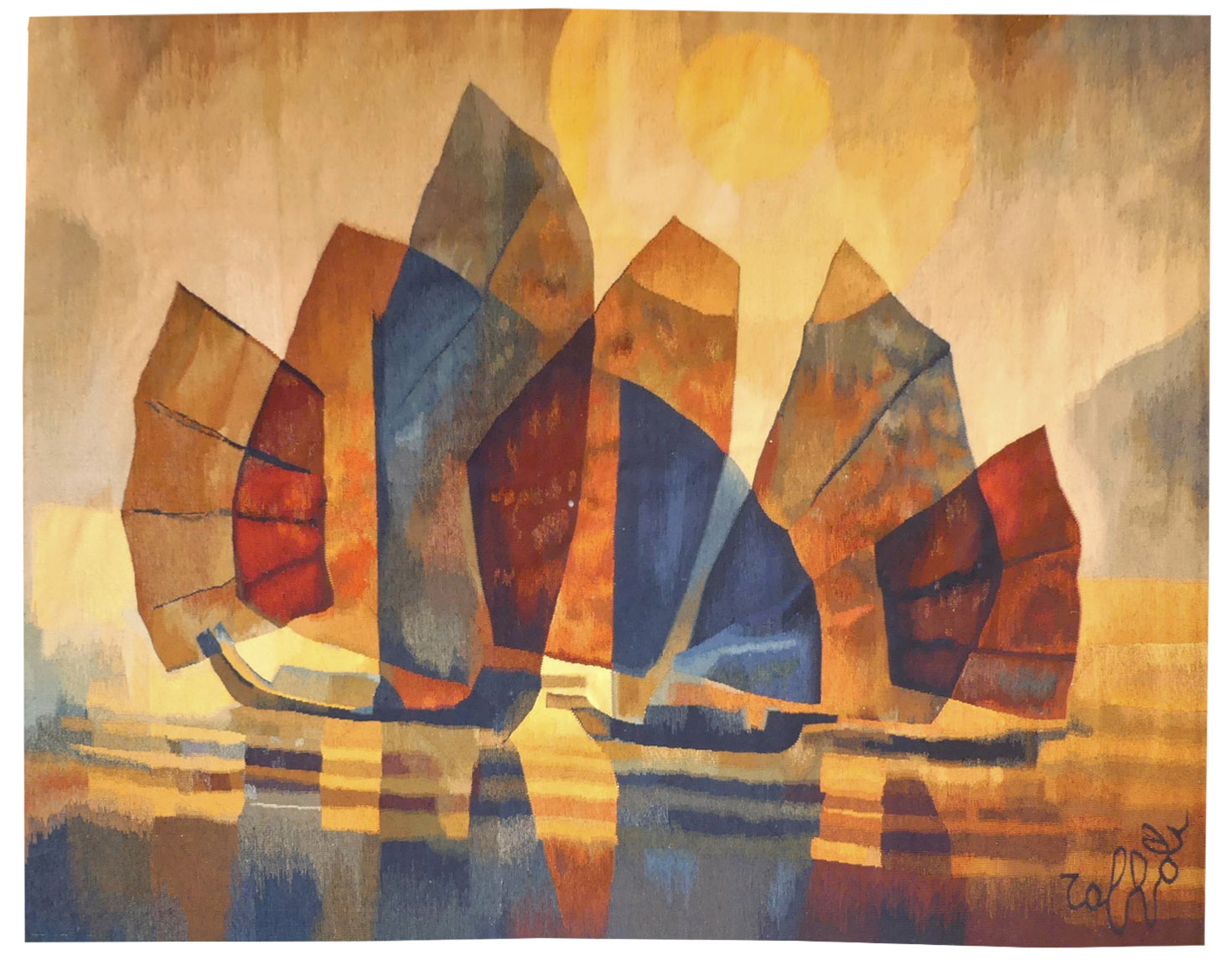
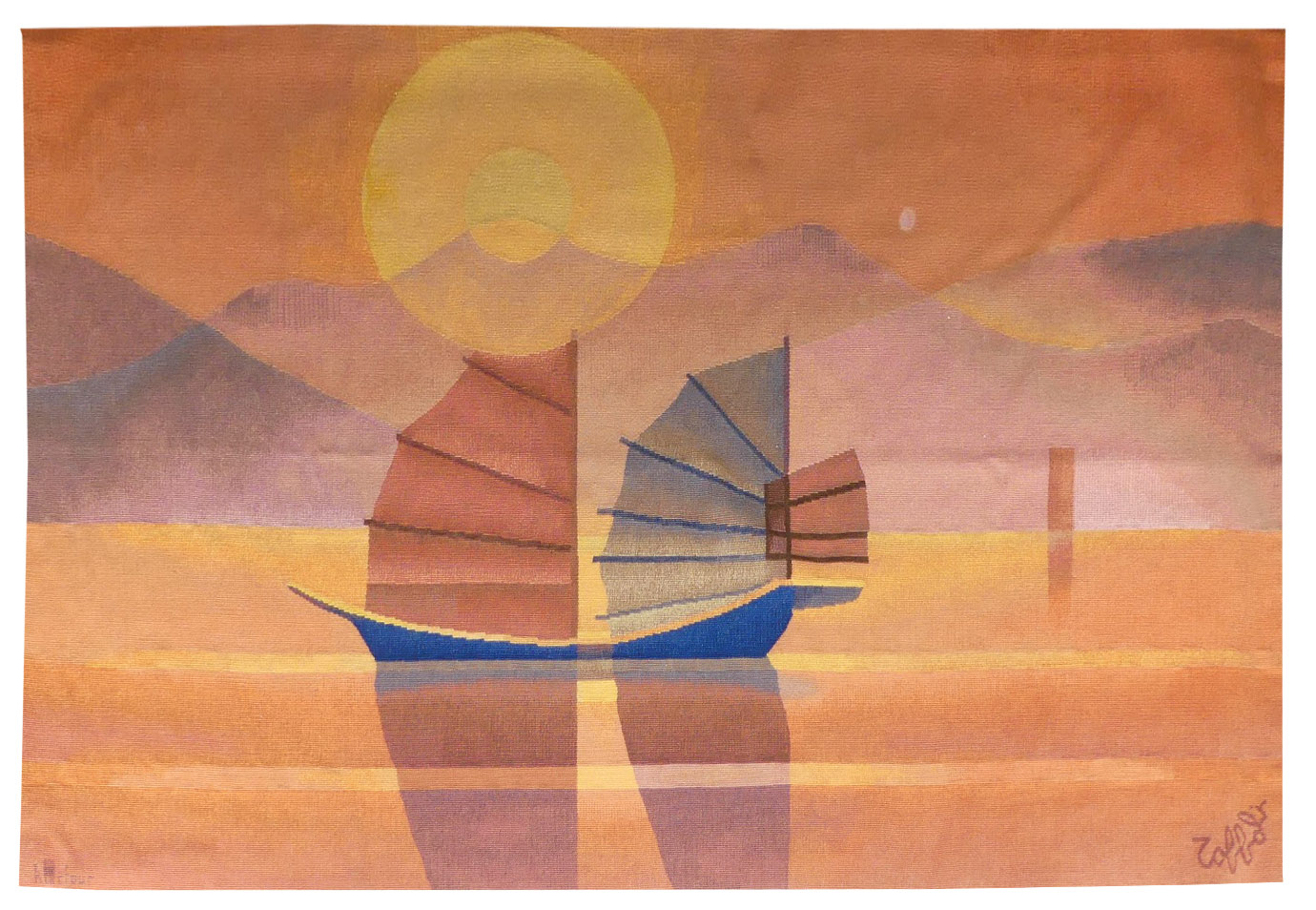
Voiles d'Orient (oriental sails)
Toffoli produced a large number of tapestries in collaboration with the Robert Four workshop from 1976 onwards, designing several hundred cartoons. In them we find post-cubist transparent effects which are characteristic of the artist, as indeed are the subjects treated. Thus Toffoli’s tapestries do not differ from his painting : travelling for inspiration, here he illustrates junks observed during trips to the far East.Aubusson tapestry woven by the Four workshop. With label, n°EA. Circa 1980. -
Trésor d'Amphitrite (Amphitrite's treasure)
Aubusson tapestry woven by the Berthaut workshop. With torn label. 1949. Jean Picart le Doux is one of the foremost figures in the renaissance of the art of tapestry. His earliest contributions to the field date back to 1943 when he designed cartoons for the passenger ship “la Marseillaise”. A close associate of Lurçat, whose theories he would adopt (limited palette, numbered cartoons…), he was a founding member of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-cartonniers de Tapisserie), and soon after, a teacher at the Ecole Nationale Supérieure des Arts Décoratifs. The state gave him several commissions most of them at the Aubusson workshop, and some at the Gobelins : the most spectacular of these being for the University of Caen, the Theatre in Le Mans, the passenger ship France or the Prefecture of the Creuse département … In as much as Picart le Doux’s aesthetic is close to that of Lurçat, so also is his inspiration and his subject matter, although in a register which is more decorative than symbolic, where he brings together heavenly bodies (the sun, the moon, the stars…), the elements, nature (wheat, vines, fish, birds…), man, literary quotation … A synthesis (as early as 1949!) between Sea and Music, omnipresent themes for the artist, in an unusual chromatic range. The theme of underwater treasure would be taken up in a more literal way by Perrot, in ‘Trésors enfouis’ (Buried treasures) for example. Bibliography : Marthe Belle-Joufray, Jean Picart le Doux, Publications filmées d’art et d’histoire, 1966 Maurice Bruzeau, Jean Picart le Doux, Murs de soleil, Editions Cercle d’art, 1972, n°18 Exhibition Catalogue, Jean Picart le Doux, tapisseries, Musée de Saint-Denis, 1976 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Picart le Doux, Musée de la Poste, 1980 -
La cage aux oiseaux (the bird cage)
Aubusson tapestry woven in the Pinton workshop. With label, n°1/6. Circa 1980. Although in his youth Lorjou was a silk fabric designer and an artist specialising in large formats used as posters for exhibitions (“la peste en Beauce” “the plague in the Beauce” 1953, measuring 250 x 360cm for example), he only turned his hand to tapestry design relatively late on : maybe he felt that his rather rough and ready style was somehow inappropriate to being woven (it is noteworthy that other artists to whom he was close, Rebeyrolle, Mottet, Sébire, ... never had their work realised as tapestries). In the 1970’s his style moved away from expressionism to something more dreamlike and it is at this point that he gave a few designs to the Pinton workshop. The colours employed, the bird motifs are all characteristic of Lorjou’s work in the 1970’s. The effects created by the thickness of the paint used are rendered in the tapestry by the use of different stitches. -
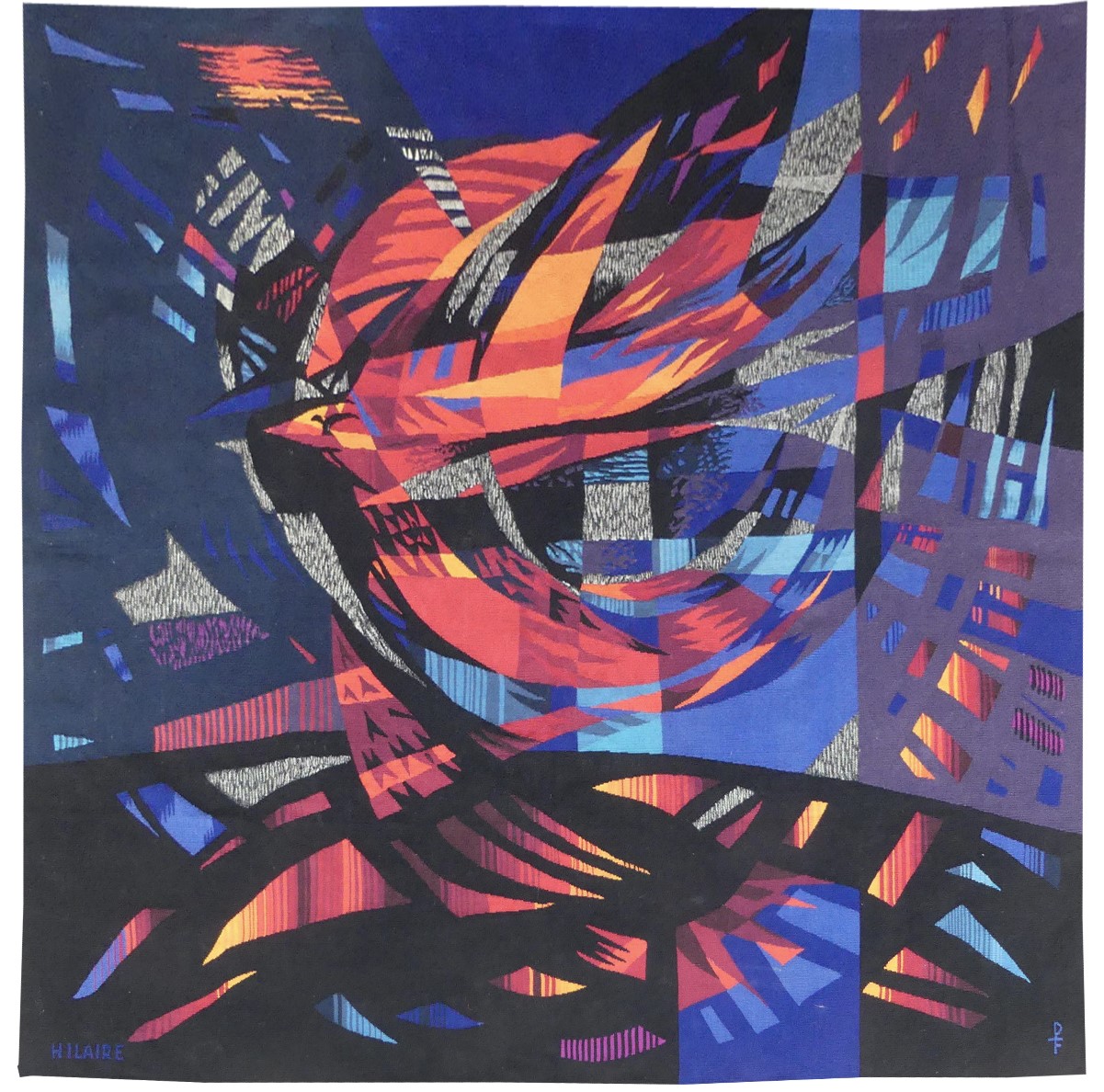
L’oiseau de feu (the firebird)
Aubusson tapestry woven in the Pinton workshop. With signed label. 1963. With a taste for the large-scale, influenced by Untersteller at the Ecole des Beaux Arts, Hilaire undertook numerous mural paintings. In the same vein, beginning in 1949, along with a number of other artists stimulated by Lurçat, (he would join the latter at the A.P.C.T. Association des Peintres-Cartonniers de Tapisserie) he designed a number of cartoons some of which were woven at Beauvais or at Les Gobelins. “L’oiseau de feu » is a rare example of the dynamic in works by Hilaire who has accustomed us to more static subjects like hothouses and forest scenes : his rather fragmentary and kaleidoscopic style is however admirably suited to conveying the idea of movement. Bibliography : Exhibition catalogue Hilaire, œuvre tissé, galerie Verrière, 1970, ill. Exhibition catalogue, du trait à la lumière, Musée Départemental Georges de la Tour, Vic-sur-Seille, 2010. -
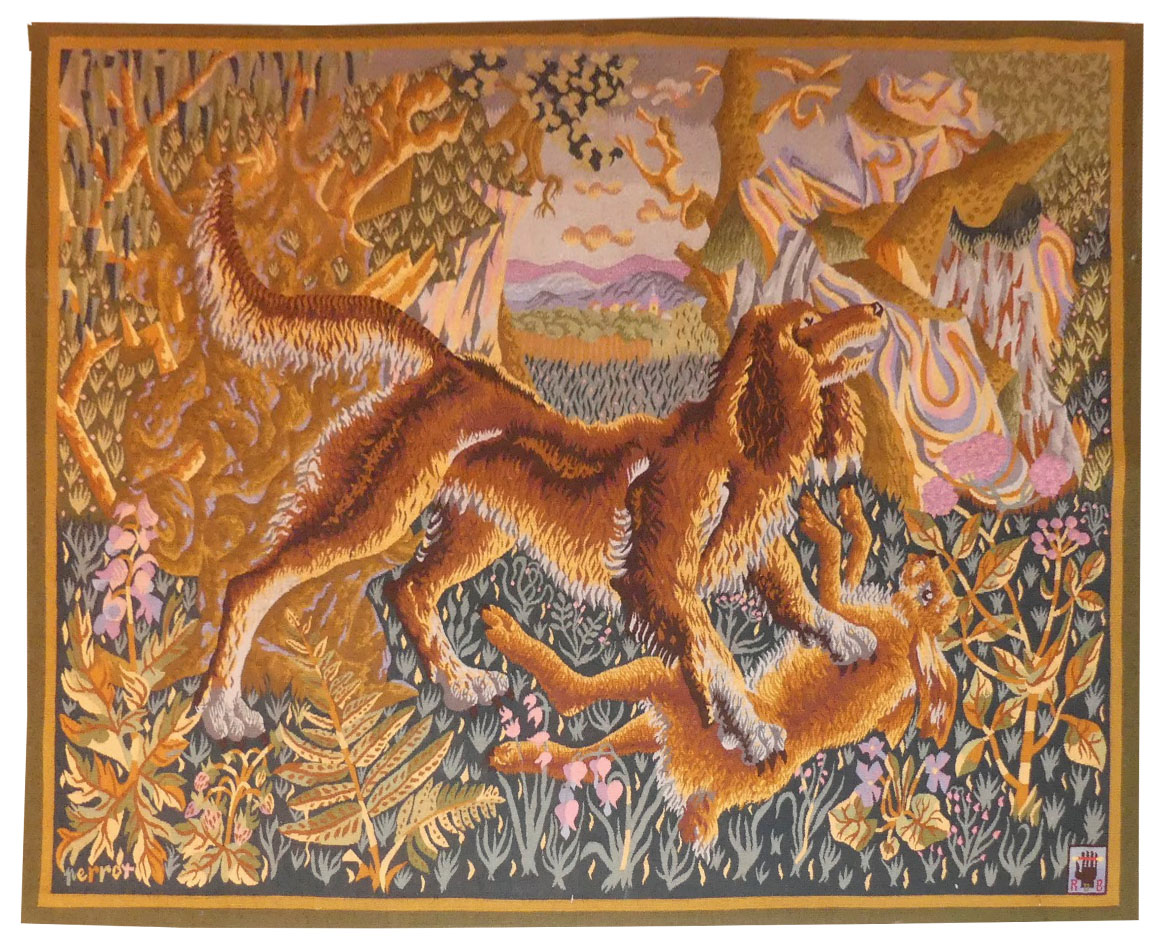
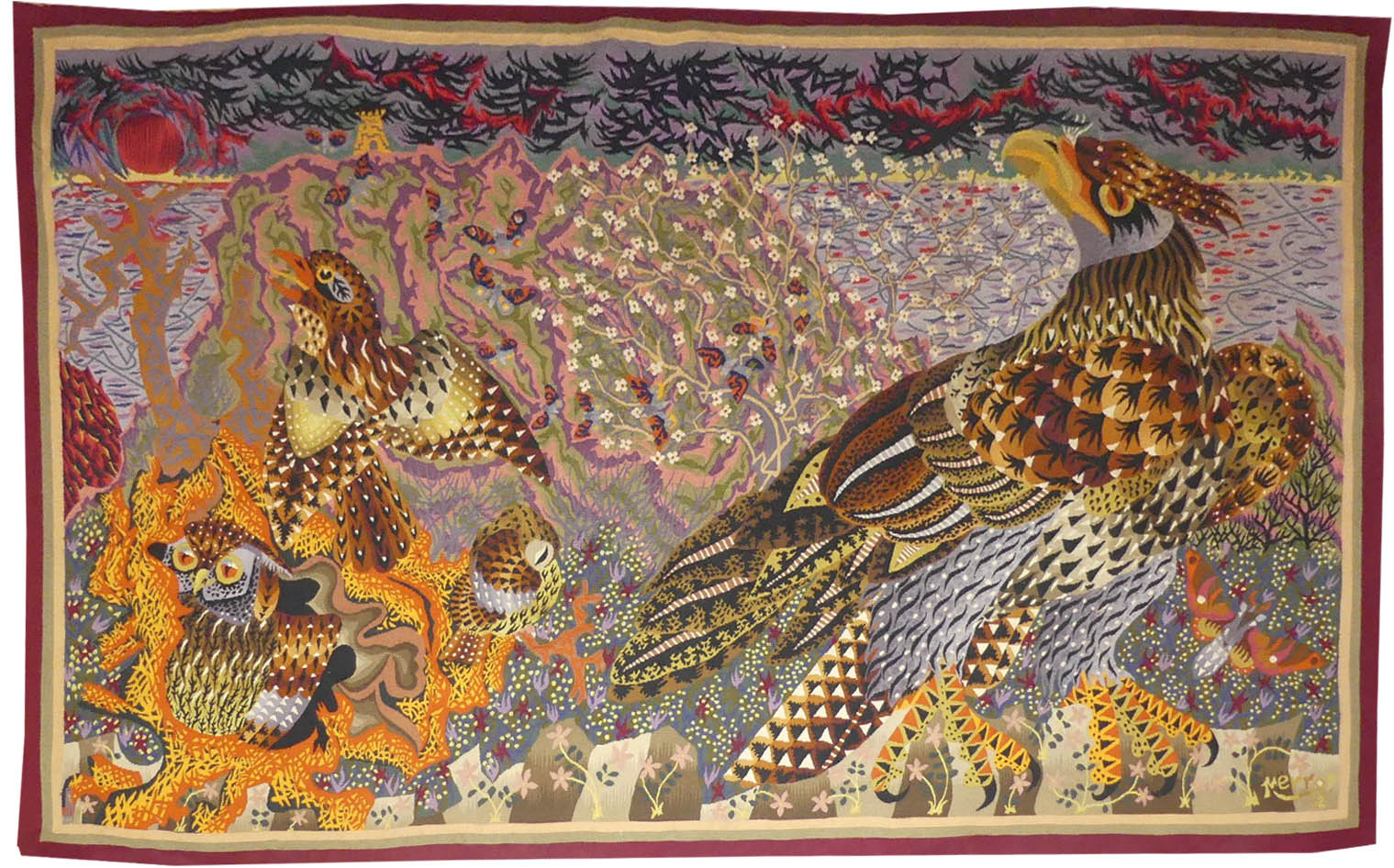
La mort du lièvre (the hare's death)
Aubusson tapestry woven by the Rivière des Borderies workshop. 1946.Perrot began his career as a cartoon designer at the end of the war, making almost 500 cartoons including numerous commissions from the state, most of which were woven at Aubusson. His style which is particularly rich and decorative is eminently recognisable : a crowd of butterflies or birds, most often, stands out against a background of vegetation, reminiscent of the millefleurs tapestries (which would also inspire Dom Robert). One of Perrot's earliest tapestries, contemporary with ‘La chasse au renard’ (‘The Fox Hunt’) which featured in the seminal 1946 exhibition, our carton bears witness to Perrot's early inspiration: a taste for Nature, animals, an interest in botany, geology and inhabited landscapes (man is absent here, but he lives in the village, he hunts)... The artist-ethnographer recycled in tapestry the observations made for the Museum of Popular Arts and Traditions during the war. Bibliography : Tapisseries, dessins, peintures, gravures de René Perrot, Dessein et Tolra, 1982, reproduced p.83 Cat. Expo. René Perrot, mon pauvre cœur est un hibou, Aubusson, Cité de la Tapisserie, 2023 -
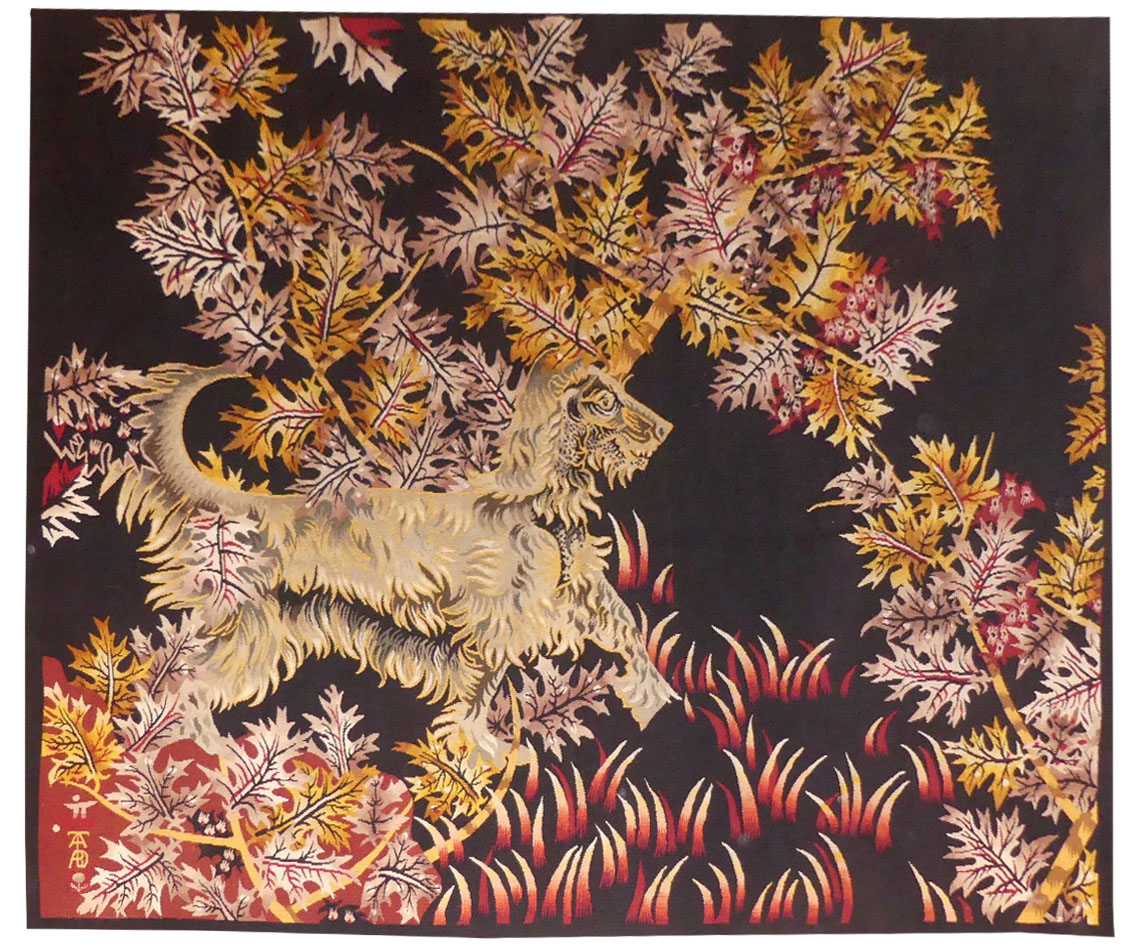
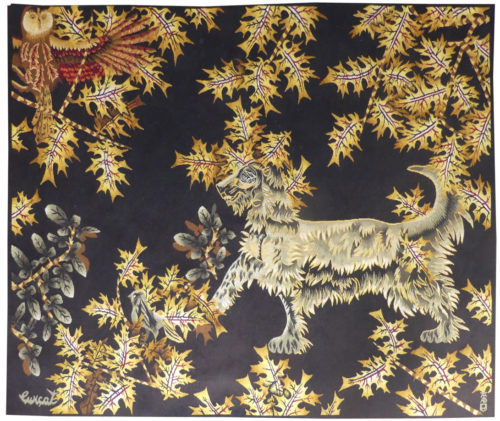
Le chien vert (the green dog)
Lurçat’s artistic production was immense : it is however his role as the renovator of the art of tapestry design which ensures his lasting renown. As early as 1917, he started producing works on canvas, then in the 20’s and 30’s, he worked with Marie Cuttoli. His first collaboration with the Gobelins workshop dates back to 1937, at the same time he discovered the tapestry of the Apocalypse which was essential in his decision to devote himself to tapestry design. He first tackled the Gobelins, 2016technical aspects with François Tabard, then on his installation at Aubusson during the war, he established his technique : broad point, a simplified palette, outlined cartoons with colours indicated by pre-ordained numbers. A huge production then follows (over 1000 cartoons) amplified by his desire to include his painter friends, the creation of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-Cartonniers de Tapisserie) and the collaboration with the art gallery La Demeure and Denise Majorel, and then by his role as a tireless advocate for the medium around the world. His tapestries reveal a pictorial world which is specifically decorative, with a very personal symbolic iconography : cosmogony (the sun, the planets, the zodiac, the four elements…) stylised vegetation, fauna (rams, cocks, butterflies, chimera …) standing out against a background without perspective (voluntarily different from painting) and, in his more ambitious work, designed as an invitation to share in a poetic (he sometimes weaves quotations into his tapestries) and philosophical (the grand themes are broached from the wartime period onwards) vision whose climax is the “Chant du Monde” (Song of the World) (Jean Lurçat Museum , ancien hôpital Saint Jean, Angers) which remained unfinished at his death. Something of a dog lover, Lurçat owned Afghan hounds. They can be found literally in his cartoons, the theme of the dog, always surrounded by sharp foliage, was omnipresent at the end of the 1940s: ‘Chien vert’ is particularly close to the contemporary ‘Basset’. Bibliography : Tapisseries de Jean Lurçat 1939-1957, Pierre Vorms Editeur, 1957 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Lurçat, Nice, Musée des Ponchettes, 1968 Exhibition Catalogue Lurçat, 10 ans après, Musée d’Art moderne de la ville de Paris, 1976 Exhibition catalogue Les domaines de Jean Lurçat, Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la tapisserie contemporaine, 1986 Symposium Jean Lurçat et la renaissance de la tapisserie in Aubusson, Aubusson, Musée départemental de la tapisserie 1992 Exhibition Catalogue Dialogues avec Lurçat, Musées de Basse-Normandie, 1992 Exhibition catalogue Jean Lurçat, Donation Simone Lurçat, Académie des Beaux-Arts, 2004 Jean Lurçat, le chant du monde Angers 2007 Gérard Denizeau, Denise Majorel, une vie pour la tapisserie, Aubusson, Musée départemental de la tapisserie Gérard Denizeau, Jean Lurçat, Liénart, 2013 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Lurçat, Meister der französischen Moderne, Halle, Kunsthalle, 2016, ill. p.76 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Lurçat au seul bruit du soleil, Paris, galerie des Gobelins, 2016 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Lurçat, la terre, le feu, l’eau, l’air, Perpignan, Musée d’art Hyacinthe Rigaud, 2024Aubusson tapestry woven in the Tabard workshop. 1949. -
Grand vol roux (great russet flight)
Aubusson tapestry woven by the Legoueix workshop. With signed label, n°3/6. 1973.A member of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-Cartonniers de Tapisserie), Wogensky is one of the many artists who would follow in Lurçat’s footsteps immediately after the war. At first influenced by his predecessor, Wogensky’s subsequent work (159 cartoons according to the 1989 exhibition catalogue) would evolve during the 1960’s towards a, not completely self-avowed, lyrical abstraction, from cosmic-astronomical themes expressed in decomposed, moving, birdlike shapes to cartoons both more refined and less dense. Although always claiming to be a painter, the artist’s conception of tapestry is extremely well thought out : “the realisation of a mural cartoon.... requires the consideration of a space which is no longer ours alone, by the nature of its dimensions, its scale, it also imposes a grand gesture which transforms and accentuates our presence.” Birds emerge as a theme in Wogensky’s work at the end of the 1960’s. In reality, if the titles of his works refer to them, their representation remains allusive, closer to images of flight frozen in time than to ornithological treatises : it is movement in space that is important, hence the titles ‘vol ...’[flight]. At this time, Wogensky was interested in the material effects obtained by weavers through the use of different stitch sizes; this is what distinguishes "Grand vol roux" from the ‘Oiseaux de septembre' [September birds], a similar cartoon, from 1970, woven in a regular and smooth manner. Bibliography : Cat. Expo. Robert Wogensky, 20 tapisseries récentes, galerie La Demeure, 1973, reproduced n°10 Exhibition catalogue Robert Wogensky, Aubusson, Musée départemental de la tapisserie, 1989 Exhibition catalogue Robert Wogensky, Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la Tapisserie Contemporaine, 1989 -
Vera Cruz
Lurçat’s artistic production was immense : it is however his role as the renovator of the art of tapestry design which ensures his lasting renown. As early as 1917, he started producing works on canvas, then in the 20’s and 30’s, he worked with Marie Cuttoli. His first collaboration with the Gobelins workshop dates back to 1937, at the same time he discovered the tapestry of the Apocalypse which was essential in his decision to devote himself to tapestry design. He first tackled the Gobelins, 2016technical aspects with François Tabard, then on his installation at Aubusson during the war, he established his technique : broad point, a simplified palette, outlined cartoons with colours indicated by pre-ordained numbers. A huge production then follows (over 1000 cartoons) amplified by his desire to include his painter friends, the creation of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-Cartonniers de Tapisserie) and the collaboration with the art gallery La Demeure and Denise Majorel, and then by his role as a tireless advocate for the medium around the world. His tapestries reveal a pictorial world which is specifically decorative, with a very personal symbolic iconography : cosmogony (the sun, the planets, the zodiac, the four elements…) stylised vegetation, fauna (rams, cocks, butterflies, chimera …) standing out against a background without perspective (voluntarily different from painting) and, in his more ambitious work, designed as an invitation to share in a poetic (he sometimes weaves quotations into his tapestries) and philosophical (the grand themes are broached from the wartime period onwards) vision whose climax is the “Chant du Monde” (Song of the World) (Jean Lurçat Museum , ancien hôpital Saint Jean, Angers) which remained unfinished at his death. His journey to Brazil in 1954 was a decisive source of inspiration for Lurçat : the flora and fauna (particularly the butterflies, a recurrent theme) of the Amazon appear repeatedly : “What interests me with the butterfly, ... is the extraordinary inventiveness of the interlacing forms, the sparkling colours, the total freedom of their coloration...” (Claude Faux, Lurçat à haute voix, 1962, p. 151). This geographical source will know several avatars: ‘Vera Cruz’ thus, but also ‘New Delhi’... will be pretexts for butterflies. Bibliography : Tapisseries de Jean Lurçat 1939-1957, Pierre Vorms Editeur, 1957 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Lurçat, Nice, Musée des Ponchettes, 1968 Exhibition Catalogue Lurçat, 10 ans après, Musée d’Art moderne de la ville de Paris, 1976 Exhibition catalogue Les domaines de Jean Lurçat, Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la tapisserie contemporaine, 1986 Symposium Jean Lurçat et la renaissance de la tapisserie in Aubusson, Aubusson, Musée départemental de la tapisserie 1992 Exhibition Catalogue Dialogues avec Lurçat, Musées de Basse-Normandie, 1992 Exhibition catalogue Jean Lurçat, Donation Simone Lurçat, Académie des Beaux-Arts, 2004 Jean Lurçat, le chant du monde Angers 2007 Gérard Denizeau, Denise Majorel, une vie pour la tapisserie, Aubusson, Musée départemental de la tapisserie Gérard Denizeau, Jean Lurçat, Liénart, 2013 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Lurçat, Meister der französischen Moderne, Halle, Kunsthalle Exhibition Catalogue Jean Lurçat au seul bruit du soleil, Paris, galerie des Gobelins, 2016 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Lurçat, la terre, le feu, l’eau, l’air, Perpignan, Musée d’art Hyacinthe Rigaud, 2024Aubusson tapestry woven in the Simone André workshop. With label signed by the artist. Circa 1955. -
Escorte (escort)
Marc Petit met Jean Lurçat in 1954, went to Aubusson in 1955, exhibited his work for the first time at La Demeure in 1956, became a member of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-Cartonniers de Tapisserie) in 1958. After this lightning start to his career, he produced hundreds of cartoons, in a style all his own, where long-legged waders and acrobats wend in and out of dreamscapes. Again, economy of means, with broad flat tints and a narrow chromatic range, for a singular theme: a heavenly body at the bottom of the sea, ‘escorted’ by worrying fish, a singular dawn (a leitmotif for the artist) of life.Aubusson tapestry woven in the Picaud workshop for the Verrière gallery. With signed label, n°EA. Circa 1970. -
Composition
Although he was one of the first Lebanese abstract artists, Assem Stétié (the brother of the better-known poet and critic Saleh Stétié, who was himself close to many artists) is unfortunately a somewhat forgotten painter today. His personal work is both lyrical and masterful, made up of signs in pure colours, a form of personal calligraphy, particularly in the 1970s, from which we can date our tapestry.Aubusson tapestry woven by the Caron workshop. Circa 1970. -
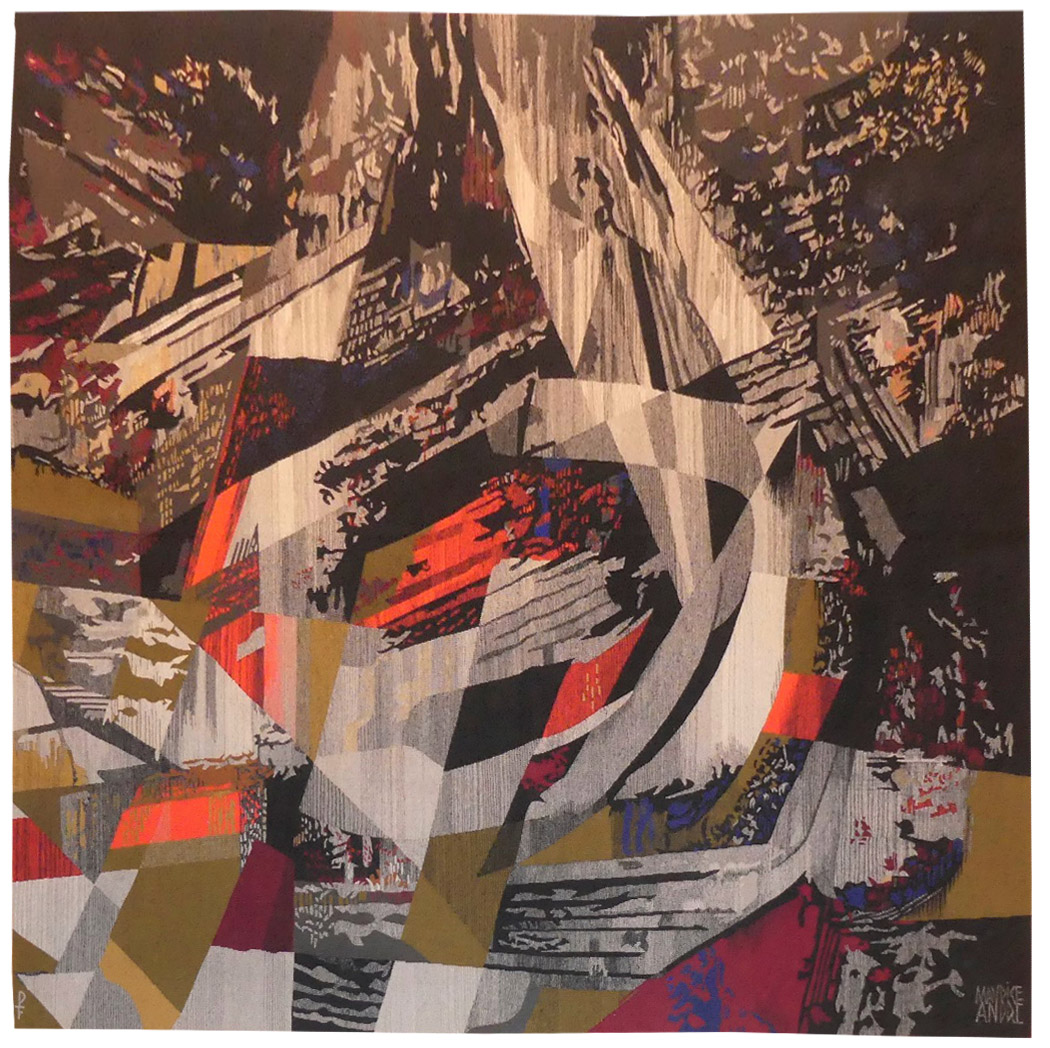
Le soleil d'Apremont (the sun of Apremont)
Aubusson tapestry woven in the Picaud workshop. With signed label, n°1/4. Circa 1965.Maurice André settled in Aubusson for the duration of the second world war. A founding member of the group “Tapisserie de France” and a member of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-Cartonniers de Tapisserie), he developed a personal style, different from that of Lurçat, characterised by rigorous, cubist-influenced flat areas of colour, often using a limited palette ; he received large-scale public commissions for the Council of Europe in Strasbourg (“L’Europe unie dans le Travail et la Paix”) or for the French pavilion at the Brussels Exhibition in 1958 (“La Technique moderne au service de l’Homme”). Gradually (as with Wogensky and Prassinos,...) his style evolved towards more abstraction, firstly lyrical and then more and more geometric, in a way very similar to Matégot. In the mid 1960’s André’s style becomes comparable to that of Matégot, made of lyrical ensembles of triangular shapes, in a homogenous colour scheme and sprinkled with stripes, stains, marks... often black, where different techniques specific to the weaver’s art are used to accentuate the impression of volume and depth. -
Nuit sidérale (astral night)
Aubusson tapestry woven in the Pinton workshop. With label. Circa 1965.Maurice André settled in Aubusson for the duration of the second world war. A founding member of the group “Tapisserie de France” and a member of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-Cartonniers de Tapisserie), he developed a personal style, different from that of Lurçat, characterised by rigorous, cubist-influenced flat areas of colour, often using a limited palette ; he received large-scale public commissions for the Council of Europe in Strasbourg (“L’Europe unie dans le Travail et la Paix”) or for the French pavilion at the Brussels Exhibition in 1958 (“La Technique moderne au service de l’Homme”). Gradually (as with Wogensky and Prassinos,...) his style evolved towards more abstraction, firstly lyrical and then more and more geometric, in a way very similar to Matégot. In the mid 1960’s André’s style becomes comparable to that of Matégot, where battage, pick and pick and shading are the norm. By its theme, its technique, its colour scheme, its format, this particular cartoon is close to « Grand nocturne » copies of which are to be found at the Musée Jean Lurçat and the musée de la tapisserie contemporaine in Angers. -
Florale n°3 (Floral n°3)
Lurçat’s artistic production was immense : it is however his role as the renovator of the art of tapestry design which ensures his lasting renown. As early as 1917, he started producing works on canvas, then in the 20’s and 30’s, he worked with Marie Cuttoli. His first collaboration with the Gobelins workshop dates back to 1937, at the same time he discovered the tapestry of the Apocalypse which was essential in his decision to devote himself to tapestry design. He first tackled the Gobelins, 2016technical aspects with François Tabard, then on his installation at Aubusson during the war, he established his technique : broad point, a simplified palette, outlined cartoons with colours indicated by pre-ordained numbers. A huge production then follows (over 1000 cartoons) amplified by his desire to include his painter friends, the creation of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-Cartonniers de Tapisserie) and the collaboration with the art gallery La Demeure and Denise Majorel, and then by his role as a tireless advocate for the medium around the world. His tapestries reveal a pictorial world which is specifically decorative, with a very personal symbolic iconography : cosmogony (the sun, the planets, the zodiac, the four elements…) stylised vegetation, fauna (rams, cocks, butterflies, chimera …) standing out against a background without perspective (voluntarily different from painting) and, in his more ambitious work, designed as an invitation to share in a poetic (he sometimes weaves quotations into his tapestries) and philosophical (the grand themes are broached from the wartime period onwards) vision whose climax is the “Chant du Monde” (Song of the World) (Jean Lurçat Museum , ancien hôpital Saint Jean, Angers) which remained unfinished at his death. The framing of motifs is a recurrent trope in Lurçat's production (one only has to think of his “armoires” - cabinets) ; nevertheless, nature, flowers, cannot be contained and tend to spill over, out of the frame. This composition partially revisits (the right-hand side) his work entitled “Nouveau jardin Marcenac”, a cartoon dating from 1955. Bibliography : Tapisseries de Jean Lurçat 1939-1957, Pierre Vorms Editeur, 1957 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Lurçat, Nice, Musée des Ponchettes, 1968 Exhibition Catalogue Lurçat, 10 ans après, Musée d’Art moderne de la ville de Paris, 1976 Exhibition catalogue Les domaines de Jean Lurçat, Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la tapisserie contemporaine, 1986 Symposium Jean Lurçat et la renaissance de la tapisserie in Aubusson, Aubusson, Musée départemental de la tapisserie 1992 Exhibition Catalogue Dialogues avec Lurçat, Musées de Basse-Normandie, 1992 Exhibition catalogue Jean Lurçat, Donation Simone Lurçat, Académie des Beaux-Arts, 2004 Jean Lurçat, le chant du monde Angers 2007 Gérard Denizeau, Denise Majorel, une vie pour la tapisserie, Aubusson, Musée départemental de la tapisserie Gérard Denizeau, Jean Lurçat, Liénart, 2013 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Lurçat, Meister der französischen Moderne, Halle, Kunsthalle Exhibition Catalogue Jean Lurçat au seul bruit du soleil, Paris, galerie des Gobelins, 2016Aubusson tapestry woven in the Pinton workshop. With label signed by the artist's widow. Circa 1955. -
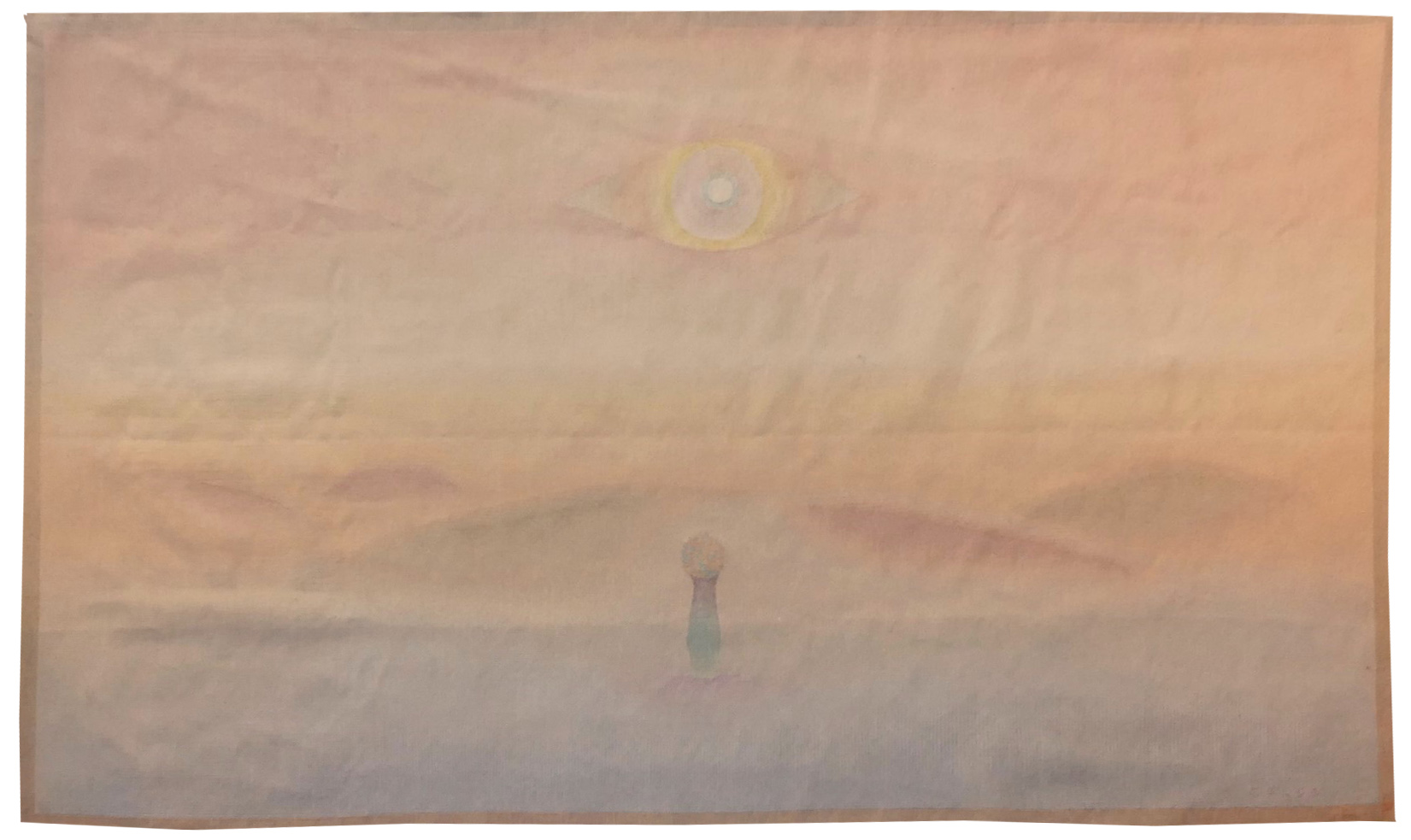
Composition
Aubusson tapestry woven by the Four workshop. N°EA2. Circa 1980.An artistic all-rounder, who defined himself as “neither a painter, nor a draughtsman, nor a poster artist, nor a writer, nor an engraver. My work is neither abstract nor figurative ... I do not pretend to understand my images, and everyone is free to understand them as they like. I have merely tried to represent my own imaginings, in the hope that others will be able to recognise their own in them”, Folon was an incredibly successful artist, from his illustrations for famous American magazines in the 1960’s, his many poster designs, the works he presented at the Biennials in Venice and in Sao Paolo to the television credits for Antenne 2,... There is therefore no reason to be surprised that he also turned his hand to tapestry design (his largest piece, 80m2 is exhibited at the Centre des Congrès in Monaco, woven, as all his other works in the genre, by the Four workshop), in his characteristic airy and understated style whose inspiration is not a thousand miles from that of his compatriot Magritte. The aesthetic employed in our tapestry is directly descended from watercolour (pale colours that melt into one another), his preferred medium (there is also a lithograph), which makes his work specific and a world away from that of other painter-cartoonists of the same period. The representation of the sun as an eye,a leitmotiv in Folon’s work, overlooking a landscape, bears witness to the particular dream-like character of the universe his art inhabits. -
Les jonques (junks)
Toffoli produced a large number of tapestries in collaboration with the Robert Four workshop from 1976 onwards, designing several hundred cartoons. In them we find post-cubist transparent effects which are characteristic of the artist, as indeed are the subjects treated. Thus Toffoli’s tapestries do not differ from his painting : travelling for inspiration, here he illustrates junks observed during trips to the far East.Aubusson tapestry woven by the Four workshop. With signed label, n°1/6. Circa 1980. -
Les hyades
Aubusson tapestry woven by the Legoueix workshop. With signed label, n°5/6. 1968.A member of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-Cartonniers de Tapisserie), Wogensky is one of the many artists who would follow in Lurçat’s footsteps immediately after the war. At first influenced by his predecessor, Wogensky’s subsequent work (159 cartoons according to the 1989 exhibition catalogue) would evolve during the 1960’s towards a, not completely self-avowed, lyrical abstraction, from cosmic-astronomical themes expressed in decomposed, moving, birdlike shapes to cartoons both more refined and less dense. Although always claiming to be a painter, the artist’s conception of tapestry is extremely well thought out : “the realisation of a mural cartoon…. requires the consideration of a space which is no longer ours alone, by the nature of its dimensions, its scale, it also imposes a grand gesture which transforms and accentuates our presence.” « Les Hyades » is a work inspired by Wogensky’s « cosmic » vein (it’s title alone bears witness to the fact) which lasted through the 1960’s and of which “Cosmos” (1968 Strasbourg University) and “Galaxy” (1970, Sénat Palais du Luxembourg) would be the high points. Shading (omnipresent) and blocks of colour co-exist in a subtle harmony, evoking a curious, unknown world with elements of the infinitely small as seen through a microscope and the infinitely large. Bibliography : Exhibition catalogue Robert Wogensky, Aubusson, Musée départemental de la tapisserie, 1989 Exhibition catalogue Robert Wogensky, Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la Tapisserie Contemporaine, 1989-1990 -
Bouquet d'artifice (Bouquet of "flowerworks")
Aubusson tapestry woven by the Pinton workshop. Avec son bolduc signé de l'artiste. Circa 1960.First a poster artist, then an artist-ethnographer during the war, Perrot began his career as a cartoon designer at its end, making almost 500 cartoons, most of which were woven at Aubusson, including numerous commissions from the state (with 33 cartoons, Perrot is the most prolific tapestry designer in the Mobilier National’s collection!). His style which is particularly rich and decorative is eminently recognisable : he illustrates in flat colours (with neither shading nor picking) an abundance of animals (most often birds), standing out with no perspective, against a background of vegetation, in a style reminiscent of the mediaeval mille-fleurs tapestries. Rather like a floral display of pyrotechnics, « Bouquet d’artifice » (Bouquet of “flowerworks”) presents an abundant spray of numerous varieties, some even slightly stylised, in a riot of colours accentuated by the black background : an ode to Nature. Bibliography : Tapisseries, dessins, peintures, gravures de René Perrot, Dessein et Tolra, 1982 Exhibition catalogue René Perrot, mon pauvre cœur est un hibou, Aubusson, Cité Internationale de la Tapisserie, 2023 -
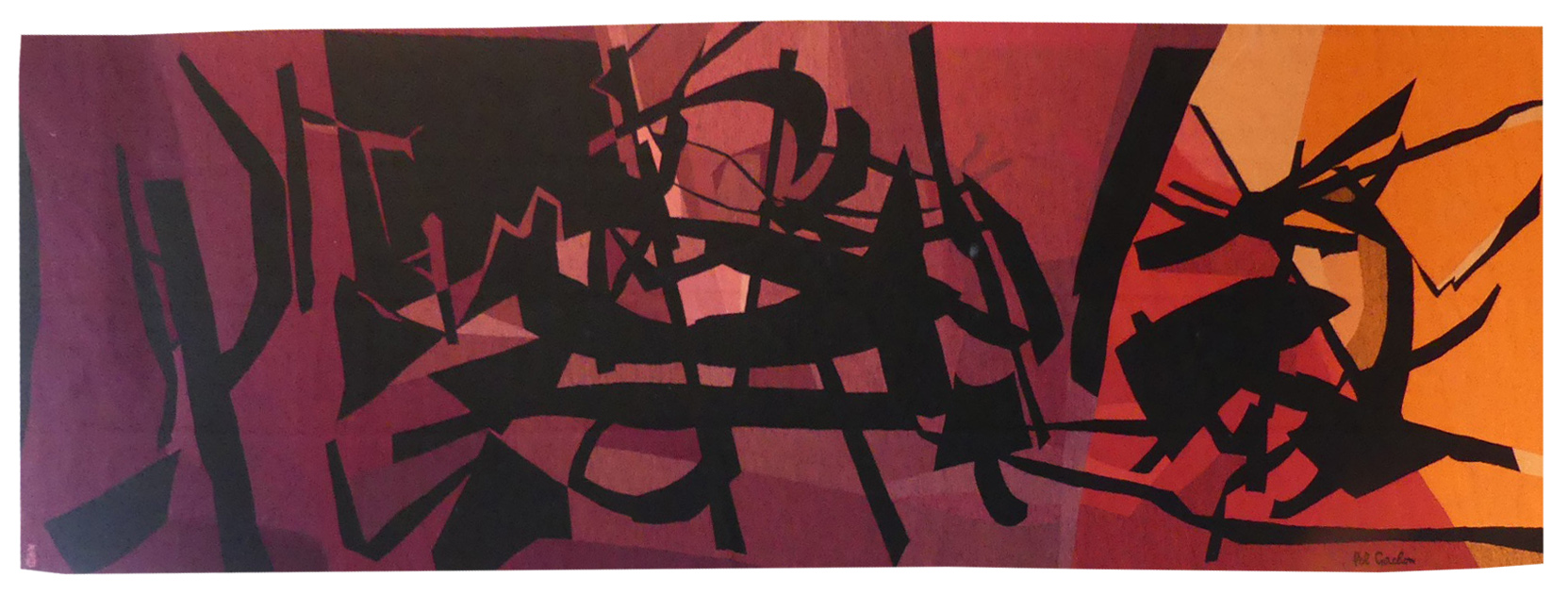
Les gaîtés du soir (evening gaieties)
Aubusson tapestry, woven in the Tabard workshop. With signed label, n°1. Circa 1968.Better known for his geometrically inspired paintings incorporating on occasion mechanical elements, Gachon designed several tapestry cartoons even from the early days of his career as his contacts with the Tabard workshop from the late 1960’s reveal. This design shows the influence on the young man of lyrical abstraction, an artistic current which finds little expression generally in tapestry. -
Vent de sable (sandstorm)
Aubusson tapestry woven in the Legoueix workshop. With signed label, n°EA/2. Circa 1970.Originally a sculptor exploiting very diverse materials (steel, concrete, clay…), Borderie came to tapestry with immense enthusiasm in the 1950’s with the weaving of his first cartoon in 1957. Receiving encouragement from Denise Majorel, he was awarded the Grand Prix National de la Tapisserie in 1962. In 1974 he was appointed as director at the Ecole Nationale des Arts Décoratifs at Aubusson but he resigned from this post shortly thereafter. He designed over 500 painted cartoons, abstracts using simple shapes, shading in a limited palette of colours and weaving with gros points. A dynamic abstraction with a limited colour scheme running from orange to brown, abstract motifs which play on the plastic effect of light passing through the colours : a classic cartoon from André Borderie. Bibliography : Exhibition catalogue André Borderie « pour l’homme simplement », Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la Tapisserie Contemporaine 1998 J.J. et B. Wattel, André Borderie et la tapisserie d'Aubusson, Editions Louvre Victoire, 2018 -
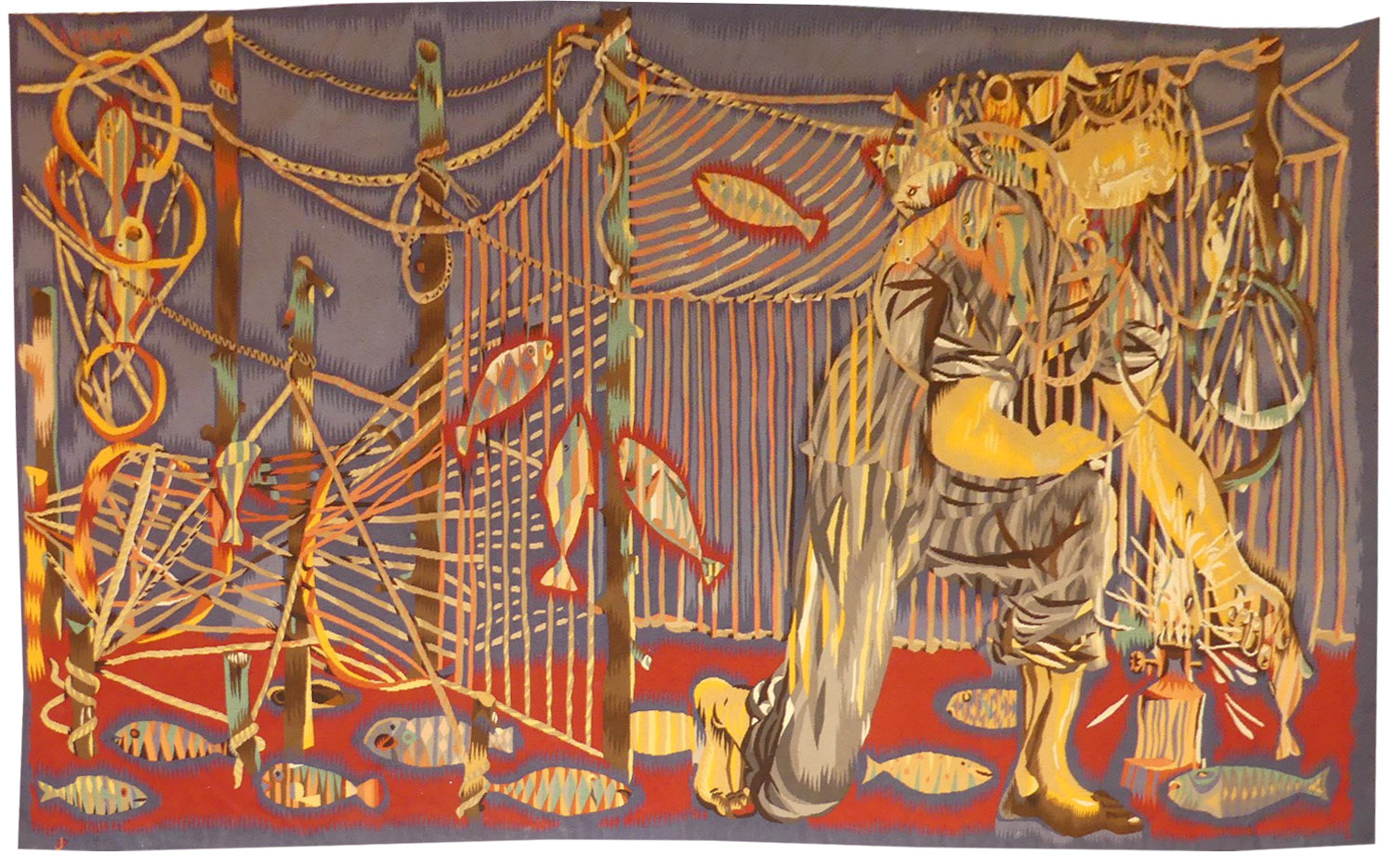
le verveux, variante (fyke net, variation)
An enthusiastic mural artist as early as 1937 (he participated in the Exposition Internationale), Lagrange designed his first cartoons in 1945, and became one of the founding members of the A.P.C.T. His early cartoons were expressionist (like Matégot and Tourlière), then his work evolved towards a stylisation (dating from his collaboration with Pierre Baudouin) which would bring him in the 1970’s to a highly refined style using very pure colours. As well as his important rôle in the tapestry renaissance movement of the period (and the state commissions that went with it), Lagrange would become a teacher at the Ecole Nationale des Beaux-Arts, a regular collaborator with Jacques Tati, a designer of monumental elements incorporated in various architectural projects and a recognised painter close to Estève and Lapicque. « Le verveux » [the fyke net] a large-scale tapestry measuring 203 x 285 cm, woven in the Tabard workshop (and whose cartoon is kept at the cité de la Tapisserie in Aubusson) is a work characteristic of Lagrange’s early style both by its theme (the anachronistic realism of evoking disappearing trades practised by simple people), and its expressionist style. This variant returns to the theme in a smaller scale version with only one human figure and a different colour scheme, however some details remain : the oil lamp, the brightly coloured fish lying on the seabed... Bibliography : Exhibition Catalogue Lagrange, Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la tapisserie contemporaine, 1987 Robert Guinot, Jacques Lagrange, les couleurs de la vie, Lucien Souny editeur, 2005 J.J. et B. Wattel, Jacques Lagrange et ses toiles : peintures, tapisseries, cinéma, Editions Louvre Victoire, 2020Tapestry probably woven in Aubusson. Circa 1947. -
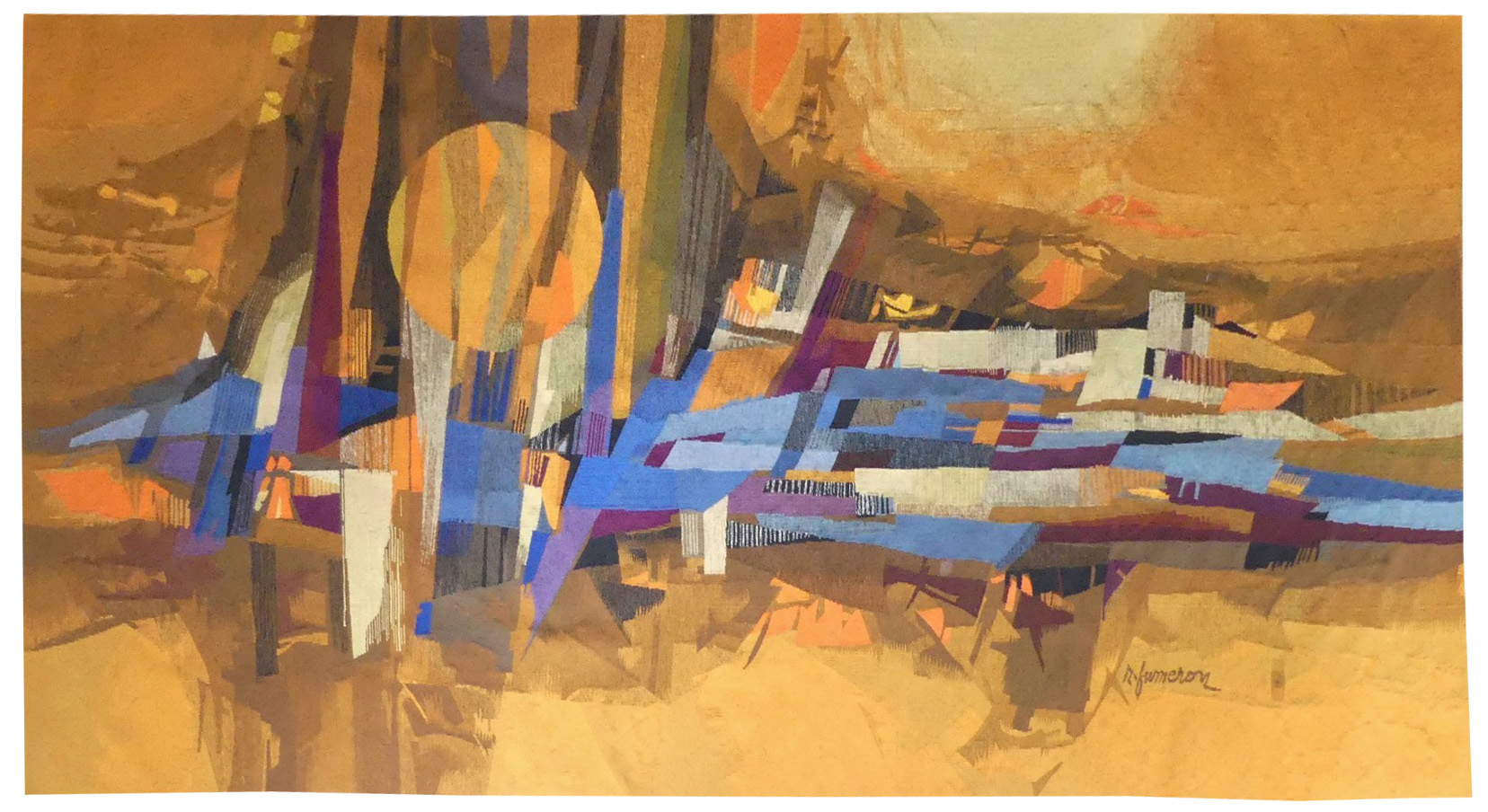
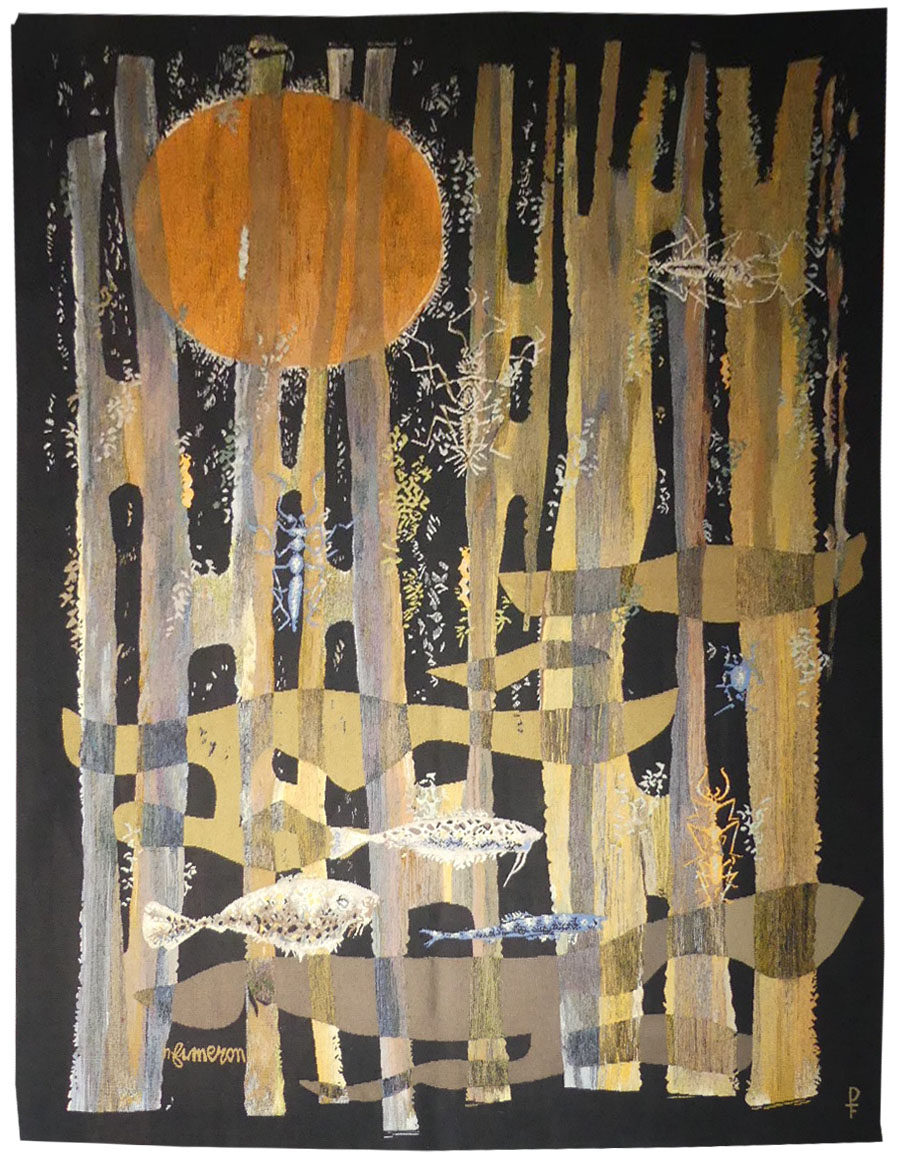
Composition
Aubusson tapestry woven by the Four workshop. n°EA. Circa 1960.Fumeron designed his first cartoons (he would ultimately make over 500) in the 1940’s, in collaboration with the Pinton workshop, he was then commissioned on numerous occasions by the state before participating in the decoration of the ocean liner “France”. His work was figurative to begin with and influenced by Lurçat, then turned towards abstraction, before coming back to a style characterised by colourful figurative and realistic depictions from the 1980’s onwards. An abstract cartoon, typical of the artist’s work, in a style (and a colour scheme !) which are redolent of Borderie or Wogensky, and whose works produced at this time have nothing of which to be ashamed when compared with those of his contemporaries. -
Faisan d'ombre (Shadow pheasant)
Lurçat’s artistic production was immense : it is however his role as the renovator of the art of tapestry design which ensures his lasting renown. As early as 1917, he started producing works on canvas, then in the 20’s and 30’s, he worked with Marie Cuttoli. His first collaboration with the Gobelins workshop dates back to 1937, at the same time he discovered the tapestry of the Apocalypse which was essential in his decision to devote himself to tapestry design. He first tackled the Gobelins, 2016technical aspects with François Tabard, then on his installation at Aubusson during the war, he established his technique : broad point, a simplified palette, outlined cartoons with colours indicated by pre-ordained numbers. A huge production then follows (over 1000 cartoons) amplified by his desire to include his painter friends, the creation of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-Cartonniers de Tapisserie) and the collaboration with the art gallery La Demeure and Denise Majorel, and then by his role as a tireless advocate for the medium around the world. His tapestries reveal a pictorial world which is specifically decorative, with a very personal symbolic iconography : cosmogony (the sun, the planets, the zodiac, the four elements…) stylised vegetation, fauna (rams, cocks, butterflies, chimera …) standing out against a background without perspective (voluntarily different from painting) and, in his more ambitious work, designed as an invitation to share in a poetic (he sometimes weaves quotations into his tapestries) and philosophical (the grand themes are broached from the wartime period onwards) vision whose climax is the “Chant du Monde” (Song of the World) (Jean Lurçat Museum , ancien hôpital Saint Jean, Angers) which remained unfinished at his death. In Lurçat’s work, the motif of the cockerel can appear under different monikers : peacock, pheasant (limiting ourselves to the ornithological, because when the plastic representation presents symbolical value the variations are infinite). As for the use of a negative outline, it is a technique used also in the piece entitled “coq dentelle” [lacy cockerel] (a piece in its own right playing on different textiles) dating from 1946. Bibliography : Tapisseries de Jean Lurçat 1939-1957, Pierre Vorms Editeur, 1957 Exhibition Catalogue Lurçat, 10 ans après, Musée d’Art moderne de la ville de Paris, 1976 Exhibition catalogue Les domaines de Jean Lurçat, Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la tapisserie contemporaine, 1986 Symposium Jean Lurçat et la renaissance de la tapisserie in Aubusson, Aubusson, Musée départemental de la tapisserie 1992 Exhibition Catalogue Dialogues avec Lurçat, Musées de Basse-Normandie, 1992 Exhibition catalogue Jean Lurçat, Donation Simone Lurçat, Académie des Beaux-Arts, 2004 Jean Lurçat, le chant du monde Angers 2007 Gérard Denizeau, Denise Majorel, une vie pour la tapisserie, Aubusson, Musée départemental de la tapisserie, ill. p.59 Gérard Denizeau, Jean Lurçat, Liénart, 2013, ill. fig. 154 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Lurçat, Meister der französischen Moderne, Halle, Kunsthalle Exhibition Catalogue Jean Lurçat au seul bruit du soleil, Paris, galerie des Gobelins, 2016Aubusson tapestry woven in the Caron workshop. With signed label. Circa 1950. -
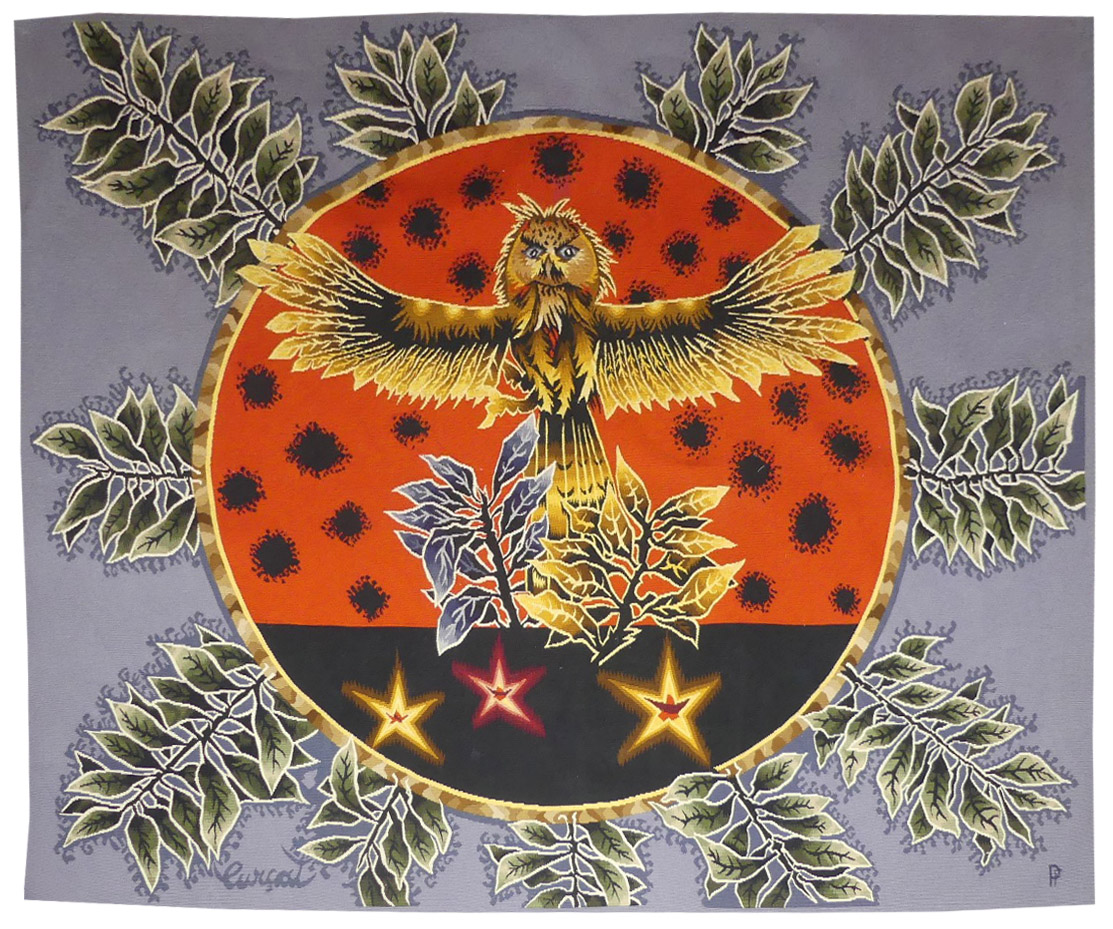
Soleil couchant (Sunset)
Lurçat’s artistic production was immense : it is however his role as the renovator of the art of tapestry design which ensures his lasting renown. As early as 1917, he started producing works on canvas, then in the 20’s and 30’s, he worked with Marie Cuttoli. His first collaboration with the Gobelins workshop dates back to 1937, at the same time he discovered the tapestry of the Apocalypse which was essential in his decision to devote himself to tapestry design. He first tackled the technical aspects with François Tabard, then on his installation at Aubusson during the war, he established his technique : broad point, a simplified palette, outlined cartoons with colours indicated by pre-ordained numbers. A huge production then follows (over 1000 cartoons) amplified by his desire to include his painter friends, the creation of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-Cartonniers de Tapisserie) and the collaboration with the art gallery La Demeure and Denise Majorel, and then by his role as a tireless advocate for the medium around the world. His tapestries reveal a pictorial world which is specifically decorative, with a very personal symbolic iconography : cosmogony (the sun, the planets, the zodiac, the four elements…) stylised vegetation, fauna (rams, cocks, butterflies, chimera …) standing out against a background without perspective (voluntarily different from painting) and, in his more ambitious work, designed as an invitation to share in a poetic (he sometimes weaves quotations into his tapestries) and philosophical (the grand themes are broached from the wartime period onwards) vision whose climax is the “Chant du Monde” (Song of the World) (Jean Lurçat Museum , ancien hôpital Saint Jean, Angers) which remained unfinished at his death. The motif of the owl with outstretched wings figuring as a protective guardian, is found in his work from the 1950's onward. Interestingly, one of the most iconic photographs of the artist shows him, arms akimbo, but with his hands on his bald head, positioned below and in front of just such a bird. Bibliography : Tapisseries de Jean Lurçat 1939-1957, Pierre Vorms Editeur, 1957 Exhibition Catalogue Lurçat, 10 ans après, Musée d’Art moderne de la ville de Paris, 1976 Exhibition catalogue Les domaines de Jean Lurçat, Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la tapisserie contemporaine, 1986 Symposium Jean Lurçat et la renaissance de la tapisserie in Aubusson, Aubusson, Musée départemental de la tapisserie 1992 Exhibition Catalogue Dialogues avec Lurçat, Musées de Basse-Normandie, 1992 Exhibition catalogue Jean Lurçat, Donation Simone Lurçat, Académie des Beaux-Arts, 2004 Jean Lurçat, le chant du monde Angers 2007 Gérard Denizeau, Jean Lurçat, Liénart, 2013 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Lurçat, Meister der französischen Moderne, Halle, Kunsthalle Exhibition Catalogue Jean Lurçat au seul bruit du soleil, Paris, galerie des Gobelins, 2016Tapestry woven in the Pinton workshop. With signed label. Circa 1950. -
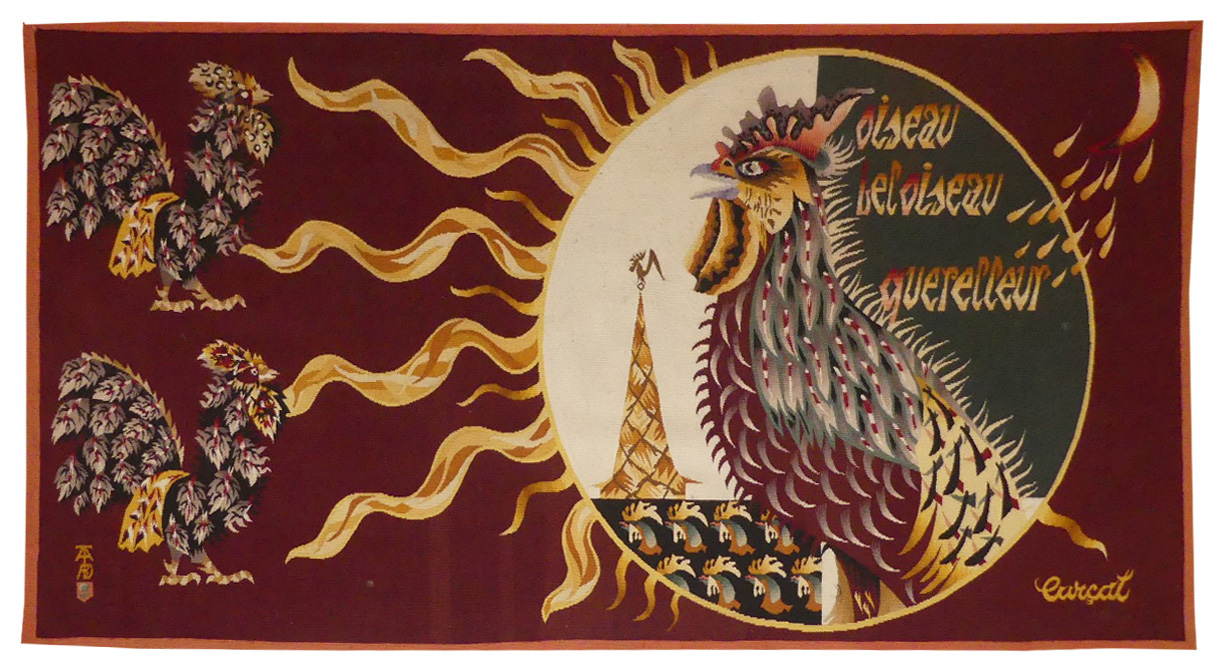
Bel oiseau querelleur (beautiful, quarrelsome bird)
Lurçat’s artistic production was immense : it is however his role as the renovator of the art of tapestry design which ensures his lasting renown. As early as 1917, he started producing works on canvas, then in the 20’s and 30’s, he worked with Marie Cuttoli. His first collaboration with the Gobelins workshop dates back to 1937, at the same time he discovered the tapestry of the Apocalypse which was essential in his decision to devote himself to tapestry design. He first tackled the technical aspects with François Tabard, then on his installation at Aubusson during the war, he established his technique : broad point, a simplified palette, outlined cartoons with colours indicated by pre-ordained numbers. A huge production then follows (over 1000 cartoons) amplified by his desire to include his painter friends, the creation of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-Cartonniers de Tapisserie) and the collaboration with the art gallery La Demeure and Denise Majorel, and then by his role as a tireless advocate for the medium around the world. His tapestries reveal a pictorial world which is specifically decorative, with a very personal symbolic iconography : cosmogony (the sun, the planets, the zodiac, the four elements…) stylised vegetation, fauna (rams, cocks, butterflies, chimera …) standing out against a background without perspective (voluntarily different from painting) and, in his more ambitious work, designed as an invitation to share in a poetic (he sometimes weaves quotations into his tapestries) and philosophical (the grand themes are broached from the wartime period onwards) vision whose climax is the “Chant du Monde” (Song of the World) (Jean Lurçat Museum , ancien hôpital Saint Jean, Angers) which remained unfinished at his death. This tapestry quotes a line from Aragon's poem « Coq », which was more lengthily quoted in « Oiseau de toutes les couleurs » (multicoloured bird) (a cartoon from 1948 of which one example is on show at the Cité de la Tapisserie in Aubusson). The use of text as an element of design is recurrent in Lurçat's work ; in this instance it unites the thematic and the symbolic (the cock), the political and the historical (the Resistance and the French Communist Party). Bibliography : Tapisseries de Jean Lurçat 1939-1957, Pierre Vorms Editeur, 1957 Exhibition Catalogue Lurçat, 10 ans après, Musée d’Art moderne de la ville de Paris, 1976 Exhibition catalogue Les domaines de Jean Lurçat, Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la tapisserie contemporaine, 1986 Symposium Jean Lurçat et la renaissance de la tapisserie in Aubusson, Aubusson, Musée départemental de la tapisserie 1992 Exhibition Catalogue Dialogues avec Lurçat, Musées de Basse-Normandie, 1992 Exhibition catalogue Jean Lurçat, Donation Simone Lurçat, Académie des Beaux-Arts, 2004 Jean Lurçat, le chant du monde Angers 2007 Gérard Denizeau, Jean Lurçat, Liénart, 2013 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Lurçat, Meister der französischen Moderne, Halle, Kunsthalle Exhibition Catalogue Jean Lurçat au seul bruit du soleil, Paris, galerie des Gobelins, 2016Tapestry woven in the Tabard workshop. With label. 1948. -
Oiseaux (birds)
Aubusson tapestry woven by the Tapisseries de France cooperative. 1952.Perrot began his career as a cartoon designer at the end of the war, making almost 500 cartoons including numerous commissions from the state, most of which were woven at Aubusson. His style which is particularly rich and decorative is eminently recognisable : a crowd of butterflies or birds, most often, stands out against a background of vegetation, reminiscent of the millefleurs tapestries (which would also inspire Dom Robert). If in Perrot's tapestries birds are often present (almost a trademark !) the use of landscape as a background is much rarer despite the artist having produced numerous works in gouache of his travels (Doubs, Auvergne, Collioure, the Canaries...), works which, despite their sensitivity, remain essentially little known. Bibliography : Tapisseries, dessins, peintures, gravures de René Perrot, Dessein et Tolra, 1982 -
Sphinx jaune (yellow hawk moth)
Lurçat’s artistic production was immense : it is however his role as the renovator of the art of tapestry design which ensures his lasting renown. As early as 1917, he started producing works on canvas, then in the 20’s and 30’s, he worked with Marie Cuttoli. His first collaboration with the Gobelins workshop dates back to 1937, at the same time he discovered the tapestry of the Apocalypse which was essential in his decision to devote himself to tapestry design. He first tackled the technical aspects with François Tabard, then on his installation at Aubusson during the war, he established his technique : broad point, a simplified palette, outlined cartoons with colours indicated by pre-ordained numbers. A huge production then follows (over 1000 cartoons) amplified by his desire to include his painter friends, the creation of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-Cartonniers de Tapisserie) and the collaboration with the art gallery La Demeure and Denise Majorel, and then by his role as a tireless advocate for the medium around the world. His tapestries reveal a pictorial world which is specifically decorative, with a very personal symbolic iconography : cosmogony (the sun, the planets, the zodiac, the four elements…) stylised vegetation, fauna (rams, cocks, butterflies, chimera …) standing out against a background without perspective (voluntarily different from painting) and, in his more ambitious work, designed as an invitation to share in a poetic (he sometimes weaves quotations into his tapestries) and philosophical (the grand themes are broached from the wartime period onwards) vision whose climax is the “Chant du Monde” (Song of the World) (Jean Lurçat Museum , ancien hôpital Saint Jean, Angers) which remained unfinished at his death. The motif of the butterfly is closely associated with his trip to Latin America and often figures in the exotic designs that were inspired by it. On occasion Lurçat designed vertical, oversized « portraits » of butterflies (« Sphinx bleu », « sphinx et coq ».... ), in a striking departure from scaled representation. Bibliography : Tapisseries de Jean Lurçat 1939-1957, Pierre Vorms Editeur, 1957 Exhibition Catalogue Lurçat, 10 ans après, Musée d’Art moderne de la ville de Paris, 1976 Exhibition catalogue Les domaines de Jean Lurçat, Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la tapisserie contemporaine, 1986 Symposium Jean Lurçat et la renaissance de la tapisserie in Aubusson, Aubusson, Musée départemental de la tapisserie 1992 Exhibition Catalogue Dialogues avec Lurçat, Musées de Basse-Normandie, 1992 Exhibition catalogue Jean Lurçat, Donation Simone Lurçat, Académie des Beaux-Arts, 2004 Jean Lurçat, le chant du monde Angers 2007 Gérard Denizeau, Jean Lurçat, Liénart, 2013 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Lurçat, Meister der französischen Moderne, Halle, Kunsthalle Exhibition Catalogue Jean Lurçat au seul bruit du soleil, Paris, galerie des Gobelins, 2016Tapestry woven in the Pinton workshop. With illegible label. Circa 1950. -
Chevaux en Camargue ( Horses in Camargue)
Although Brayer designed on occasion large-scale mural pieces (notably sets for the Paris Opera), he did not devote much of his time to tapestry : the works he produced in this particular domain are in fact reproductions of pre-existing paintings featuring typically provençal subjects.Aubusson tapestry woven by the Pinton workshop. N°1/6. Circa 1980. -
Reflets d'argent (silver reflections)
Aubusson tapestry woven by the Pinton workshop. With signed label. Circa 1960.Fumeron designed his first cartoons (he would ultimately make over 500) in the 1940’s, in collaboration with the Pinton workshop, he was then commissioned on numerous occasions by the state before participating in the decoration of the ocean liner “France”. His work was figurative to begin with and influenced by Lurçat, then turned towards abstraction, before coming back to a style characterised by colourful figurative and realistic depictions from the 1980’s onwards. The vertical fronds, through which fish weave in and out, partially hide a flaming red sun : in this piece we recognise all the elements of Fumeron’s characteristically fantastical vision. -
Paris moderne (modern Paris)
Little is known about the artist, but she created a number of cartoons, which would be woven by Antoine Behna’s ART workshop. The panoramic topographical view was one of the specialities of the workshop, “Paris moderne” being a sort of riposte to Bobot's “Vieux Paris 1650”. An example of each of these tapestries was offered as a gift to President Truman. Bibliography : G. Janneau, A. Behna, Tapisseries de notre temps, 1950, ill. n°3 Millon-Robert sale catalogue 3.10.1990 n°1, 31Tapestry woven by the Colombes workshop for ART (Atelier de Rénovation de la Tapisserie). 1945. -
Coucher de soleil sur l'Orient (eastern sunset)
Toffoli produced a large number of tapestries in collaboration with the Robert Four workshop from 1976 onwards, designing several hundred cartoons. In them we find post-cubist transparent effects which are characteristic of the artist, as indeed are the subjects treated. Thus Toffoli’s tapestries do not differ from his painting : travelling for inspiration, here he illustrates junks observed during trips to the far East.Aubusson tapestry woven by the Four workshop. With label, n°3/6. Circa 1990. -
Le secret (the secret)
Having established himself in the 1930's in the region around Nantes, Morin worked as an artist in advertising as well as painting and engraving, at first in a figurative style and then evolving towards abstraction from 1954 onwards. His interest in monumental art is revealed in his use of mosaic (particularly within the framework of the government 1% subsidy for art in works produced for schools of the greater Nantes area) but also in tapestry. As early as 1952 he received the first commissions for religious-themed works which would be produced by the Plasse le Caisne workshop (who also worked for Manessier, Le Moal...), before collaborating with Pierre Daquin's Atelier de Saint-Cyr, a major player in the French movement for la Nouvelle Tapisserie, and having several pieces exhibited at the Demeure gallery. From then onwards, until 1982, other designs would be produced by the workshops of the Ecole Regionale des Beaux-Arts in Angers, and later by the artist's own daughter who was herself a weaver. In his collaboration with Daquin (as in the latter's own works) the medium became one with the message, the technical mastery was absolute : the surfaces are animated and vibrant with a complexity of different textures and stitches... and Morin's poetic designs with their delicately symetrical signs, found an ideal expression. Bibliographie : Exhibition Catalogue Jorj Morin, tapisseries, gravures à l'eau-forte, et quelques stèles de mosaïques, Paris, galerie La Demeure, 1974, reproduced Exhibition catalogue Jorj Morin, tapisseries, peintures, gravures, mosaïques, Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la tapisserie contemporaine, 1991-1992Tapestry woven by the Saint-Cyr workshop. With signed label, n°I/VI. 1971. -
Métamorphoses (metamorphosis)
A disciple of Jacques Adnet, Pothier produced his first cartoons (of which « Metamorphoses » is one) for the former, woven in the Pinton workshop for the Compagnie des Arts français, before moving on to produce 5 more for the Manufactures Nationales. His work which is exuberant, dense, strongly influenced by surrealism but also references Arcimboldo (a claim he made himself), is like no other. It does however inevitably refer back, like other artists working at the same time and in the same domain, to the mille-fleurs style of the middle ages. To these diverse influences (which give a strange dreamlike quality to this cartoon) Pothier brings, in « Métamorphoses », his predilection for a limited colour palette (3 distinct hues !) and a sense of humour (the discreet signature incorporated into the body of the figure (?) on the left). This design would be reversed and enlarged in the tapestry (woven in 1961 at Les Gobelins) « Madrépores en fleurs ».Aubusson tapestry woven by the Pinton workshop, for the Compagnie des Arts Français. With illegible label. Circa 1950. -
Coquillage étoilé II (Starry seashell II)
Aubusson tapestry woven by the Picaud workshop. With label signed by the artist, n°2/6. Circa 1975. Jean Picart le Doux is one of the foremost figures in the renaissance of the art of tapestry. His earliest contributions to the field date back to 1943 when he designed cartoons for the passenger ship “la Marseillaise”. A close associate of Lurçat, whose theories he would adopt (limited palette, numbered cartoons...), he was a founding member of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-cartonniers de Tapisserie), and soon after, a teacher at the Ecole Nationale Supérieure des Arts Décoratifs. The state gave him several commissions most of them at the Aubusson workshop, and some at the Gobelins : the most spectacular of these being for the University of Caen, the Theatre in Le Mans, the passenger ship France or the Prefecture of the Creuse département ... In as much as Picart le Doux’s aesthetic is close to that of Lurçat, so also is his inspiration and his subject matter, although in a register which is more decorative than symbolic, where he brings together heavenly bodies (the sun, the moon, the stars...), the elements, nature (wheat, vines, fish, birds...), man, literary quotation ... « Coquillage étoilé » (Starry seashell) dates from 1959 and thenceforth the motif reappears regularly, in « l’Eau et le Feu » (Water and Fire) (1959), « la Mer et la Terre » (Sea and Land) (1960) or « l’Homme et la Mer » (The man and the sea) (1964)… as an evocation of the sea. This cartoon places the motif at the centre whilst another tapestry, with the same name, uses a vertical format. Bibliography : Marthe Belle-Joufray, Jean Picart le Doux, Publications filmées d’art et d’histoire, 1966 Maurice Bruzeau, Jean Picart le Doux, Murs de soleil, Editions Cercle d’art, 1972 Exhibition Catalogue, Jean Picart le Doux, tapisseries, Musée de Saint-Denis, 1976 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Picart le Doux, Musée de la Poste, 1980 -
Soleil d'hiver (Winter sun)
Michel Degand, is an artist who expresses himself in many different media (painting, sculpture, illustration,…) and who has in 50 creative years, conceived over a hundred tapestry cartoons, whose inspiration is perpetually evolving, sometimes dreamlike or cosmic (reminiscent of Wogensky), at other times « technological » (like Millecamps), often lyrical, with a marked interest in the material itself, and most of his work has been woven in the Pinton workshop at Felletin. The sun is a regular leitmotiv for this artist ; but in this fragmented composition he works in fragments of older tapestries (using finer stiching), as would Sautour-Gaillard in the 1990’s, making them appear to be glued into the original motif, a technique which results in thought-provoking juxtapositions.Aubusson tapestry woven in the Pinton workshop. N°1/1. Circa 1980. -
La voix du reliquaire (the voice of the reliquary)
Aubusson tapestry woven in the Legoueix workshop. With signed label, n°1/3. 1975.Sautour-Gaillard had his first cartoon woven in 1971 by the Legoueix workshop (a collaboration which was to last), and from then on he designed many very large-scale projects of which the most spectacular was “Pour un certain idéal” a series of 17 tapestries dealing with the theme of Olympianism (property of the Musée de l’Olympisme in Lausanne). If at first close to lyrical abstraction, the artist produced in the 1990’s cartoons superimposing different decorative motifs, textures and figures whose unity originated in the woven texture itself. « La voix du reliquaire » reveals a certain proximity of the artist, in his early work, to the abstract world of Soulages or Schneider. We recognise, transposed into the wool medium, the gestures,the overflows, characteristic of the artists of the “envolée lyrique”, in a severely limited range of colours. Bibliography : D. Cavelier, Jean-René Sautour-Gaillard, la déchirure, Lelivredart, 2013, ill.p.163 -
La terre et la mer II (Earth and sea II)
Aubusson tapestry woven by the Hecquet workshop. With label signed by the artist's widow, n°1/6. 1960. Jean Picart le Doux is one of the foremost figures in the renaissance of the art of tapestry. His earliest contributions to the field date back to 1943 when he designed cartoons for the passenger ship “la Marseillaise”. A close associate of Lurçat, whose theories he would adopt (limited palette, numbered cartoons...), he was a founding member of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-cartonniers de Tapisserie), and soon after, a teacher at the Ecole Nationale Supérieure des Arts Décoratifs. The state gave him several commissions most of them at the Aubusson workshop, and some at the Gobelins : the most spectacular of these being for the University of Caen, the Theatre in Le Mans, the passenger ship France or the Prefecture of the Creuse département ... In as much as Picart le Doux’s aesthetic is close to that of Lurçat, so also is his inspiration and his subject matter, although in a register which is more decorative than symbolic, where he brings together heavenly bodies (the sun, the moon, the stars...), the elements, nature (wheat, vines, fish, birds...), man, literary quotation ... This cartoon is a smaller reworking of his original version (170 x 272 cm) dating from 1960. At that time, Picart le Doux was beginning his series of binary tapestries with allegorical associations of different elements. A system was being established (fish + shells = water or the sea, butterflies + roots = the earth) which Picard le Doux would use for the rest of his career. Bibliography : Marthe Belle-Joufray, Jean Picart le Doux, Publications filmées d’art et d’histoire, 1966 Maurice Bruzeau, Jean Picart le Doux, Murs de soleil, Editions Cercle d’art, 1972, n°103 Exhibition Catalogue, Jean Picart le Doux, tapisseries, Musée de Saint-Denis, 1976 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Picart le Doux, Musée de la Poste, 1980 -
Synthèse (synthesis)
Aubusson tapestry woven by the Hamot workshop. 1961. Jean Picart le Doux is one of the foremost figures in the renaissance of the art of tapestry. His earliest contributions to the field date back to 1943 when he designed cartoons for the passenger ship “la Marseillaise”. A close associate of Lurçat, whose theories he would adopt (limited palette, numbered cartoons...), he was a founding member of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-cartonniers de Tapisserie), and soon after, a teacher at the Ecole Nationale Supérieure des Arts Décoratifs. The state gave him several commissions most of them at the Aubusson workshop, and some at the Gobelins : the most spectacular of these being for the University of Caen, the Theatre in Le Mans, the passenger ship France or the Prefecture of the Creuse département ... In as much as Picart le Doux’s aesthetic is close to that of Lurçat, so also is his inspiration and his subject matter, although in a register which is more decorative than symbolic, where he brings together heavenly bodies (the sun, the moon, the stars...), the elements, nature (wheat, vines, fish, birds...), man, literary quotation ... « Synthèse » is a reworking of the motifs in « Cosmogonie » (1948) : an arrangement of elements representing scientific knowledge, an astrolabe, a compass, a pyramid, a book of natural science... Bibliography : Marthe Belle-Joufray, Jean Picart le Doux, Publications filmées d’art et d’histoire, 1966, n°15 Maurice Bruzeau, Jean Picart le Doux, Murs de soleil, Editions Cercle d’art, 1972, n°107 Exhibition Catalogue, Jean Picart le Doux, tapisseries, Musée de Saint-Denis, 1976 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Picart le Doux, Musée de la Poste, 1980 -
La loi (Law)
Aubusson tapestry woven by the Rivière des Borderies workshop. With label. 1951.Perrot began his career as a cartoon designer at the end of the war, making almost 500 cartoons including numerous commissions from the state, most of which were woven at Aubusson. His style which is particularly rich and decorative is eminently recognisable : a crowd of butterflies or birds, most often, stands out against a background of vegetation, reminiscent of the millefleurs tapestries (which would also inspire Dom Robert). Ornithological representations in all their various manifestations are extremely common in Perrot’s work : for example “la discorde” and “la méditation” designed for the Palais de Justice (High Court) in Paris which are illustrated respectively by grouse and owls. What else to illustrate “La Loi” and inspire respect in the observor than the severe glare of a majestic eagle. Bibliography : Tapisseries, dessins, peintures, gravures de René Perrot, Dessein et Tolra, 1982 -
Reflets (reflections)
Aubusson tapestry woven by the Pinton workshop. With label, n°6/6. Circa 1960.Fumeron designed his first cartoons (he would ultimately make over 500) in the 1940’s, in collaboration with the Pinton workshop, he was then commissioned on numerous occasions by the state before participating in the decoration of the ocean liner “France”. His work was figurative to begin with and influenced by Lurçat, then turned towards abstraction, before coming back to a style characterised by colourful figurative and realistic depictions from the 1980’s onwards. Beneath the red sun, fish, insects , a lobster all frolic in a dream-like composition typical of the artist : numerous examples of these motifs can be found for instance in “Avant l’homme” Before man, woven by the Gobelins (cf Exhibition Catalogue “le Mobilier National et les Manufactures Nationales des Gobelins et de Beauvais sous la IVe République”, Beauvais 1997) -
L'Odyssée (the Odyssey)
Aubusson tapestry woven in the Pinton workshop. With signed label, n°1/6. Circa 1965.Fumeron designed his first cartoons (he would ultimately make over 500) in the 1940’s, in collaboration with the Pinton workshop, he was then commissioned on numerous occasions by the state before participating in the decoration of the ocean liner “France”. His work was figurative to begin with and influenced by Lurçat, then turned towards abstraction, before coming back to a style characterised by colourful figurative and realistic depictions from the 1980’s onwards. During the 1960’s Fumeron evolved towards abstraction as did some of his contemporaries (Matégot, Wogensky,...). His compositions of this period are sometimes inspired by literary subjects (Cf. Hamlet) which are interpreted in a kaleidoscope of colours which are immediately recognisable. -
La chouette (the owl )
Lurçat’s artistic production was immense : it is however his role as the renovator of the art of tapestry design which ensures his lasting renown. As early as 1917, he started producing works on canvas, then in the 20’s and 30’s, he worked with Marie Cuttoli. His first collaboration with the Gobelins workshop dates back to 1937, at the same time he discovered the tapestry of the Apocalypse which was essential in his decision to devote himself to tapestry design. He first tackled the technical aspects with François Tabard, then on his installation at Aubusson during the war, he established his technique : broad point, a simplified palette, outlined cartoons with colours indicated by pre-ordained numbers. A huge production then follows (over 1000 cartoons) amplified by his desire to include his painter friends, the creation of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-Cartonniers de Tapisserie) and the collaboration with the art gallery La Demeure and Denise Majorel, and then by his role as a tireless advocate for the medium around the world. His tapestries reveal a pictorial world which is specifically decorative, with a very personal symbolic iconography : cosmogony (the sun, the planets, the zodiac, the four elements…) stylised vegetation, fauna (rams, cocks, butterflies, chimera …) standing out against a background without perspective (voluntarily different from painting) and, in his more ambitious work, designed as an invitation to share in a poetic (he sometimes weaves quotations into his tapestries) and philosophical (the grand themes are broached from the wartime period onwards) vision whose climax is the “Chant du Monde” (Song of the World) (Jean Lurçat Museum , ancien hôpital Saint Jean, Angers) which remained unfinished at his death. This choice of a vertical rectangular format containing a delineated circular motif against a burgundy background recurrs regularly in Lurçat’s work in the later 1940’s (cf. “Bosquet” for example). If the owl motif referred to in the title is indeed often used by Lurçat, in this particular example it more closely resembles a cockerel, another frequently recurring motif, a confusion in which this artist delighted. Bibliography : Cat. Expo. La tapisserie française, Musée d’art moderne, Paris, 1946 Tapisseries de Jean Lurçat 1939-1957, Pierre Vorms Editeur, 1957 Cat. Expo. Jean Lurçat, tapisseries de la fondation Rothmans, Musée de Metz, 1969 Exhibition Catalogue Lurçat, 10 ans après, Musée d’Art moderne de la ville de Paris, 1976 Exhibition catalogue Les domaines de Jean Lurçat, Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la tapisserie contemporaine, 1986 Symposium Jean Lurçat et la renaissance de la tapisserie in Aubusson, Aubusson, Musée départemental de la tapisserie 1992 Exhibition Catalogue Dialogues avec Lurçat, Musées de Basse-Normandie, 1992 Exhibition catalogue Jean Lurçat, Donation Simone Lurçat, Académie des Beaux-Arts, 2004 Jean Lurçat, le chant du monde Angers 2007 Gérard Denizeau, Jean Lurçat, Liénart, 2013 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Lurçat, Meister der französischen Moderne, Halle, Kunsthalle Exhibition Catalogue Jean Lurçat au seul bruit du soleil, Paris, galerie des Gobelins, 2016Tapestry woven in the Tabard workshop. With label. Circa 1945. -
Soleil de corail (coral sun)
Aubusson tapestry woven in the Pinton workshop. With signed label. Circa 1960.Fumeron designed his first cartoons (he would ultimately make over 500) in the 1940’s, in collaboration with the Pinton workshop, he was then commissioned on numerous occasions by the state before participating in the decoration of the ocean liner “France”. His work was figurative to begin with and influenced by Lurçat, then turned towards abstraction, before coming back to a style characterised by colourful figurative and realistic depictions from the 1980’s onwards. The vertical fronds, through which mottled fish weave in and out, partially hide a flaming red sun : in this piece we recognise all the elements of Fumeron’s characteristically fantastical vision. -
Bel canto
Lurçat approached Saint-Saëns, originally a painter of murals, in 1940. And during the war the latter produced the first of his allegorical masterpieces, tapestries reflecting indignation, combat, resistance : “les Vierges folles (the foolish virgins), “Thésée et le Minotaure” (Theseus and the Minotaur). At the end of the war, as a natural development he joined up with Lurçat, whose convictions he shared (concerning a simplified palette, outlined cartoons with colours indicated by pre-ordained numbers, and the specific nature of tapestry design…) at the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-cartonniers de Tapisserie). His universe, where the human figure, stretched, elongated, ooccupies an important place (particularly when compared to his companions Lurçat or Picart le Doux), pivots around traditional themes : woman, the Commedia dell’arte, Greek mythology… refined by the brilliance of the colours and the simplification of the layout. His work would evolve later, in the 1960’s, towards cartoons of a more lyrical design, almost abstract where elemental and cosmic forces would dominate. If Music as a theme is ever-present in Saint-Saëns’s work, the changes that his style underwent in the 1960’s towards a vision that is both more informal and biomorphic, influenced his treatment of it ; but is not the lyricism evident in this piece ideally suited to the expression “Bel Canto” ? Bibliography : Exhibition catalogue La tapisserie française du Moyen-âge à nos jours, Paris, Musée d’art moderne, 1946 Exhibition catalogue Saint-Saëns, Paris, galerie La Demeure, 1970, ill. Exhibition catalogue Saint-Saëns, the tapestries, Aubusson, Musée départemental de la Tapisserie, 1987 Exhibition catalogue Marc Saint-Saëns, tapestries, 1935-1979, Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la Tapisserie Contemporaine 1997-1998Aubusson tapestry woven by the Tabard workshop. N°4. 1964. -
Hommage à Yukio Mishima (A tribute to Yukio Mishima)
Tapestry woven in the Saint-Cyr workshop. With signed label, n°EA1. 1972.Jacques Brachet was an important protagonist of the « New Tapestry » movement ; woven by Pierre Daquin, exhibited by the « La Demeure » gallery in the 1970’s, his innovative and experimental approach to the medium, from the 1950’s onwards, was recognised by the Centre International d’études pédagogiques in Sèvres, by the scenography of “La Tapisserie en France, 1945 – 1985, la tradition vivante” at the Ecole Nationale Supérieure des Beaux-Arts, and by his inclusion in various promotional events right up to the present day. Brachet travelled to Japan in 1972. The specific techniques of his tapestry designs (as opposed to painting) : innovative use of shape and texture, themes taken from the natural world... would take off in new directions as a result. Paradoxically this particulat hommage to one of the most flamboyant and tragic figures of post-war Japan is, as a textile object, rather tame respecting the 2 dimensional norm, a classic wool weave... The brightly coloured motifs (dominated by a red disk-shaped sun) are in contrast with the white background, like a shard of light on the blade of the seppuku. Bibliography : Madeleine Jarry, la tapisserie art du XXe siècle, Office du livre, 1974, ill. n°157 Exhibition catalogue Jacques Brachet, mémoires océanes, Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la tapisserie contemporaine, 1996 -
Le feu (Fire)
Lurçat approached Saint-Saëns, originally a painter of murals, in 1940. And during the war the latter produced the first of his allegorical masterpieces, tapestries reflecting indignation, combat, resistance : “les Vierges folles (the foolish virgins), “Thésée et le Minotaure” (Theseus and the Minotaur). At the end of the war, as a natural development he joined up with Lurçat, whose convictions he shared (concerning a simplified palette, outlined cartoons with colours indicated by pre-ordained numbers, and the specific nature of tapestry design…) at the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-cartonniers de Tapisserie). His universe, where the human figure, stretched, elongated, ooccupies an important place (particularly when compared to his companions Lurçat or Picart le Doux), pivots around traditional themes : woman, the Commedia dell’arte, Greek mythology… refined by the brilliance of the colours and the simplification of the layout. His work would evolve later, in the 1960’s, towards cartoons of a more lyrical design, almost abstract where elemental and cosmic forces would dominate. « Le Feu » is the 4th in the series « les Quatre éléments », commissioned by Jansen, woven by Dumontet and exhibited in 1946 at the Musée d’Art Moderne. Myths and allegory were a frequent source of inspiration for the artist at this period : “Orion”, “Diane”, “Thésée et le Minotaure” are all contemporary. Here the muscular figure of a Vulcanite blacksmith whose colour evokes glowing embers in dark relief against a flaming background leaves the observer with a long-lasting impression. Bibliography : Exhibition catalogue La tapisserie française du Moyen-âge à nos jours, Paris, Musée d’art moderne, 1946 Exhibition catalogue Saint-Saëns, Paris, galerie La Demeure, 1970, ill. Exhibition catalogue Saint-Saëns, the tapestries, Aubusson, Musée départemental de la Tapisserie, 1987 Exhibition catalogue Marc Saint-Saëns, tapestries, 1935-1979, Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la Tapisserie Contemporaine 1997-1998Aubusson tapestry woven by the Glaudin-Brivet workshop. With signed label, n°EX. 1945. -
La cueillette (Harvest)
Tapestry. 1943. Artiste polyvalent (graveur, médailleur, céramiste, fresquiste…), Savin est sollicité pendant la guerre par Guillaume Janneau, qui admire la monumentalité intemporelle et réaliste de son esthétique (et dont il soupçonnait qu’elle n’aurait nul besoin de transposition pour convenir à la Tapisserie), pour concevoir des cartons pour les Manufactures Nationales : « les plaisirs et les travaux champêtres » ( 4 cartons), puis les « 12 mois de l’année » sont créés simultanément à son travail avec la Compagnie des Arts Français. L’influence des aspects techniques de la tapisserie médiévale est très prégnante chez l’artiste, attentif aux colorants naturels en gamme réduite, aux formes simples permises par la technique du gros point,… Il fut l’un des artistes les plus représentés à l’exposition séminale de 1946, avec 7 pièces (seuls Lurçat, Saint-Saëns et Gromaire en eurent plus). « La cueillette » est contemporaine du carton conçu pour les Gobelins : « La cueillette des pommes », issue de la tenture sur « les plaisirs et travaux champêtres ». On y trouve les mêmes caractéristiques propres à l’artiste : gamme chromatique limitée mais vive, formes simplifiées et monumentales, densité de la composition, et une saveur rustique tout droit venue de la tapisserie médiévale. Bibliographie : Cat. Expo. La tapisserie française du Moyen-âge à nos jours, Paris, Musée d’art moderne, 1946 Cat. Expo. Le Mobilier National et les Manufactures Nationales sous la IVe République, Beauvais, Galerie nationale de la Tapisserie, 1997 Cat. Expo. La Manufacture des Gobelins dans la 1ère moitié du XXe siècle, Beauvais, Galerie nationale de la Tapisserie, 1999 -
Oiseau pilote (Pilot bird)
Aubusson tapestry woven in the Legoueix workshop. With signed label, n°1/6. 1969.A member of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-Cartonniers de Tapisserie), Wogensky is one of the many artists who would follow in Lurçat’s footsteps immediately after the war. At first influenced by his predecessor, Wogensky’s subsequent work (159 cartoons according to the 1989 exhibition catalogue) would evolve during the 1960’s towards a, not completely self-avowed, lyrical abstraction, from cosmic-astronomical themes expressed in decomposed, moving, birdlike shapes to cartoons both more refined and less dense. Although always claiming to be a painter, the artist’s conception of tapestry is extremely well thought out : “the realisation of a mural cartoon…. requires the consideration of a space which is no longer ours alone, by the nature of its dimensions, its scale, it also imposes a grand gesture which transforms and accentuates our presence.” « Oiseau pilote » in the singular, like its path « time-weaving » its way through a red sky (cf. “Oiseaux de Midi”, or “Envol” from the same year) forming a shape (or even a veritable dynamic!) showing the way and guiding us to follow... Bibliography : Exhibition catalogue Robert Wogensky, Aubusson, Musée départemental de la tapisserie, 1989 Exhibition catalogue Robert Wogensky, Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la Tapisserie Contemporaine, 1989 Exhibition Catalogue Tissages d’ateliers-tissages d’artistes, Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la Tapisserie Contemporaine, 2004 -
Univers végétal (Plant universe)
Aubusson tapestry woven for Jansen. 1944.Lurçat’s artistic production was immense : it is however his role as the renovator of the art of tapestry design which ensures his lasting renown. As early as 1917, he started producing works on canvas, then in the 20’s and 30’s, he worked with Marie Cuttoli. His first collaboration with the Gobelins workshop dates back to 1937, at the same time he discovered the tapestry of the Apocalypse which was essential in his decision to devote himself to tapestry design. He first tackled the technical aspects with François Tabard, then on his installation at Aubusson during the war, he established his technique : broad point, a simplified palette, outlined cartoons with colours indicated by pre-ordained numbers. A huge production then follows (over 1000 cartoons) amplified by his desire to include his painter friends, the creation of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-Cartonniers de Tapisserie) and the collaboration with the art gallery La Demeure and Denise Majorel, and then by his role as a tireless advocate for the medium around the world. His tapestries reveal a pictorial world which is specifically decorative, with a very personal symbolic iconography : cosmogony (the sun, the planets, the zodiac, the four elements…) stylised vegetation, fauna (rams, cocks, butterflies, chimera …) standing out against a background without perspective (voluntarily different from painting) and, in his more ambitious work, designed as an invitation to share in a poetic (he sometimes weaves quotations into his tapestries) and philosophical (the grand themes are broached from the wartime period onwards) vision whose climax is the “Chant du Monde” (Song of the World) (Jean Lurçat Museum , ancien hôpital Saint Jean, Angers) which remained unfinished at his death. « Univers végétal » presents a paradox : there are more animals than plants pictured within. Thus already in 1944 Lurçat displays his penchant for framing the space within his compositions as with the cabinets and bestiaries : stuffed animals, as if in a cabinet of curiosities, are exhibited on shelves suspended on chains, hanging in starry skies in a poetic vision whose aim is to illustrate the unity of the natural world. This design was woven in various formats, as can be seen in the 1946 exhibition : a vertical rectangle, a square (2m x 2m, and also 3m x 3m) for Jansen, a Paris-based interior decorator, whose trade mark can be seen woven into this piece despite his not having a workshop in Aubusson (his commissions were woven by the Dumontet workshop). Bibliography : Cat. Expo. La tapisserie française, Musée d’art moderne, Paris, 1946, n°278-279 Sieben Jahrhunderte Französische Wandteppiche, Wort und Tat, ill. Tapisseries de Jean Lurçat 1939-1957, Pierre Vorms Editeur, 1957, ill. n°31, 99 (details) Cat. Expo. Jean Lurçat, tapisseries de la fondation Rothmans, Musée de Metz, 1969, cat. n°6 Exhibition Catalogue Lurçat, 10 ans après, Musée d’Art moderne de la ville de Paris, 1976 Exhibition catalogue Les domaines de Jean Lurçat, Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la tapisserie contemporaine, 1986 Symposium Jean Lurçat et la renaissance de la tapisserie in Aubusson, Aubusson, Musée départemental de la tapisserie 1992 Exhibition Catalogue Dialogues avec Lurçat, Musées de Basse-Normandie, 1992 Exhibition catalogue Jean Lurçat, Donation Simone Lurçat, Académie des Beaux-Arts, 2004 Jean Lurçat, le chant du monde Angers 2007 Gérard Denizeau, Jean Lurçat, Liénart, 2013 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Lurçat, Meister der französischen Moderne, Halle, Kunsthalle Exhibition Catalogue Jean Lurçat au seul bruit du soleil, Paris, galerie des Gobelins, 2016 -
Foujita is one of a number of artists whose work was woven at Bièvres at the Moulin de Vauboyen (hence the mark MV woven into the tapestries), which was transformed by Pierre de Tartas into an arts centre in 1959 and devoted to figurative art. Many noteworthy names would pass through including Cocteau, Foujita, Erni, Volti … among others, who would produce much work, often monumental, as well as realisations in the applied arts (notably book illustrations) Foujita realised only a few tapestry cartoons, all of which were produced at Bièvres by Pierre de Tartas. This one (an original watercolour 147 x 157 cm) was sold on 8th December 2015 by Tajan, and another preparatory drawing appeared in the Kimiyo Foujita succession (Cornette de St Cyr, 28th October 2013, n°167c). Likenesses of children become (even more) common in the period post 2nd world war : all with the same physical type a large forehead, widely spaced eyes, thin nose, full lips and regularly represented in slightly archaic roles redolent of Poulbot’s work.
Marchande de lait (Milkmaid)
Tapestry woven in the Moulin de Vauboyen workshop. 1965. -
Mirage
Fumeron designed his first cartoons (he would ultimately make over 500) in the 1940’s, in collaboration with the Pinton workshop, he was then commissioned on numerous occasions by the state before participating in the decoration of the ocean liner “France”. His work was figurative to begin with and influenced by Lurçat, then turned towards abstraction, before coming back to a style characterised by colourful figurative and realistic depictions from the 1980’s onwards. This is a particularly interesting cartoon by Fumeron, one of his best in an abstract vein which puts him on an equal footing with Matégot.Aubusson tapestry woven in the Pinton workshop. With label. Circa 1965. -
Chili
Lurçat’s artistic production was immense : it is however his role as the renovator of the art of tapestry design which ensures his lasting renown. As early as 1917, he started producing works on canvas, then in the 20’s and 30’s, he worked with Marie Cuttoli. His first collaboration with the Gobelins workshop dates back to 1937, at the same time he discovered the tapestry of the Apocalypse which was essential in his decision to devote himself to tapestry design. He first tackled the technical aspects with François Tabard, then on his installation at Aubusson during the war, he established his technique : broad point, a simplified palette, outlined cartoons with colours indicated by pre-ordained numbers. A huge production then follows (over 1000 cartoons) amplified by his desire to include his painter friends, the creation of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-Cartonniers de Tapisserie) and the collaboration with the art gallery La Demeure and Denise Majorel, and then by his role as a tireless advocate for the medium around the world. His tapestries reveal a pictorial world which is specifically decorative, with a very personal symbolic iconography : cosmogony (the sun, the planets, the zodiac, the four elements…) stylised vegetation, fauna (rams, cocks, butterflies, chimera …) standing out against a background without perspective (voluntarily different from painting) and, in his more ambitious work, designed as an invitation to share in a poetic (he sometimes weaves quotations into his tapestries) and philosophical (the grand themes are broached from the wartime period onwards) vision whose climax is the “Chant du Monde” (Song of the World) (Jean Lurçat Museum , ancien hôpital Saint Jean, Angers) which remained unfinished at his death. As is often the case, the title makes a reference to Latin America. As for the circular motif accompanying the owl, it is a classic as in, for example, “Forêt bleue” or “La chouette des figuiers”,... Bibliography : Tapisseries de Jean Lurçat 1939-1957, Pierre Vorms Editeur, 1957 Exhibition Catalogue Lurçat, 10 ans après, Musée d’Art moderne de la ville de Paris, 1976 Exhibition catalogue Les domaines de Jean Lurçat, Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la tapisserie contemporaine, 1986 Symposium Jean Lurçat et la renaissance de la tapisserie in Aubusson, Aubusson, Musée départemental de la tapisserie 1992 Exhibition Catalogue Dialogues avec Lurçat, Musées de Basse-Normandie, 1992 Exhibition catalogue Jean Lurçat, Donation Simone Lurçat, Académie des Beaux-Arts, 2004 Jean Lurçat, le chant du monde Angers 2007 Gérard Denizeau, Jean Lurçat, Liénart, 2013 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Lurçat, Meister der französischen Moderne, Halle, Kunsthalle, 2016 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Lurçat au seul bruit du soleil, Paris, galerie des Gobelins, 2016Aubusson tapestry woven in the Pinton workshop. With signed label. Circa 1955. -
Faiseur d'étoiles (Starmaker)
After the traditional completion of some mural paintings in the 1930’s, he then arrived in Aubusson in 1936, became closely associated with Picart le Doux in 1947 and then joined the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-Cartonniers de Tapisserie). From then on he devoted himself to tapestry with zeal and designed 167 cartoons, at first figurative following on from Picart le Doux and Saint-Saëns, then, influenced by the scientific themes that he dealt with, tending more towards abstraction. In 1981, two years before his death, he donated his studio to the Musée départemental de la tapisserie in Aubusson. Jullien’s interest in science and technology was evident early on in his career, at the end of the 1950’s, and this position singled him out somewhat among the other designers of the post-war period known in France as the “30 glorieuses” (despite a few works by Matégot, Maurice André and particularly Millecamps). Jullien imagined in 1961 an exhibition of his works entitled “Espace Poétique de l’Industrie” (Poetry in Industry) where he exhibited “Diamant noir” (the coal mine), Métropolis (oil refineries), ..., and this piece “Faiseur d’étoiles”, an allegory of autogenous welding. Bibliography : Exhibition Catalogue, Espace poétique de l'industrie, galerie La Demeure, 1961 (ill.) Exhibition catalogue Hommage à Louis-Marie Jullien, Aubusson, Musée départemental de la Tapisserie, 1983Aubusson tapestry woven in the André workshop. With signed label, n°3/3. 1957. -
La Lyre (The lyre)
Aubusson tapestry woven in the Pinton workshop. Circa 1960. Jean Picart le Doux is one of the foremost figures in the renaissance of the art of tapestry. His earliest contributions to the field date back to 1943 when he designed cartoons for the passenger ship “la Marseillaise”. A close associate of Lurçat, whose theories he would adopt (limited palette, numbered cartoons...), he was a founding member of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-cartonniers de Tapisserie), and soon after, a teacher at the Ecole Nationale Supérieure des Arts Décoratifs. The state gave him several commissions most of them at the Aubusson workshop, and some at the Gobelins : the most spectacular of these being for the University of Caen, the Theatre in Le Mans, the passenger ship France or the Prefecture of the Creuse département ... In as much as Picart le Doux’s aesthetic is close to that of Lurçat, so also is his insipiration and his subject matter, although in a register which is more decorative than symbolic, where he brings together heavenly bodies (the sun, the moon, the stars...), the elements, nature (wheat, vines, fish, birds...), man, literary quotation ... The image of the lyre, and also that of the harp, is one of the leitmotivs of the artist. Representative of Apollo, the lyre regularly appears with the sun (cf for example “Soleil-lyre”; Bruzeau n°82), but also as a symbol of the passing of time (similar to the use of the pendulum in the XVIIIth century, interestingly one of the artist’s cartoons is titled “the Pendulum”, auction in Lille 17.06.01 n°464) : “les Phases du temps” (the phases of time, cf Armelle Bouchet Mazas, le paquebot France, Editions Norma, 2006, p.72) which adorned the 1st class smoking room on the France. Strangely enough, our tapestry does not figure in Bruzeau’s book : possibly because it was specially commissioned for a scientific or industrial organisation, if one considers the form which appears with the lyre. Bibliography : Maurice Bruzeau, Jean Picart le Doux, Murs de soleil, Editions Cercle d'art, 1972 Armelle Bouchet Mazas, le paquebot France, Editions Norma, 2006 -
L'étang (the pond)
Aubusson tapestry woven in theTabard workshop. With label. Circa 1950.Lurçat’s artistic production was immense : it is however his role as the renovator of the art of tapestry design which ensures his lasting renown. As early as 1917, he started producing works on canvas, then in the 20’s and 30’s, he worked with Marie Cuttoli. His first collaboration with the Gobelins workshop dates back to 1937, at the same time he discovered the tapestry of the Apocalypse which was essential in his decision to devote himself to tapestry design. He first tackled the technical aspects with François Tabard, then on his installation at Aubusson during the war, he established his technique : broad point, a simplified palette, outlined cartoons with colours indicated by pre-ordained numbers. A huge production then follows (over 1000 cartoons) amplified by his desire to include his painter friends, the creation of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-Cartonniers de Tapisserie) and the collaboration with the art gallery La Demeure and Denise Majorel, and then by his role as a tireless advocate for the medium around the world. His tapestries reveal a pictorial world which is specifically decorative, with a very personal symbolic iconography : cosmogony (the sun, the planets, the zodiac, the four elements…) stylised vegetation, fauna (rams, cocks, butterflies, chimera …) standing out against a background without perspective (voluntarily different from painting) and, in his more ambitious work, designed as an invitation to share in a poetic (he sometimes weaves quotations into his tapestries) and philosophical (the grand themes are broached from the wartime period onwards) vision whose climax is the “Chant du Monde” (Song of the World) (Jean Lurçat Museum , ancien hôpital Saint Jean, Angers) which remained unfinished at his death. Fish in their natural habitat surrounded by foliage in a characteristically profuse style. An owl, also a habitual character, looks on. Bibliography : Tapisseries de Jean Lurçat 1939-1957, Pierre Vorms Editeur, 1957 Exhibition Catalogue Lurçat, 10 ans après, Musée d'Art moderne de la ville de Paris, 1976 Exhibition catalogue Les domaines de Jean Lurçat, Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la tapisserie contemporaine, 1986 Symposium Jean Lurçat et la renaissance de la tapisserie in Aubusson, Aubusson, Musée départemental de la tapisserie 1992 Exhibition Catalogue Dialogues avec Lurçat, Musées de Basse-Normandie, 1992 Exhibition catalogue Jean Lurçat, Donation Simone Lurçat, Académie des Beaux-Arts, 2004 Jean Lurçat, le chant du monde Angers 2007 Gérard Denizeau, Jean Lurçat, Liénart, 2013 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Lurçat au seul bruit du soleil, Paris, galerie des Gobelins, 2016 -
Holger was a student at the Ecole Nationale d’Art Décoratif d’Aubusson and worked with Lurçat before the latter’s death in 1966. He designed numerous dream-like cartoons woven by the Aubusson workshop. Now settled in the United States, he remains a tireless advocate for, and witness to, modern tapestry design, organising exhibitions and lectures on the subject.
Kosmische Vision (Cosmic vision)
Aubusson tapestry woven in the Pintron frères workshop. With certificate of origin. Circa 1970. -
Composition
Aubusson tapestry woven in the Picaud workshop. Circa 1960.Born in 1912, Farvèze is one of the second generation of painter-cartonniers whose heyday dates from the end of the 1950’s, with the likes of Grékoff, Ferréol, Petit, Potin, … Influenced both by his meeting with Gleizes and a trip to Senegal which brought prestigious state commissions, he would be chosen to participate in the second Biennale de Lausanne in 1965. This piece is characterised by a highly stylised and very colourful design ; the absence of the certificate of origin means that we have no indication of the title or subject - although various animal-shaped forms can be distinguished. -
Composition
Fumeron designed his first cartoons (he would ultimately make over 500) in the 1940’s, in collaboration with the Pinton workshop, he was then commissioned on numerous occasions by the state before participating in the decoration of the ocean liner “France”. His work was figurative to begin with and influenced by Lurçat, then turned towards abstraction, before coming back to a style characterised by colourful figurative and realistic depictions from the 1980’s onwards. An abstract cartoon, typical of the artist’s work, in a style which are redolent of Borderie or Wogensky, and which bear witness to the unceasing originality of his creativity.Aubusson tapestry woven in the Pinton workshop. N°1/6. Circa 1960. -
Les Jumelles (the twins)
Tapestry woven in the Moulin de Vauboyen workshop. With signed label, n°3/8. 1966.Carzou is one of a number of artists whose work was woven at Bièvres at the Moulin de Vauboyen (hence the mark MV woven into the tapestries), which was transformed by Pierre de Tartas into an arts centre in 1959 and devoted to figurative art. Many noteworthy names would pass through including Cocteau, Foujita, Erni, Volti ... among others, who would produce much work, often monumental, as well as realisations in the applied arts (notably book illustrations) Carzou was most noted at the start of his career as a decorative painter (notably for the theatre), and his work for tapestry is relatively rare. His style is immediately recognisable in this cartoon, the busy hatching illustrating dream-like subjects, not unlike work produced by Lucien Coutaud. -
Le veilleur (the watchman)
A member of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-Cartonniers de Tapisserie), Wogensky is one of the many artists who would follow in Lurçat’s footsteps immediately after the war. At first influenced by his predecessor, Wogensky’s subsequent work (159 cartoons according to the 1989 exhibition catalogue) would evolve during the 1960’s towards a, not completely self-avowed, lyrical abstraction, from cosmic-astronomical themes expressed in decomposed, moving, birdlike shapes to cartoons both more refined and less dense. Although always claiming to be a painter, the artist’s conception of tapestry is extremely well thought out : “the realisation of a mural cartoon…. requires the consideration of a space which is no longer ours alone, by the nature of its dimensions, its scale, it also imposes a grand gesture which transforms and accentuates our presence.” Symptomatic of the heroic period at the end of the 1940’s, which also saw the blossoming of such talents as Tourlière, Lagrange, Matégot,..., all of whom were still young, inspired by Lurçat, and at the same time trying to assert their independent styles, whilst still remaining figurative, “le veilleur” affirms in a lyrical and brightly coloured style, its proximity to daily life (viz the detail of the striped jacket), and, at the same time, a highly symbolic connotation : a figure on the look-out in uncertain times. Bibliography : J. Cassou, M. Damain, R. Moutard-Uldry, la tapisserie française et les peintres cartonniers, Tel, 1957, ill. p.131 Exhibition catalogue Robert Wogensky, Aubusson, Musée départemental de la tapisserie, 1989, ill. p.15 Exhibition catalogue Robert Wogensky, Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la Tapisserie Contemporaine, 1989 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Lurçat, compagnons de route et passants considérables, Felletin, Eglise, 1992, ill. p.46Aubusson tapestry woven by the Legoueix workshop. With label. 1948. -
Vercors
Aubusson tapestry woven by the Pinton workshop. With signed label, n°2/6. Circa 1965.Maurice André settled in Aubusson for the duration of the second world war. A founding member of the group “Tapisserie de France” and a member of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-Cartonniers de Tapisserie), he developed a personal style, different from that of Lurçat, characterised by rigorous, cubist-influenced flat areas of colour, often using a limited palette ; he received large-scale public commissions for the Council of Europe in Strasbourg (“L’Europe unie dans le Travail et la Paix”) or for the French pavilion at the Brussels Exhibition in 1958 (“La Technique moderne au service de l’Homme”). Gradually (as with Wogensky and Prassinos,...) his style evolved towards more abstraction, firstly lyrical and then more and more geometric, in a way very similar to Matégot. In the mid 1960’s André’s style becomes comparable to that of Matégot, where battage, pick and pick and shading are the norm. Varying shades of green and triangular shapes are the means of evoking the peaks of the Vercors. -
Allégorie des métiers (Allegory of trades)
Aubusson tapestry woven by the Braquenié workshop. 1958.A curious cartoon where, against a vaguely hexagonal (reference to France, often referred to as “l’hexagone”) star-shaped background are pictured the family, traditional trades (fisherman, farmer,...) placed in front of gasometres, cranes and other emblems of modernity : a hymn to reconstruction, a political allegory, a work of propaganda,... ? -
Eaux vives (Wild water)
Aubusson tapestry woven in the Legoueix workshop. Complete with signed label, n°1/6. Circa 1970.Originally a sculptor exploiting very diverse materials (steel, concrete, clay…), Borderie came to tapestry with immense enthusiasm in the 1950’s with the weaving of his first cartoon in 1957. Receiving encouragement from Denise Majorel, he was awarded the Grand Prix National de la Tapisserie in 1962. In 1974 he was appointed as director at the Ecole Nationale des Arts Décoratifs at Aubusson but he resigned from this post shortly thereafter. He designed over 500 painted cartoons, abstracts using simple shapes, shading in a limited palette of colours and weaving with gros points. Despite its warm colours and lyrical shapes (notably the sinuous vertical swirl, ressembling water currents), “Eaux vives” remains a one-off in Borderie’s work : the habitual muted colour scheme is broken here by the striking central red oval. Bibliography : Exhibition catalogue André Borderie « pour l’homme simplement », Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la Tapisserie Contemporaine 1998 J.J. et B. Wattel, André Borderie et la tapisserie d'Aubusson, Editions Louvre Victoire, 2018 -
Cuivres (Copper-coloured)
Lurçat’s artistic production was immense : it is however his role as the renovator of the art of tapestry design which ensures his lasting renown. As early as 1917, he started producing works on canvas, then in the 20’s and 30’s, he worked with Marie Cuttoli. His first collaboration with the Gobelins workshop dates back to 1937, at the same time he discovered the tapestry of the Apocalypse which was essential in his decision to devote himself to tapestry design. He first tackled the technical aspects with François Tabard, then on his installation at Aubusson during the war, he established his technique : broad point, a simplified palette, outlined cartoons with colours indicated by pre-ordained numbers. A huge production then follows (over 1000 cartoons) amplified by his desire to include his painter friends, the creation of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-Cartonniers de Tapisserie) and the collaboration with the art gallery La Demeure and Denise Majorel, and then by his role as a tireless advocate for the medium around the world. His tapestries reveal a pictorial world which is specifically decorative, with a very personal symbolic iconography : cosmogony (the sun, the planets, the zodiac, the four elements…) stylised vegetation, fauna (rams, cocks, butterflies, chimera …) standing out against a background without perspective (voluntarily different from painting) and, in his more ambitious work, designed as an invitation to share in a poetic (he sometimes weaves quotations into his tapestries) and philosophical (the grand themes are broached from the wartime period onwards) vision whose climax is the “Chant du Monde” (Song of the World) (Jean Lurçat Museum , ancien hôpital Saint Jean, Angers) which remained unfinished at his death. Copper-coloured is used to describe certain butterflies whose wings recall this brightly coloured metal. This cartoon is a re-take on “Sphinx and Cockerel” (but without the cockerel) in a highly decorative positive/negative contrast of yellow against a black background. Bibliography : Tapisseries de Jean Lurçat 1939-1957, Pierre Vorms Editeur, 1957 Exhibition Catalogue Lurçat, 10 ans après, Musée d'Art moderne de la ville de Paris, 1976 Exhibition catalogue Les domaines de Jean Lurçat, Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la tapisserie contemporaine, 1986 Symposium Jean Lurçat et la renaissance de la tapisserie in Aubusson, Aubusson, Musée départemental de la tapisserie 1992 Exhibition Catalogue Dialogues avec Lurçat, Musées de Basse-Normandie, 1992 Exhibition catalogue Jean Lurçat, Donation Simone Lurçat, Académie des Beaux-Arts, 2004 Jean Lurçat, le chant du monde Angers 2007 Gérard Denizeau, Jean Lurçat, Liénart, 2013 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Lurçat au seul bruit du soleil, Paris, galerie des Gobelins, 2016Aubusson tapestry woven by the Pinton workshop. With signed label. Circa 1950. -
Composition
Aubusson tapestry woven in the Pinton workshop. N°1/6. Circa 1970.Maurice André settled in Aubusson for the duration of the second world war. A founding member of the group “Tapisserie de France” and a member of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-Cartonniers de Tapisserie), he developed a personal style, different from that of Lurçat, characterised by rigorous, cubist-influenced flat areas of colour, often using a limited palette ; he received large-scale public commissions for the Council of Europe in Strasbourg (“L’Europe unie dans le Travail et la Paix”) or for the French pavilion at the Brussels Exhibition in 1958 (“La Technique moderne au service de l’Homme”). Gradually (as with Wogensky and Prassinos,...) his style evolved towards more abstraction, firstly lyrical and then more and more geometric, in a way very similar to Matégot. Characteristic of André’s final period, the geometric shapes and flat areas of colour are tempered by hatching, stripes and shading. -
Le basset (Basset hound)
Aubusson tapestry woven in the Tabard worshop. Complete with label. Circa 1950. Lurçat’s artistic production was immense : it is however his role as the renovator of the art of tapestry design which ensures his lasting renown. As early as 1917, he started producing works on canvas, then in the 20’s and 30’s, he worked with Marie Cuttoli. His first collaboration with the Gobelins workshop dates back to 1937, at the same time he discovered the tapestry of the Apocalypse which was essential in his decision to devote himself to tapestry design. He first tackled the technical aspects with François Tabard, then on his installation at Aubusson during the war, he established his technique : broad point, a simplified palette, outlined cartoons with colours indicated by pre-ordained numbers. A huge production then follows (over 1000 cartoons) amplified by his desire to include his painter friends, the creation of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-Cartonniers de Tapisserie) and the collaboration with the art gallery La Demeure and Denise Majorel, and then by his role as a tireless advocate for the medium around the world. His tapestries reveal a pictorial world which is specifically decorative, with a very personal symbolic iconography : cosmogony (the sun, the planets, the zodiac, the four elements…) stylised vegetation, fauna (rams, cocks, butterflies, chimera …) standing out against a background without perspective (voluntarily different from painting) and, in his more ambitious work, designed as an invitation to share in a poetic (he sometimes weaves quotations into his tapestries) and philosophical (the grand themes are broached from the wartime period onwards) vision whose climax is the “Chant du Monde” (Song of the World) (Jean Lurçat Museum , ancien hôpital Saint Jean, Angers) which remained unfinished at his death. Something of a dog lover, Lurçat owned Afghan hounds. They can be found occasionally in his cartoons and seemingly Lurçat found it difficult not to be influenced by their aspect : his basset hound (similar in style to another cartoon entitled “le chien vert” the green dog, but without the owl) scarcely merits its name. Bibliography : Tapisseries de Jean Lurçat 1939-1957, Pierre Vorms Editeur, 1957 Exhibition Catalogue Lurçat, 10 ans après, Musée d'Art moderne de la ville de Paris, 1976 Exhibition catalogue Les domaines de Jean Lurçat, Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la tapisserie contemporaine, 1986 Symposium Jean Lurçat et la renaissance de la tapisserie in Aubusson, Aubusson, Musée départemental de la tapisserie 1992 Exhibition Catalogue Dialogues avec Lurçat, Musées de Basse-Normandie, 1992 Exhibition catalogue Jean Lurçat, Donation Simone Lurçat, Académie des Beaux-Arts, 2004 Jean Lurçat, le chant du monde Angers 2007 Gérard Denizeau, Jean Lurçat, Liénart, 2013 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Lurçat au seul bruit du soleil, Paris, galerie des Gobelins, 2016 -
Sphinx gris (grey hawk moth)
Aubusson tapestry woven in the Braquenié workshop. With signed label. Circa 1955. Lurçat’s artistic production was immense : it is however his role as the renovator of the art of tapestry design which ensures his lasting renown. As early as 1917, he started producing works on canvas, then in the 20’s and 30’s, he worked with Marie Cuttoli. His first collaboration with the Gobelins workshop dates back to 1937, at the same time he discovered the tapestry of the Apocalypse which was essential in his decision to devote himself to tapestry design. He first tackled the technical aspects with François Tabard, then on his installation at Aubusson during the war, he established his technique : broad point, a simplified palette, outlined cartoons with colours indicated by pre-ordained numbers. A huge production then follows (over 1000 cartoons) amplified by his desire to include his painter friends, the creation of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-Cartonniers de Tapisserie) and the collaboration with the art gallery La Demeure and Denise Majorel, and then by his role as a tireless advocate for the medium around the world. His tapestries reveal a pictorial world which is specifically decorative, with a very personal symbolic iconography : cosmogony (the sun, the planets, the zodiac, the four elements…) stylised vegetation, fauna (rams, cocks, butterflies, chimera …) standing out against a background without perspective (voluntarily different from painting) and, in his more ambitious work, designed as an invitation to share in a poetic (he sometimes weaves quotations into his tapestries) and philosophical (the grand themes are broached from the wartime period onwards) vision whose climax is the “Chant du Monde” (Song of the World) (Jean Lurçat Museum , ancien hôpital Saint Jean, Angers) which remained unfinished at his death. The grey hawk moth (or occasionally yellow, in another cartoon), moths and butterflies are a leitmotiv in Lurçat’s work. Here the colours are less contrasted than is his wont, in a highly nuanced composition. Bibliography : Tapisseries de Jean Lurçat 1939-1957, Pierre Vorms Editeur, 1957 Exhibition Catalogue Lurçat, 10 ans après, Musée d'Art moderne de la ville de Paris, 1976 Exhibition catalogue Les domaines de Jean Lurçat, Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la tapisserie contemporaine, 1986 Symposium Jean Lurçat et la renaissance de la tapisserie in Aubusson, Aubusson, Musée départemental de la tapisserie 1992 Exhibition Catalogue Dialogues avec Lurçat, Musées de Basse-Normandie, 1992 Exhibition catalogue Jean Lurçat, Donation Simone Lurçat, Académie des Beaux-Arts, 2004 Jean Lurçat, le chant du monde Angers 2007 Gérard Denizeau, Jean Lurçat, Liénart, 2013 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Lurçat au seul bruit du soleil, Paris, galerie des Gobelins, 2016 -
Ô soleil (O Sun)
Aubusson tapestry woven by the Hamot workshop. With signed label, n°2/8. 1968. Jean Picart le Doux is one of the foremost figures in the renaissance of the art of tapestry. His earliest contributions to the field date back to 1943 when he designed cartoons for the passenger ship “la Marseillaise”. A close associate of Lurçat, whose theories he would adopt (limited palette, numbered cartoons...), he was a founding member of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-cartonniers de Tapisserie), and soon after, a teacher at the Ecole Nationale Supérieure des Arts Décoratifs. The state gave him several commissions most of them at the Aubusson workshop, and some at the Gobelins : the most spectacular of these being for the University of Caen, the Theatre in Le Mans, the passenger ship France or the Prefecture of the Creuse département ... In as much as Picart le Doux’s aesthetic is close to that of Lurçat, so also is his inspiration and his subject matter, although in a register which is more decorative than symbolic, where he brings together heavenly bodies (the sun, the moon, the stars...), the elements, nature (wheat, vines, fish, birds...), man, literary quotation ... « The inclusion of text constitutes a closer means of communication with the poet” says Picart le Doux (a process used also by Lurçat) who will quote Apollinaire as here (“la jolie rousse”) but also Whitman, Eluard, Saint John Perse,... Illustrated by an ardent heart and, in a literal reflection of the text, by the sun, he associates the zodiac, one of his recurrent motifs, with the love poem. Bibliography : Maurice Bruzeau, Jean Picart le Doux, Murs de soleil, Editions Cercle d’art, 1972, ill. n°161 Exhibition Catalogue, Jean Picart le Doux, tapisseries, Musée de Saint-Denis, 1976 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Picart le Doux, Musée de la Poste, 1980 -
Musique et coquillage (music and shell)
Aubusson tapestry woven by the Tabard workshop. Complete with label. Circa 1950. Lurçat’s artistic production was immense : it is however his role as the renovator of the art of tapestry design which ensures his lasting renown. As early as 1917, he started producing works on canvas, then in the 20’s and 30’s, he worked with Marie Cuttoli. His first collaboration with the Gobelins workshop dates back to 1937, at the same time he discovered the tapestry of the Apocalypse which was essential in his decision to devote himself to tapestry design. He first tackled the technical aspects with François Tabard, then on his installation at Aubusson during the war, he established his technique : broad point, a simplified palette, outlined cartoons with colours indicated by pre-ordained numbers. A huge production then follows (over 1000 cartoons) amplified by his desire to include his painter friends, the creation of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-Cartonniers de Tapisserie) and the collaboration with the art gallery La Demeure and Denise Majorel, and then by his role as a tireless advocate for the medium around the world. His tapestries reveal a pictorial world which is specifically decorative, with a very personal symbolic iconography : cosmogony (the sun, the planets, the zodiac, the four elements…) stylised vegetation, fauna (rams, cocks, butterflies, chimera …) standing out against a background without perspective (voluntarily different from painting) and, in his more ambitious work, designed as an invitation to share in a poetic (he sometimes weaves quotations into his tapestries) and philosophical (the grand themes are broached from the wartime period onwards) vision whose climax is the “Chant du Monde” (Song of the World) (Jean Lurçat Museum , ancien hôpital Saint Jean, Angers) which remained unfinished at his death. This piece (of which a copy is exhibited at the Cité de la Tapisserie in Aubusson) is a typical example of the laden table, recurrent in Lurçat’s work. The juxtaposition of a musical instrument and shellfish is a direct reference to the work of Picart le Doux. Bibliography : Tapisseries de Jean Lurçat 1939-1957, Pierre Vorms Editeur, 1957 Exhibition Catalogue Lurçat, 10 ans après, Musée d'Art moderne de la ville de Paris, 1976 Exhibition catalogue Les domaines de Jean Lurçat, Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la tapisserie contemporaine, 1986 Symposium Jean Lurçat et la renaissance de la tapisserie in Aubusson, Aubusson, Musée départemental de la tapisserie 1992 Exhibition Catalogue Dialogues avec Lurçat, Musées de Basse-Normandie, 1992 Exhibition catalogue Jean Lurçat, Donation Simone Lurçat, Académie des Beaux-Arts, 2004 Jean Lurçat, le chant du monde Angers 2007 R. Guinot, la tapisserie d’Aubusson et de Felletin, Lucien Souny, 2009, ill. p.96 Gérard Denizeau, Jean Lurçat, Liénart, 2013 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Lurçat au seul bruit du soleil, Paris, galerie des Gobelins, 2016 -
Le réveille-matin (the alarm clock)
Tapestry woven in the Baudonnet workshop. Complete with signed label. 1959. Lurçat approached Saint-Saëns, originally a painter of murals, in 1940. And during the war the latter produced the first of his allegorical masterpieces, tapestries reflecting indignation, combat, resistance : “les Vierges folles (the foolish virgins), “Thésée et le Minotaure” (Theseus and the Minotaur). At the end of the war, as a natural development he joined up with Lurçat, whose convictions he shared (concerning a simplified palette, outlined cartoons with colours indicated by pre-ordained numbers, and the specific nature of tapestry design...) at the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-cartonniers de Tapisserie). His universe, where the human figure, stretched, elongated, ooccupies an important place (particularly when compared to his companions Lurçat or Picart le Doux), pivots around traditional themes : woman, the Commedia dell’arte, Greek mythology... refined by the brilliance of the colours and the simplification of the layout. His work would evolve later, in the 1960’s, towards cartoons of a more lyrical design, almost abstract where elemental and cosmic forces would dominate. “Saint-Saens who produced a series of birds in 1949 only rarely represented the cock, a recurrent subject for Lurçat. In this piece the cock has no symbolic value but merely announces with gales of crowing and colour the arrival of the new day.” (Exhibition Catalogue Sain-Saëns, œuvre tissé, Aubusson, Musée départemental de la Tapisserie, 1987 p.48) Bibliography : Exhibition catalogue Saint-Saëns, galerie La Demeure, 1970 Exhibition catalogue Saint-Saëns, the tapestries, Aubusson, Musée départemental de la Tapisserie, 1987, ill. p.49 Exhibition catalogue Marc Saint-Saëns, tapestries, 1935-1979, Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la Tapisserie Contemporaine 1997-1998 -
La harpe des forêts (harp of the forests)
Tapestry woven in the Berthaut workshop. Complete with certificate of origin. 1953. Jean Picart le Doux is one of the foremost figures in the renaissance of the art of tapestry. His earliest contributions to the field date back to 1943 when he designed cartoons for the passenger ship “la Marseillaise”. A close associate of Lurçat, whose theories he would adopt (limited palette, numbered cartoons...), he was a founding member of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-cartonniers de Tapisserie), and soon after, a teacher at the Ecole Nationale Supérieure des Arts Décoratifs. The state gave him several commissions most of them at the Aubusson workshop, and some at the Gobelins : the most spectacular of these being for the University of Caen, the Theatre in Le Mans, the passenger ship France or the Prefecture of the Creuse département ... In as much as Picart le Doux’s aesthetic is close to that of Lurçat, so also is his inspiration and his subject matter, although in a register which is more decorative than symbolic, where he brings together heavenly bodies (the sun, the moon, the stars...), the elements, nature (wheat, vines, fish, birds...), man, literary quotation ... The tree/ harp is recurrent with Picart le Doux (occasionally one can find also a tree/ lyre, Bruzeau n° 44) reflecting his sensitivity to the inter-penetration of Nature and Music, and also to the decorative interest of multicoloured string-stripes, here set against a green, humus-scented background. Bibliography : Maurice Bruzeau, Jean Picart le Doux, Murs de soleil, Editions Cercle d’art, 1972, ill. n°45 Exhibition Catalogue, Jean Picart le Doux, tapisseries, Musée de Saint-Denis, 1976 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Picart le Doux, Musée de la Poste, 1980 -
le tiercelet (the sparrow hawk)
Aubusson tapestry woven by the Legoueix workshop. Complete with certificate of origin signed by the artist's beneficiary, n° E.A.1 1942. Elie Maingonnat governed the Ecole Nationale des Arts Décoratifs d’Aubusson from 1930 until 1958 where he took over from Marium Martin (who already recommended the use of a limited number of colours and the use of hachures, a similar technique to hatching) of whom he was a pupil. As well as assuming the responsibilities of his position, Maingonnat devoted himself to designing cartoons : motifs of dense vegetation animated by the presence of a few animals, both of which were inspired by the flora and fauna of the Limousin area of France revitalising the traditional theme of greenery used in the XVIIth and XVIIIth centuries. This cartoon is typical of Maingonnat’s work : local flora and fauna (here a diminutive sparrow hawk among gentians on the bank of a mountain stream) are illustrated in a limited grey-green spectrum which is reflected and emphasised by the browns of the stones in the river. Bibliographie : Exhibition Catalogue Elie Maingonnat, Aubusson, Musée départemental de la tapisserie, 1986-1987, Ill. -
Vega
Aubusson tapestry woven in the Legoueix workshop. Certificate of origin signed by the artist n° 2 of 4. 1967. A member of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-Cartonniers de Tapisserie), Wogensky is one of the many artists who would follow in Lurçat’s footsteps immediately after the war. At first influenced by his predecessor, Wogensky’s subsequent work (159 cartoons according to the 1989 exhibition catalogue) would evolve during the 1960’s towards a, not completely self-avowed, lyrical abstraction, from cosmic-astronomical themes expressed in decomposed, moving, birdlike shapes to cartoons both more refined and less dense. Although always claiming to be a painter, the artist’s conception of tapestry is extremely well thought out : “the realisation of a mural cartoon.... requires the consideration of a space which is no longer ours alone, by the nature of its dimensions, its scale, it also imposes a grand gesture which transforms and accentuates our presence.” « Vega » is a work inspired by Wogensky’s « cosmic » vein (it’s title alone bears witness to the fact) which lasted through the 1960’s and of which “Cosmos” (1968 Strasbourg University) and “Galaxy” (1970, Sénat Palais du Luxembourg) would be the high points. Shading (omnipresent) and blocks of colour co-exist in a subtle harmony, evoking a curious, unknown world with elements of the infinitely small as seen through a microscope and the infinitely large. Bibliography : Exhibition catalogue Robert Wogensky, Aubusson, Musée départemental de la tapisserie, 1989 Exhibition catalogue Robert Wogensky, Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la Tapisserie Contemporaine, 1989 -
Les oiseaux s'envolent (birds fly)
Aubusson tapestry woven in the Berthaut workshop. Complete with certificate of origin signed by the artist. 1949. Jean Picart le Doux is one of the foremost figures in the renaissance of the art of tapestry. His earliest contributions to the field date back to 1943 when he designed cartoons for the passenger ship “la Marseillaise”. A close associate of Lurçat, whose theories he would adopt (limited palette, numbered cartoons…), he was a founding member of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-cartonniers de Tapisserie), and soon after, a teacher at the Ecole Nationale Supérieure des Arts Décoratifs. The state gave him several commissions most of them at the Aubusson workshop, and some at the Gobelins : the most spectacular of these being for the University of Caen, the Theatre in Le Mans, the passenger ship France or the Prefecture of the Creuse département … In as much as Picart le Doux’s aesthetic is close to that of Lurçat, so also is his inspiration and his subject matter, although in a register which is more decorative than symbolic, where he brings together heavenly bodies (the sun, the moon, the stars…), the elements, nature (wheat, vines, fish, birds…), man, literary quotation … “Les oiseaux s’envolent” (the flight of the birds) was intended as a symbolic representation of the Liberation of France, a theme which recurrs in the “la cage ouverte’ (the open cage) in 1953. Bibliography : Maurice Bruzeau, Jean Picart le Doux, Murs de soleil, Editions Cercle d’art, 1972, n°13 Exhibition Catalogue, Jean Picart le Doux, tapisseries, Musée de Saint-Denis, 1976 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Picart le Doux, Musée de la Poste, 1980 -
Dragon dans la nuit (a dragon in the night)
Aubusson tapestry woven in the Pinton workshop. Complete with certificate of origin signed by the artist, n°1/6. Circa 1965. Matégot, originally a decorator, then creator of artefacts and furniture (an activity he abandoned in 1959) met François Tabard in 1945 and gave him his first cartoons, first of all figurative then rapidly of abstract design in the 1950’s. He became a member of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres Cartonniers de Tapisserie) in 1949, participated in many international exhibitions (Matégot, like Lurçat before him, was an untiring advocate of the art of tapestry) fulfilled numerous public commissions, sometimes of monumental proportions (“Rouen” 85m2 for the Préfecture of the Seine Maritime département, and also tapestries for Orly Airport, for the Maison de la Radio, for the IMF...) and designed no fewer than 629 cartoons up until the 1970’s. In 1990 the Matégot foundation for contemporary tapestry was inaugurated in Bethesda, U.S.A. Matégot is an artist, like Wogensky, Tourlière or Prassinos, who turns wool textiles resolutely towards the abstract: at first lyrical, geometric in the 70’s, exploiting various technical aspects of the loom : colour graduations, shading, irregularities... The cartoon is characterised by the habitual contrast of light and shadow, typical of those of this period ; the title, however, conveys a more figurative context, evoking a fantastic beast breathing flames (and indeed illustrated in fire) to disperse the darkness. Bibliography : Exhibition catalogue, Matégot, Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la Tapisserie Contemporaine, 1990-1991 Patrick Favardin, Mathieu Matégot, Editions Norma, 2014 -
Le luth et les colombes (the lute and the doves)
Aubusson tapestry woven in the Berthaut workshop. Complete with certificate of origin signed by the artist, n°6/8. Circa 1955. Jean Picart le Doux is one of the foremost figures in the renaissance of the art of tapestry. His earliest contributions to the field date back to 1943 when he designed cartoons for the passenger ship “la Marseillaise”. A close associate of Lurçat, whose theories he would adopt (limited palette, numbered cartoons...), he was a founding member of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-cartonniers de Tapisserie), and soon after, a teacher at the Ecole Nationale Supérieure des Arts Décoratifs. The state gave him several commissions most of them at the Aubusson workshop, and some at the Gobelins : the most spectacular of these being for the University of Caen, the Theatre in Le Mans, the passenger ship France or the Prefecture of the Creuse département ... In as much as Picart le Doux’s aesthetic is close to that of Lurçat, so also is his inspiration and his subject matter, although in a register which is more decorative than symbolic, where he brings together heavenly bodies (the sun, the moon, the stars...), the elements, nature (wheat, vines, fish, birds...), man, literary quotation ... The lute and the doves is a reworking of a larger and more densely decorated cartoon dating from 1949 and titled “les oiseaux s’envolent” (the flight of the birds) which was intended as a symbolic representation of the Liberation of France, a theme which recurrs in the “la cage ouverte’ (the open cage) in 1953. Bibliography : Marthe Belle-Jouffray, Jean Picart le Doux, Publications filmées d’art et d’histoire, 1966, ill. n°3 Maurice Bruzeau, Jean Picart le Doux, Murs de soleil, Editions Cercle d’art, 1972 Exhibition Catalogue, Jean Picart le Doux, tapisseries, Musée de Saint-Denis, 1976 Exhibition Catalogue Jean Picart le Doux, Musée de la Poste, 1980 -
Fleur de roc (rock flower)
Aubusson tapestry woven in the Legoueix workshop. n°2/4. Circa 1970. Originally a sculptor exploiting very diverse materials (steel, concrete, clay…), Borderie came to tapestry with immense enthusiasm in the 1950’s with the weaving of his first cartoon in 1957. Receiving encouragement from Denise Majorel, he was awarded the Grand Prix National de la Tapisserie in 1962. In 1974 he was appointed as director at the Ecole Nationale des Arts Décoratifs at Aubusson but he resigned from this post shortly thereafter. He designed over 500 painted cartoons, abstracts using simple shapes, shading in a limited palette of colours and weaving with gros points. A dynamic abstraction with a limited colour scheme running from orange to brown, abstract motifs which play on the plastic effect of light passing through the colours : a classic cartoon from André Borderie. Bibliography : Exhibition catalogue André Borderie « pour l’homme simplement », Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la Tapisserie Contemporaine 1998. J.J. et B. Wattel, André Borderie et la tapisserie d'Aubusson, Editions Louvre Victoire, 2018, ill. p.22 -
Galathée
Aubusson tapestry woven by the Picaud workshop. Complete with certificate of origin signed by the artist, n° 1 of 4. 1970. Loewer designed his first cartoon in 1953 ; his early works are first figurative before turning to abstraction (like Matégot) which is exclusively geometric in Loewer’s case. He designed over 180 cartoons, most of which were woven by his friend, Raymond Picaud. Only one example of this tapestry was woven according to the catalogue raisonné, « Galathée » is representative of the artist’s style around 1970 where the recurrent design motif is the square used in superpositions. Bibliography : Claude Loewer, l’évasion calculée : travaux de 1939 à 1993, catalogue raisonné des tapisseries de 1953 à 1974, Sylvio Acatos, Charlotte Hug, Walter Tschopp and Marc-Olivier Wahler, Artcatos, 1994, n°120 -
Les comédiens (The actors)
Aubusson tapestry woven in the Legoueix workshop. N°4/6. 1959. Lurçat approached Saint-Saëns, originally a painter of murals, in 1940. And during the war the latter produced the first of his allegorical masterpieces, tapestries reflecting indignation, combat, resistance : “les Vierges folles (the foolish virgins), “Thésée et le Minotaure” (Theseus and the Minotaur). At the end of the war, as a natural development he joined up with Lurçat, whose convictions he shared (concerning a simplified palette, outlined cartoons with colours indicated by pre-ordained numbers, and the specific nature of tapestry design...) at the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-cartonniers de Tapisserie). His universe, where the human figure, stretched, elongated, ooccupies an important place (particularly when compared to his companions Lurçat or Picart le Doux), pivots around traditional themes : woman, the Commedia dell’arte, Greek mythology... refined by the brilliance of the colours and the simplification of the layout. His work would evolve later, in the 1960’s, towards cartoons of a more lyrical design, almost abstract where elemental and cosmic forces would dominate. Themes of music, drama and more specifically the Commedia dell’Arte (« la Comédie Italienne », a cartoon dating from 1947) are omnipresent in Saint-Saëns’s production : here he presents the figures of Lelio and Isabelle, strikingly drawn, slightly humorous figures, presented here in their traditional costumes. Bibliography : Exhibition catalogue Saint-Saëns, galerie La Demeure, 1970 Exhibition catalogue Saint-Saëns, the tapestries, Aubusson, Musée départemental de la Tapisserie, 1987 Exhibition catalogue Marc Saint-Saëns, tapestries, 1935-1979, Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la Tapisserie Contemporaine 1997-1998 -
Normands sur la Seine (Norsemen on the Seine)
Tapestry woven at Aubusson by the Pinton workshop. Signed certificate of origin n° 1. 1961. Lars Gynning is one of the numerous artists of various origins whose work would be woven in Aubusson during the years from the 50’s to the 70’s, at a period when tapestry imposed itself as an artistic medium. From a thematic point of view, this cartoon can be seen as a referrence, across the centuries, to Franco-Scandinavian relations seen through the prism of Viking incursions up the Seine estuary : an inevitable throw-back to the Bayeux tapestry. However, rather than a historic or diplomatic statement by Gynning, the cartoon in fact illustrates a saga by Evart Taube, the 20th century Swedish national poet (an extract from the text is woven at the bottom of the tapestry) ; added to the subject itself, the textile rendition of an epic saga is a gesture in the direction of the great mediaeval tapestry tradition, which was an inevitable model for many painter-cartoonists of the period. The aesthetic, which is resolutely contemporary and influenced by cubism, revitalises an ancient subject. -
La harpe des mers (Harp of the ocean)
Tapestry woven in the Berthaut workshop. Complete with certificate of origin signed by the artist. 1954. Jean Picart le Doux is one of the foremost figures in the renaissance of the art of tapestry. His earliest contributions to the field date back to 1943 when he designed cartoons for the passenger ship “la Marseillaise”. A close associate of Lurçat, whose theories he would adopt (limited palette, numbered cartoons...), he was a founding member of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-cartonniers de Tapisserie), and soon after, a teacher at the Ecole Nationale Supérieure des Arts Décoratifs. The state gave him several commissions most of them at the Aubusson workshop, and some at the Gobelins : the most spectacular of these being for the University of Caen, the Theatre in Le Mans, the passenger ship France or the Prefecture of the Creuse département ... In as much as Picart le Doux’s aesthetic is close to that of Lurçat, so also is his insipiration and his subject matter, although in a register which is more decorative than symbolic, where he brings together heavenly bodies (the sun, the moon, the stars...), the elements, nature (wheat, vines, fish, birds...), man, literary quotation ... « La harpe des mers » (Harp of the ocean) (Bruzeau n° 60) just as its companion piece « La harpe des forêts” (Harp of the forest), identical in size, is one of a set of cartoons by Picart le Doux dealing with the theme of the lyre and the harp : the geometrical rigour and graphic power of the parallel strings were a particular inspiration to the artist. Here, music and nature are closely associated (cf “l’arbre-lyre” the tree lyre from 1953) and Orphée Orpheus (a cartoon from 1952) is the single figure which encapsulates this assimilation. Bibliography : Maurice Bruzeau, Jean Picart le Doux, Murs de soleil, Editions Cercle d’art, 1972 Exhibition catalogue Jean Picart le Doux, Musée de la Poste, 1980 -
La flamme (the flame)
Portalegre tapestry woven by the Fino workshop. Complete with certificate of origin signed by the artist, n°2/6. Circa 1965. Matégot, originally a decorator, then creator of artefacts and furniture (an activity he abandoned in 1959) met François Tabard in 1945 and gave him his first cartoons, first of all figurative then rapidly of abstract design in the 1950’s. He became a member of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres Cartonniers de Tapisserie) in 1949, participated in many international exhibitions (Matégot, like Lurçat before him, was an untiring advocate of the art of tapestry) fulfilled numerous public commissions, sometimes of monumental proportions (“Rouen” 85m2 for the Préfecture of the Seine Maritime département, and also tapestries for Orly Airport, for the Maison de la Radio, for the IMF...) and designed no fewer than 629 cartoons up until the 1970’s. In 1990 the Matégot foundation for contemporary tapestry was inaugurated in Bethesda, U.S.A. Matégot is an artist, like Wogensky, Tourlière or Prassinos, who turns wool textiles resolutely towards the abstract: at first lyrical, geometric in the 70’s, exploiting various technical aspects of the loom : colour graduations, shading, irregularities... An abstract cartoon characteristic of the artist’s production in the mid-1960’s : the evocation of the flame, stylised and in an agressive violet hue, refers directly to Matégot’s interest in industry and all things technical but also to the interplay of woven transparencies of which he made himself a master. Bibliography : Exhibition catalogue, Matégot, Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la Tapisserie Contemporaine, 1990-1991 -
Combat devant Florence (Combat before Florence)
Aubusson tapestry woven by the Goubely-Gatien workshop. With partially erased certificate of origin. 1966. An enthusiastic mural artist as early as 1937 (he participated in the Exposition Internationale), Lagrange designed his first cartoons in 1945, and became one of the founding members of the A.P.C.T. His early cartoons were expressionist (like Matégot and Tourlière), then his work evolved towards a stylisation (dating from his collaboration with Pierre Baudouin) which would bring him in the 1970’s to a highly refined style using very pure colours. As well as his important rôle in the tapestry renaissance movement of the period (and the state commissions that went with it), Lagrange would become a teacher at the Ecole Nationale des Beaux-Arts, a regular collaborator with Jacques Tati, a designer of monumental elements incorporated in various architectural projects and a recognised painter close to Estève and Lapicque. In the 1960’s, the artist made various large-scale works based on the mediaeval theme of battles and tournaments, in a geometrical and stylised vision, of which the most noted example is the “Hommage to Paulo Uccello” (280 x 680 cm, of which a copy is kept at the Faculty of Science in Besançon). Here, in a style that is still figurative, Lagrange illustrates a battle scene against the city of Florence in the background with its highly recognisable monuments (the Duomo, the bell tower of the Palazzo Vecchio..) The frieze-like scene, inspired by Uccello’s paintings, shows spears, horses and knights intermingled. Of note : the marled beige and brown background against which these elements stand out is specific to Lagrange and was only rarely used by his co-designers. Bibliography : Cat. Exh. Lagrange tapisseries, Galerie La demeure, 1968, n°4 (reproduit) Cat. Exh. Tapisseries d'Aubusson, Galerie d'Art Municipale, Luxembourg, n°4 in the catalogue (not illustrated) Robert Guinot, Jacques Lagrange, les couleurs de la vie, Lucien Souny editeur, 2005, n°40, illustrated (dimensions given 226 x 268 cm) J.J. et B. Wattel, Jacques Lagrange et ses toiles : peintures, tapisseries, cinéma, Editions Louvre Victoire, 2020 -
Nymphes et chasseurs (Nymphs and hunters)
Aubusson tapestry woven in the Pinton workshop for the Compagnie des Arts Français. 1941. The place occupied by André Planson in the history of tapestry-making is a direct result of the role that was alotted to him by Jacques Adnet in the synthesis of art and design advocated by the Compagnie des Arts Français of which he was the director. As early as 1941, Adnet approached several painters (Brianchon, Vera,... and Planson) to design tapestry cartoons in the context of furniture and interior design : “our intention was to demonstrate that contemporary tapestries have much to contribute to the integrated design of a room” (L. Chéronnet, Jacques Adnet, Art et Industrie 1948). The Compagnie des Arts Français organised throughout the 1940’s tapestry exhibitions on its premises. These ambitious decorative aspirations, which were important in encouraging the renewal of the art of the tapestry, remain however somewhat irrelevant to the preoccupations of Lurçat and his followers. The gracious and joyful attributes (compare with the contemporary creations of Lurçat or Gromaire) of the Compagnie are plainly evident in this cartoon dating from 1941 which brings right up to date the traditional tapestry themes of the hunting scene and bucolic pleasures in a voluntarily innovative style which is highly decorative. Although certain technical innovations typical of the Lurçat doctrine are already assimilated (limited palette, irregular stitch size) it is to be noted that this decorative intention is still influenced by techniques associated with painting (the use of perspective, and shading for flesh colours...) -
Automne-Hiver (Autumn-Winter)
Aubusson tapestry woven by the Pinton workshop. Complete with certificate of origin n° 6 of 6. Circa 1975. Jean Picart le Doux is one of the foremost figures in the renaissance of the art of tapestry. His earliest contributions to the field date back to 1943 when he designed cartoons for the passenger ship “la Marseillaise”. A close associate of Lurçat, whose theories he would adopt (limited palette, numbered cartoons...), he was a founding member of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-cartonniers de Tapisserie), and soon after, a teacher at the Ecole Nationale Supérieure des Arts Décoratifs. The state gave him several commissions most of them at the Aubusson workshop, and some at the Gobelins : the most spectacular of these being for the University of Caen, the Theatre in Le Mans, the passenger ship France or the Prefecture of the Creuse département ... In as much as Picart le Doux’s aesthetic is close to that of Lurçat, so also is his insipiration and his subject matter, although in a register which is more decorative than symbolic, where he brings together heavenly bodies (the sun, the moon, the stars...), the elements, nature (wheat, vines, fish, birds...), man, literary quotation ... The theme of the seasons is a classic in the history of tapestry which was enthusiastically ressuscitated by the 20th century cartoon artists, of whom Lurçat was foremost (cf his Seasons wall hanging commissioned by the state in 1939). For Picart le Doux the inspiration is two-fold : Nature obviously but also Music ; “l’Hiver” (Winter) an allegorical treatment of the theme and one of the best-known works of this artist dates from 1950, but it is the “Hommage à Vivaldi” (Homage to Vivaldi) from 1963, with its 4 seasons represented in symbolic fashion by coloured suns, featuring symbols from the zodiac and fronds of vegetation that is the source of this cartoon where the motifs are reworked in a horizontal format. Bibliography : Maurice Bruzeau, Jean Picart le Doux, Murs de soleil, Editions Cercle d'art, 1972 -
Rambouillet
Aubusson tapestry woven in the Pinton workshop. Complete with certificate of origin signed by the artist, n° 1 of 6. Circa 1970. Perrot began his career as a cartoon designer at the end of the war, making almost 500 cartoons including numerous commissions from the state, most of which were woven at Aubusson. His style which is particularly rich and decorative is eminently recognisable : a crowd of butterflies or birds, most often, stands out against a background of vegetation, reminiscent of the millefleurs tapestries (which would also inspire Dom Robert). René Perrot is essentially an animal artist who habitually uses stylisation. His decorative style is counterweighted here by the extreme realism with which the stag is represented, rare in post-war tapestry. The title of the cartoon is a throw-back to the grand French hunting tradition which he abundantly illustrated, for example in “Sologne”, which was donated to the Musée de la Chasse in Gien by the Mobilier National. -
Concert champêtre (Outdoor concert)
Aubusson tapestry woven in the Picaud workshop for the Verriere Gallery of Lyons. Complete with its certificate signed by the artist ; n° 1 of 4. Circa 1970 « It is thus easy to understand that, having based my painting on my love of tapestry, it was relatively easy for me, and particularly tempting, to produce tapestries which were faithful to my painting” writes the artist in the exhibition catalogue for the 1970 show at the Galerie Verrière. It is not until 1961 that he started making designs (over 50) both for woven tapestries (at Aubusson, but also for the Mobilier National with, on occasion, the collaboration of Pierre Baudoin), but also those employing needlepoint. The artist’s very audacious palette is immediately recognisable in these cartons, with their use of primary colours or, as here, revolving around a very vivid pink with a rather dislocated storyline between the concert in the foreground and the hunting scene in the distance. Bibliography : Exhibition catalogue, Expo Lapicque, Lyons, Galerie Verrière 1970 -
Remous (swell)
Aubusson tapestry woven in the Tabard workshop. Circa 1960. Matégot, originally a decorator, then creator of artefacts and furniture (an activity he abandoned in 1959) met François Tabard in 1945 and gave him his first cartoons, first of all figurative then rapidly of abstract design in the 1950’s. He became a member of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres Cartonniers de Tapisserie) in 1949, participated in many international exhibitions (Matégot, like Lurçat before him, was an untiring advocate of the art of tapestry) fulfilled numerous public commissions, sometimes of monumental proportions (“Rouen” 85m2 for the Préfecture of the Seine Maritime département, and also tapestries for Orly Airport, for the Maison de la Radio, for the IMF...) and designed no fewer than 629 cartoons up until the 1970’s. In 1990 the Matégot foundation for contemporary tapestry was inaugurated in Bethesda, U.S.A. Matégot is an artist, like Wogensky, Tourlière or Prassinos, who turns wool textiles resolutely towards the abstract: at first lyrical, geometric in the 70’s, exploiting various technical aspects of the loom : colour graduations, shading, irregularities... Remous can be seen as representative of Matégot’s production around 1960 : lyrical, playing with transparency, using all the technical expertise of the weavers (colour shading and grading…) Its evocative title is a reminder of the artist’s interest for aquatic subjects (cf “Régates”) treated in an abstract-metaphorical way. Bibliography : Exhibition Cat. Les tapisseries de Mathieu Matégot, galerie La Demeure, 1962 (ill.) Exhibition catalogue, Matégot, Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la Tapisserie Contemporaine, 1990-1991 -
Papillons (Butterflies)
Aubusson tapestry woven by the Pinton frères workshop. With original certificate Lurçat’s artistic production was immense : it is however his role as the renovator of the art of tapestry design which ensured his lasting renown. As early as 1917, he started producing works on canvas, then in the 20’s and 30’s, he worked with Marie Cuttoli. His first collaboration with the Gobelins workshop dates back to 1937, at the same time he discovered the tapestry of the Apocalypse which was essential in his decision to devote himself to tapestry design. He first tackled the technical aspects with François Tabard, then on his installation at Aubusson during the war, he established his technique : broad point, a simplified palette, drawn and numbered cartons. A huge production then follows (over 1000 cartons) amplified by his desire to include his painter friends, the creation of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-Cartonniers de Tapiisserie) and the collaboration with the art gallery La Demeure and Denise Majorel, and then by his assumed role promotion the medium around the world (le Monde ?) His tapestries reveal a pictorial world which is specifically decorative, with a very personal symbolic iconography, cosmogonical (the sun, the planets, the zodiac, the four elements…) stylised vegetation, fauna (rams, cocks, butterflies, chimera …) standing out against a background without perspective (voluntarily different from painting) and, in his more ambitious work, designed as an invitation to share in a poetic (he sometimes weaves quotations into his tapestries) and philosophical (the grand themes are broached from the wartime period onwards) vision whose climax is the “Chant du Monde” (Song of the World) (Jean Lurçat Museum , ancien hôpital Saint Jean, Angers) which remained unfinished at his death. His journey to Brazil in 1954 was a decisive source of inspiration for Lurçat : the flora and fauna (particularly the butterflies, a recurrent theme) of the Amazon appear repeatedly : “What interests me with the butterfly, ... is the extraordinary inventiveness of the interlacing forms, the sparkling colours, the total freedom of their coloration...” (Claude Faux, Lurçat à haute voix, 1962, p. 151). Butterflies on a yellow background are a motif which recurs in several cartons : “Paon de nuit”, “Copacabana”, “Papillons Marcenac”... Bibliography : Exhibition Cat. Jean Lurçat, Tapisseries nouvelles, Maison de la pensée Française, 1956 Exhibition Cat.. Les domaines de Jean Lurçat, Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la tapisserie contemporaine, 1986 Symposium Jean Lurçat et la renaissance de la tapisserie à Aubusson, Aubusson, Musée départemental de la Tapisserie, 1992 Exhibition Cat. Jean Lurçat, Donation Simone Lurçat, Académie des Beaux-Arts, 2004 Jean Lurçat, le chant du Monde, Angers, 2007 -
Le Chalut (the trawler)
Aubusson tapestry woven by the Berthaut workshop. Complete with certificate of origin signed by the artist. 1952. Jean Picart le Doux is one of the foremost figures in the renaissance of the art of tapestry. His earliest contributions to the field date back to 1943 when he designed cartoons for the passenger ship “la Marseillaise”. A close associate of Lurçat, whose theories he would adopt (limited palette, numbered cartoons...), he was a founding member of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres-cartonniers de Tapisserie), and soon after, a teacher at the Ecole Nationale Supérieure des Arts Décoratifs. The state gave him several commissions most of them at the Aubusson workshop, and some at the Gobelins : the most spectacular of these being for the University of Caen, the Theatre in Le Mans, the passenger ship France or the Prefecture of the Creuse département ... In as much as Picart le Doux’s aesthetic is close to that of Lurçat, so also is his insipiration and his subject matter, although in a register which is more decorative than symbolic, where he brings together heavenly bodies (the sun, the moon, the stars...), the elements, nature (wheat, vines, fish, birds...), man, literary quotation ... « One of the best-known of Picart le Doux’s tapestries : it is highly organised and the generous curves of the trawl net underline the choice of a large and simple graphic.” Is how Maurice Bruzeau describes this tapestry (n° 37 in his book) in the commentary he devotes to it. “The trawler” is typical of the marine themes which are omnipresent in this artist’s work, particularly at this period : “Dieu Marin (marine god), “La Sirène” (the mermaid), “le Dauphin” (the dolphin), “Fruits de mer” (shellfish), “Etoiles de mer” (starfish), in a range of muted colours revolving around kaki and silver grey. Here the treatment of the theme is more documentary (apart from the presence of a trident) : the subject is fishing, as it appears to Picart le Doux. Bibliography : Léon Moussinac, Jean Picart le Doux, Editions Cercle d’art,1964 (ill. Pl.10) Marthe Belle-Jouffray, Jean Picart le Doux, Publications filmées d’art et d’histoire, 1966, ill. n°4 Exhibition catalogue, Hommage à Jean Picart le Doux, Centre artistique et littéraire de Rochechouart, 1968 (ill.) Maurice Bruzeau, Jean Picart le Doux, Murs du soleil, Editions Cercle d’art 1972 Exhibition catalogue Jean Picart le Doux, Paris, Musée de la Poste, 1980 (ill.) Exhibition Catalogue Picart le Doux, château d'Olonne, 1992 (ill.) -
Ombres et lumières (light and shadow)
Aubusson tapestry woven in the Pinton workshop. Complete with certificate of origin signed by the artist. Circa 1965. Matégot, originally a decorator, then creator of artefacts and furniture (an activity he abandoned in 1959) met François Tabard in 1945 and gave him his first cartoons, first of all figurative then rapidly of abstract design in the 1950’s. He became a member of the A.P.C.T. (Association des Peintres Cartonniers de Tapisserie) in 1949, participated in many international exhibitions (Matégot, like Lurçat before him, was an untiring advocate of the art of tapestry) fulfilled numerous public commissions, sometimes of monumental proportions (“Rouen” 85m2 for the Préfecture of the Seine Maritime département, and also tapestries for Orly Airport, for the Maison de la Radio, for the IMF...) and designed no fewer than 629 cartoons up until the 1970’s. In 1990 the Matégot foundation for contemporary tapestry was inaugurated in Bethesda, U.S.A. Matégot is an artist, like Wogensky, Tourlière or Prassinos, who turns wool textiles resolutely towards the abstract: at first lyrical, geometric in the 70’s, exploiting various technical aspects of the loom : colour graduations, shading, irregularities... This tapestry reveals Matégot’s preoccupation with the interplay of light and shadow which is often revealed in the titles of his works (cf. “Lumière d’été”, auctioned Millon-Robert 7.11.90, n° 31, reproduced on the cover of the catalogue, “Piège de lumière” preserved at the Musée Jean Lurçat et de la Tapisserie Contemporaine and reproduced p 47 of the exhibition catalogue). Here the cartoon uses an abrupt contrast, like a ray of light, between two opaque (with faults however) and black (but shaded) blocks. In fact all of Matégot’s works reveal the interplay of transparency and superposition, as if light (albeit fatal to the colours he uses) was trying to force its way through the wool. Origin : contents of the Pinton workshop Bibliography : Exhibition catalogue, Matégot, Angers, Musée Jean Lurçat et de la Tapisserie Contemporaine, 1990-1991